
Damage to pump volute casings can be caused by a variety of factors, including cavitation, erosion, corrosion, and mechanical stress. Cavitation occurs when vapor bubbles collapse within the casing, leading to pitting and erosion. Corrosion can result from exposure to corrosive fluids or environments, weakening the casing over time. Mechanical stress from improper installation or operation can also cause cracks or deformations in the casing, compromising its integrity.
To effectively repair corrosion in pump volute casings, the damaged area must be cleaned and prepared by removing any rust or debris. A suitable corrosion-resistant material, such as stainless steel or epoxy coatings, can then be applied to the affected area to restore the casing's protective barrier. Proper surface preparation and application techniques are essential to ensure a durable and long-lasting repair.
George Dahl was one of the architects who built Dallas. He certainly was the drive behind Fair Park, leading the planning and construction of 26 Art Deco-style buildings ahead of the 1936 Texas Centennial Exposition. He divided the park into four sub-districts, centered upon the 700-foot-long Esplanade that led to the ornate Hall of State. … Continued The post <i>D Magazine’</i>s 50 Greatest Stories: The Tragic End of Architect George Dahl’s Life appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-15
Blackstone is a new investor in Dallas-based Aligned Data Centers. The world’s largest alternative asset manager, with $1 trillion in assets, has provided a $600 million senior secured credit facility to support the development of Aligned’s newest and largest data center in Utah, a two-story, 80 MW build-to suit project. “Blackstone’s support contributes to Aligned’s continued growth in … Continued The post Blackstone Provides Aligned Data Centers with $600 Million Credit Facility appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-15
People are coming to North Texas, but they are not moving to Dallas. The regional success story told in this week’s Census data dump—8.1 million people now call the region home for the first time—is not actually a tale about the center of our metro area, Dallas County, which charted a meager growth that was … Continued The post The Depressing Reality About Dallas in the New U.S. Census Numbers appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-15
Welding cracks in pump volute casings involves several steps to ensure a strong and reliable repair. The cracked area must be cleaned and prepped, and any stress risers or sharp edges should be removed. A skilled welder can then use appropriate welding techniques, such as TIG or MIG welding, to fill in the crack and reinforce the casing. Post-welding inspections and testing are crucial to verify the integrity of the repair.
When patching holes in pump volute casings, it is recommended to use materials that are compatible with the casing material and the operating conditions. Common materials for patching holes include metal alloys, epoxy compounds, and polymer coatings. The patch should be securely bonded to the casing and properly sealed to prevent leaks or further damage.
Addressing erosion damage in pump volute casings involves identifying the root cause of the erosion, such as high flow velocities or abrasive particles in the fluid. Once the cause is addressed, the eroded area can be repaired using erosion-resistant materials, such as ceramic coatings or hardened alloys. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help prevent future erosion damage and prolong the life of the casing.
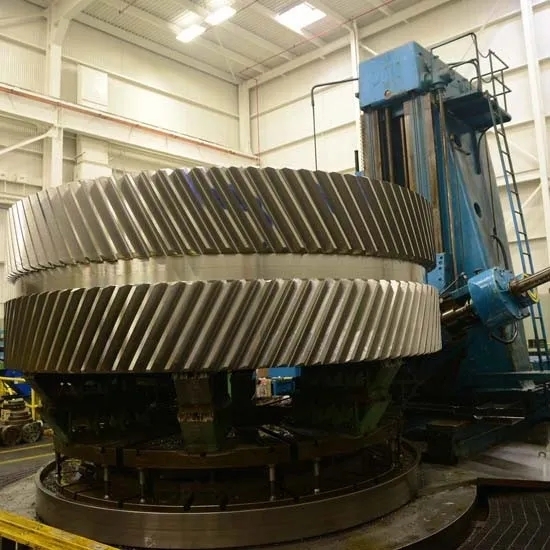

To reinforce weakened areas in pump volute casings, various techniques can be employed, such as adding structural supports, installing reinforcement plates, or applying composite materials. The choice of reinforcement method will depend on the extent of the weakening and the operating conditions of the pump. Proper installation and bonding are essential to ensure that the reinforcement effectively strengthens the casing.
