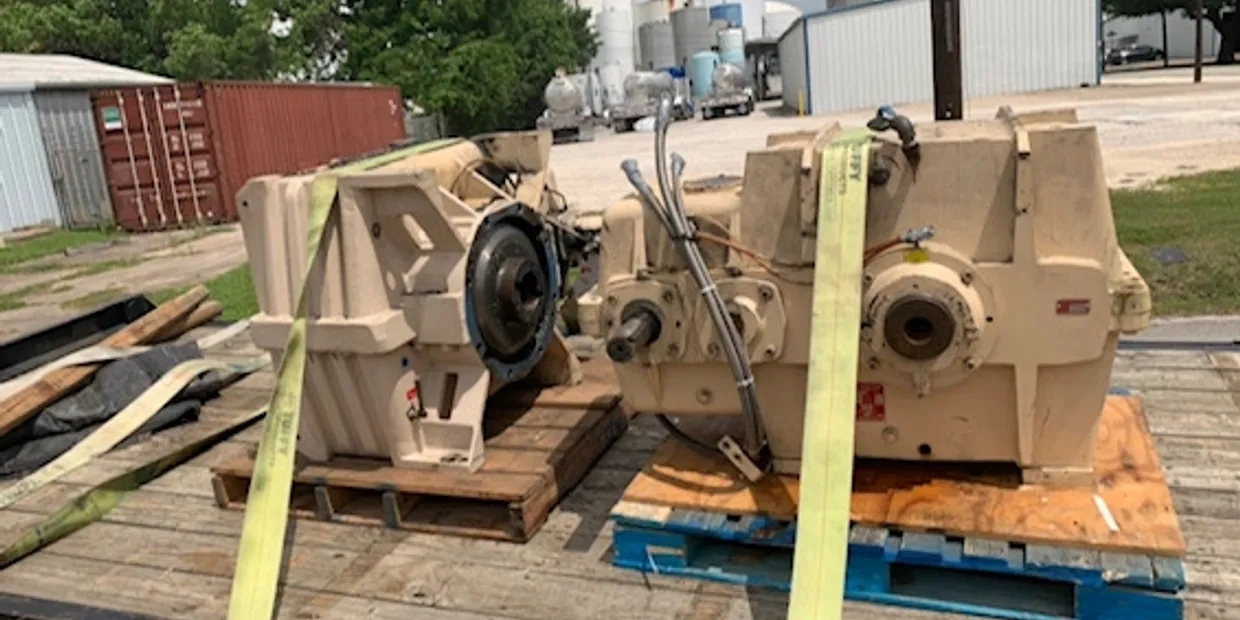


The material composition of a gearbox gear plays a crucial role in determining its susceptibility to tooth fracture. Materials with high strength and hardness, such as alloy steels, are less likely to experience fractures compared to softer materials. Additionally, factors like the presence of impurities, inclusions, and heat treatment processes can also influence the material's resistance to fracture. Proper material selection based on the specific application and operating conditions is essential to minimize the risk of gear tooth fractures.
The operating temperature of a gearbox can significantly impact the initiation of gear tooth fractures. High temperatures can lead to thermal expansion, which may affect the gear meshing process and increase the likelihood of fatigue failure. Heat generated during operation can also accelerate wear and reduce the lubrication effectiveness, further contributing to tooth fractures. Maintaining optimal operating temperatures through proper cooling systems and lubrication can help prevent premature gear failures.