Specialized coatings are available for protecting pump volute casings from future damage, such as corrosion-resistant coatings, abrasion-resistant coatings, and chemical-resistant coatings. These coatings can be applied to the interior or exterior of the casing to provide an additional layer of protection against wear, corrosion, and other forms of damage. Regular inspections and maintenance of the coatings are necessary to ensure their continued effectiveness in prolonging the life of the pump casing.
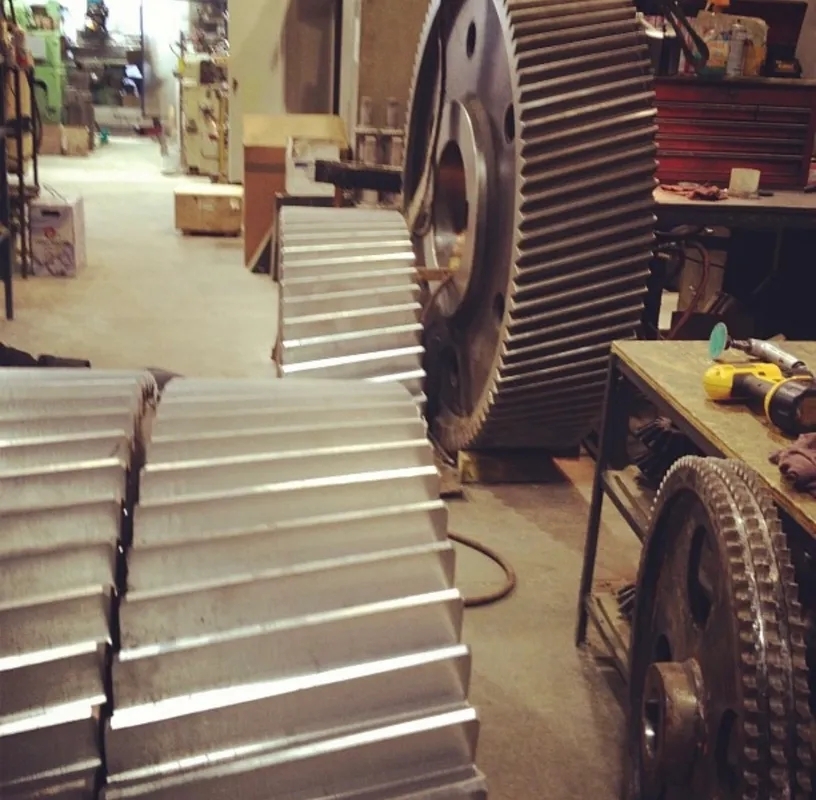

Diagnosing and repairing pump suction cavitation involves first identifying the symptoms such as noise, vibration, reduced flow rate, and decreased performance. The next step is to inspect the pump for any blockages, leaks, or worn components that could be causing the cavitation. Common causes of cavitation include high suction lift, inadequate NPSH, undersized suction piping, or a clogged strainer. Once the root cause is determined, repairs may involve adjusting the pump speed, increasing the suction pipe diameter, installing a larger pump, or improving the system's NPSH. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the pump system can help prevent cavitation issues in the future.
To identify and repair pump suction side erosion, one must first inspect the pump components for signs of wear, such as pitting, corrosion, or rough surfaces. Common causes of erosion on the suction side of a pump include cavitation, abrasive particles in the fluid, and high flow velocities. To repair the erosion, one can use methods such as applying protective coatings, replacing worn components, or adjusting the pump operation to reduce erosion. It is important to address suction side erosion promptly to prevent further damage to the pump and ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the pump system can help prevent erosion issues in the future.