Plano Pooped on Dallas. A mechanical failure at a water station dumped more than 1.5 million gallons of hell into White Rock Creek. It started Thursday and was fixed Saturday. The Corinthian Sailing Club on White Rock Lake moved its annual regatta to Lake Ray Hubbard over the weekend, but officials yesterday said they are … Continued The post Leading Off (3/19/24) appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-19
The Old Monk, the beloved Henderson Avenue pub, plans to open a second location in Oak Cliff this fall. An alert and pub-loving reader alerted us to this news a few weeks ago, when he wrote to ask about a building being renovated into a restaurant at 810 W. Davis St., next to Bbbop Seoul … Continued The post The Old Monk Will Open a Second Location in Oak Cliff This Fall appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-18
Hey! The Cowboys beat the 49ers. In the playoffs? No. On the field at all? No. But they did flip linebacker Eric Kendricks from an initial agreement to sign with San Francisco to join them on a one-year deal. Rejoice! You’re going to have to. Because that is essentially the only thing the Cowboys have … Continued The post Did You Like That Free Agency? I Hope You Did. I Hope You Did Very Much. appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-18
It seems like just yesterday that we were celebrating Mardi Gras, but Easter is almost here. And that means a busy week of entertaining out-of-town in-laws, stuffing plastic eggs with candy in the middle of the night, coordinating family photos in some flower bed, and comforting little ones scared of the giant Easter bunny costume. … Continued The post 26 Ways to Celebrate Easter in Dallas-Fort Worth This Month appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-18
Joy and Kevin met at a homeless shelter in Texarkana. Joy is a registered stockbroker and Kevin is a minister who says he intended to go it alone, but “God had decided to bring Joy into my life—we fell in love.” The couple assessed their strengths and recently hopped a Greyhound bus for Dallas, spending … Continued The post Dallas Public Library Introduces Homeless Community Through New Podcast appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-18
The design of the gear tooth profile can indeed impact the likelihood of fracture occurring in a gearbox. Factors such as tooth geometry, pressure angle, and tooth thickness distribution can affect the distribution of stress and load along the tooth surface. Well-designed tooth profiles with proper contact ratios and tooth profiles can help distribute loads evenly, reducing stress concentrations and minimizing the risk of fractures. Advanced design techniques like tooth modifications and optimization can further enhance the durability and reliability of gearbox gears.

Surface roughness and lubrication are critical factors that influence the fatigue life of gearbox gears and their resistance to fracture. A smooth surface finish can reduce friction and wear, while proper lubrication can help dissipate heat and prevent metal-to-metal contact. Inadequate lubrication or high surface roughness can lead to increased friction, wear, and pitting, ultimately weakening the gear teeth and making them more susceptible to fractures. Regular maintenance and monitoring of surface conditions and lubrication levels are essential for ensuring the longevity of gearbox gears.
Common failure modes associated with gear tooth fractures in gearboxes include pitting, spalling, and tooth breakage. Pitting occurs due to surface fatigue caused by repeated contact stress, while spalling results from subsurface material fatigue. Tooth breakage can occur due to overload or excessive bending stress. Understanding these failure modes and their root causes is crucial for implementing preventive measures and improving the overall reliability of gearbox systems.

Stress analysis techniques such as finite element analysis (FEA) can be used to predict and prevent gear tooth fractures in gearboxes. FEA allows engineers to simulate the behavior of gears under different loading conditions, identify potential stress concentrations, and optimize the design to minimize stress levels. By analyzing factors like tooth geometry, material properties, and operating conditions, FEA can help engineers optimize gear designs for maximum strength and durability, reducing the risk of fractures.
Specific standards and guidelines, such as ISO 6336 and AGMA 2001, provide best practices for preventing gear tooth fractures in gearbox design and maintenance. These standards outline recommended design criteria, material selection guidelines, and maintenance procedures to ensure the reliability and longevity of gearbox systems. Adhering to these standards can help manufacturers and operators mitigate the risk of gear tooth fractures, improve performance, and extend the service life of gearbox components.
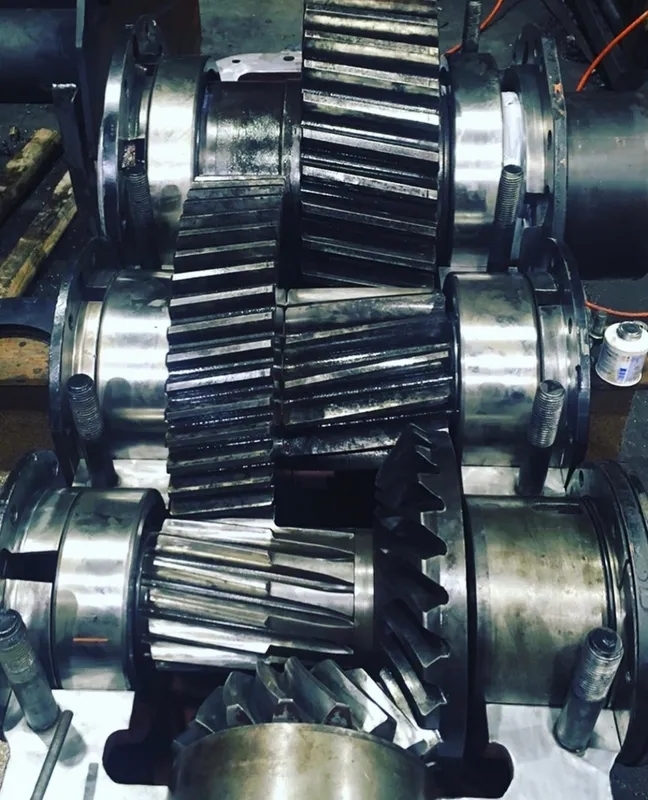
When it comes to industrial gearbox repair, selecting the appropriate lubricant is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Some suitable lubricants for industrial gearbox repair include synthetic oils, mineral oils, gear oils, and grease. Synthetic oils are known for their high performance in extreme temperatures and heavy-duty applications. Mineral oils are commonly used for general-purpose lubrication in industrial gearboxes. Gear oils are specifically formulated to provide protection against wear, corrosion, and oxidation in gear systems. Grease is a semi-solid lubricant that is ideal for applications where oil leakage is a concern. Overall, choosing the right lubricant for industrial gearbox repair depends on factors such as operating conditions, load capacity, and speed requirements.