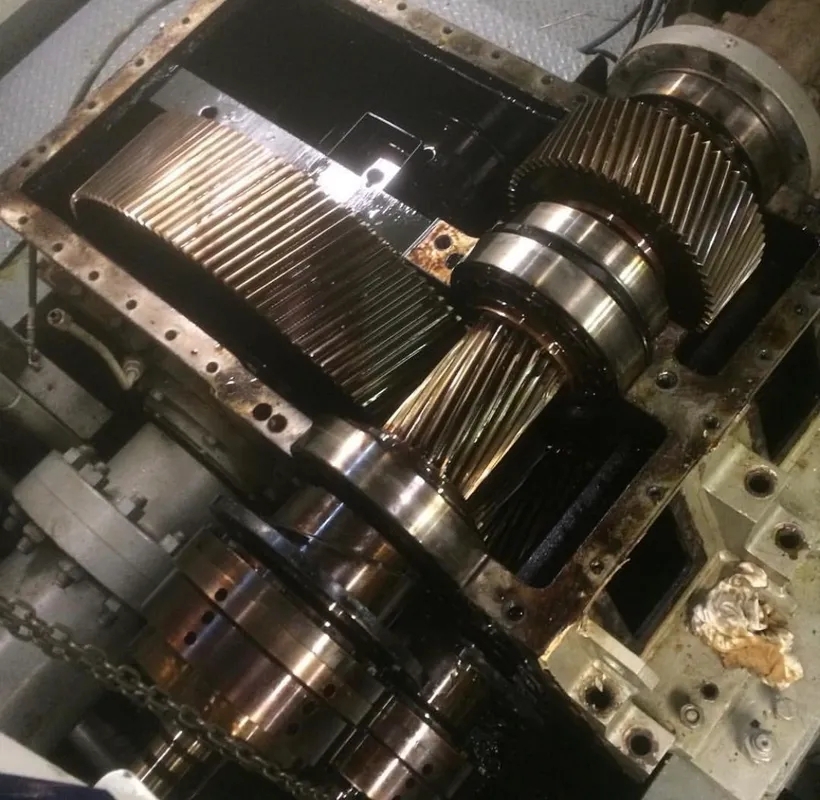
Gearbox bearing failure can be identified by several key signs, including unusual noises such as grinding, whining, or rumbling coming from the transmission. Other indicators may include difficulty shifting gears, vibrations felt through the gear stick or floorboard, and leaks of transmission fluid. In some cases, there may also be a burning smell or visible metal shavings in the transmission fluid. It is important to address these symptoms promptly, as gearbox bearing failure can lead to more extensive damage to the transmission if left untreated. Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent gearbox bearing failure and ensure the longevity of the transmission system.
To calculate the expected pump bearing lifespan, one must consider various factors such as the type of bearing used, the load and speed at which the pump operates, the lubrication system in place, and the environmental conditions in which the pump is located. By analyzing these factors and consulting manufacturer specifications, engineers can estimate the expected lifespan of the pump bearing. Additionally, conducting regular maintenance and monitoring the condition of the bearing can help prolong its lifespan and prevent unexpected failures. It is important to consider all these factors in order to accurately predict the expected lifespan of a pump bearing.
Gearbox gear teeth can indeed be coated with various materials to improve wear resistance. Coatings such as diamond-like carbon (DLC), nitride, and ceramic coatings are commonly used to enhance the durability and longevity of gear teeth. These coatings provide a protective barrier against friction, abrasion, and corrosion, ultimately extending the lifespan of the gears. Additionally, coatings can also improve the overall performance of the gearbox by reducing maintenance requirements and increasing efficiency. Overall, coating gear teeth is a proven method to enhance wear resistance and optimize the functionality of gear systems.
To check gearbox backlash, the technician should first secure the gearbox in place to prevent any movement during the inspection. Next, they should rotate the input shaft in both directions while measuring the amount of free play or movement in the output shaft. This measurement will indicate the amount of backlash present in the gearbox. The technician should compare this measurement to the manufacturer's specifications to determine if the backlash is within acceptable limits. If the backlash is found to be excessive, adjustments may need to be made to the gearbox components to reduce the amount of play and ensure proper operation. Regular monitoring of gearbox backlash is essential to prevent premature wear and damage to the gearbox components.