To detect and repair gearbox leaks, one can start by visually inspecting the gearbox for any signs of oil stains or puddles underneath the vehicle. Using a flashlight, one can check for any visible cracks or damage to the gearbox casing. Additionally, one can perform a pressure test to identify any leaks in the gearbox seals or gaskets. To repair the leaks, one may need to replace the damaged seals or gaskets, tighten any loose bolts, or repair any cracks in the gearbox casing. It is important to use the appropriate tools and equipment to ensure a proper repair and prevent further leaks in the gearbox. Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent gearbox leaks in the future.
One way to identify symptoms of bearing failure in a pump is to listen for any unusual noises such as grinding, squealing, or knocking sounds coming from the pump. Additionally, an increase in vibration or heat coming from the pump could indicate bearing failure. Another sign to look out for is leaking fluid around the pump, which may be caused by a damaged bearing. It is also important to check for any irregularities in the pump's performance, such as decreased flow rate or pressure. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the pump can help detect bearing failure early on and prevent further damage to the equipment.
Gearbox lubricants can be filtered and reused in some cases, depending on the level of contamination and the type of filtration system used. Filtration processes such as oil purification, centrifugal separation, and magnetic filtration can help remove contaminants like dirt, metal particles, and water from the lubricant, extending its lifespan. However, in cases of severe contamination or degradation, replacement of the lubricant may be necessary to ensure optimal gearbox performance and prevent damage. Regular monitoring of lubricant condition and implementing proper maintenance practices can help determine whether filtration and reuse are viable options for a specific gearbox system.
During gearbox repair, it is possible to straighten gearbox shafts in some cases, depending on the extent of the damage. Straightening a gearbox shaft involves using specialized tools and techniques to carefully bend the shaft back into its original shape. However, if the shaft is severely bent or damaged beyond repair, replacement may be necessary to ensure the gearbox functions properly. It is important to consult with a professional mechanic or technician to determine the best course of action for repairing gearbox shafts. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent shaft damage and prolong the lifespan of the gearbox.
To diagnose and repair gearbox oil oxidation issues, one must first conduct a thorough inspection of the gearbox system to identify any signs of oxidation, such as a darkening of the oil color, a burnt smell, or increased viscosity. Once oxidation is confirmed, the next step is to drain the old oil and flush the gearbox system to remove any contaminants. After cleaning the system, fresh gearbox oil with antioxidant additives should be added to prevent further oxidation. It is also important to check for any leaks or damaged seals that may be allowing air to enter the system and accelerate oxidation. Regular maintenance and monitoring of oil condition can help prevent gearbox oil oxidation issues in the future.
To diagnose and rectify gear tooth scoring, one must first inspect the gear teeth for any signs of wear, damage, or scoring. This can be done by visually examining the gear teeth or using specialized equipment such as a borescope or gear inspection tool. Once the scoring is identified, the root cause must be determined, which could be due to factors such as improper lubrication, misalignment, overload, or contamination. To rectify the issue, the gear teeth may need to be repaired or replaced, the lubrication system may need to be improved, the gear alignment may need to be adjusted, or the operating conditions may need to be optimized. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the gear system can help prevent future instances of gear tooth scoring.