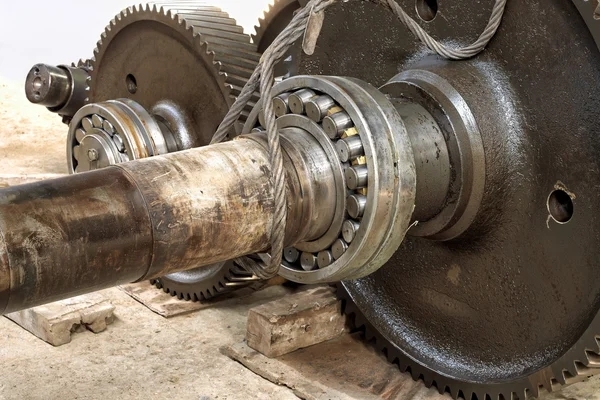


The purpose of a wear ring in a pump impeller is to minimize the clearance between the impeller and the pump casing, reducing internal recirculation and improving pump efficiency. By providing a close clearance, the wear ring helps to maintain the pump's performance and prevent damage to the impeller over time.
You can tell if a wear ring in a pump impeller needs to be replaced by inspecting it for signs of wear, such as grooves, scratches, or uneven surfaces. If the wear ring shows significant wear or damage, it may lead to increased clearance between the impeller and casing, resulting in reduced pump efficiency and potential damage to the impeller.
Plano Pooped on Dallas. A mechanical failure at a water station dumped more than 1.5 million gallons of hell into White Rock Creek. It started Thursday and was fixed Saturday. The Corinthian Sailing Club on White Rock Lake moved its annual regatta to Lake Ray Hubbard over the weekend, but officials yesterday said they are … Continued The post Leading Off (3/19/24) appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-19
The Old Monk, the beloved Henderson Avenue pub, plans to open a second location in Oak Cliff this fall. An alert and pub-loving reader alerted us to this news a few weeks ago, when he wrote to ask about a building being renovated into a restaurant at 810 W. Davis St., next to Bbbop Seoul … Continued The post The Old Monk Will Open a Second Location in Oak Cliff This Fall appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-18
Hey! The Cowboys beat the 49ers. In the playoffs? No. On the field at all? No. But they did flip linebacker Eric Kendricks from an initial agreement to sign with San Francisco to join them on a one-year deal. Rejoice! You’re going to have to. Because that is essentially the only thing the Cowboys have … Continued The post Did You Like That Free Agency? I Hope You Did. I Hope You Did Very Much. appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-18
It seems like just yesterday that we were celebrating Mardi Gras, but Easter is almost here. And that means a busy week of entertaining out-of-town in-laws, stuffing plastic eggs with candy in the middle of the night, coordinating family photos in some flower bed, and comforting little ones scared of the giant Easter bunny costume. … Continued The post 26 Ways to Celebrate Easter in Dallas-Fort Worth This Month appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-18
Common materials used for wear rings in pump impellers include bronze, stainless steel, and composite materials like carbon-filled PTFE. These materials are chosen for their durability, resistance to wear, and ability to maintain a tight clearance between the impeller and casing.

There are specific guidelines for the clearance between the wear ring and impeller in a pump, typically ranging from 0.001 to 0.005 inches. Maintaining the correct clearance is crucial for optimal pump performance and efficiency. Deviating from these guidelines can lead to increased internal recirculation and reduced pump efficiency.
The steps involved in replacing a wear ring in a pump impeller include shutting down the pump, removing the impeller, inspecting the wear ring for damage, replacing the worn wear ring with a new one, reassembling the pump, and testing it to ensure proper functioning. It is important to follow manufacturer guidelines and recommendations during the replacement process.
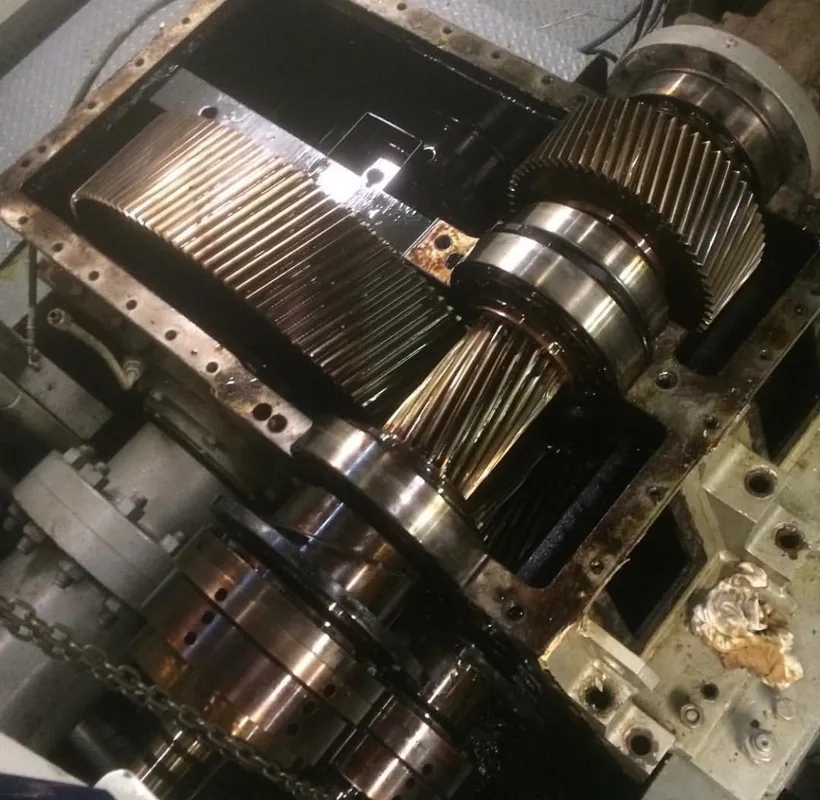
Wear rings in pump impellers should be inspected for wear and tear regularly, typically during routine maintenance checks or whenever the pump is shut down for servicing. Depending on the operating conditions and the type of material used for the wear ring, inspections may be required more frequently to ensure optimal pump performance.
Common issues that can arise from not replacing a worn wear ring in a pump impeller include reduced pump efficiency, increased internal recirculation, damage to the impeller, and potential pump failure. Neglecting to replace a worn wear ring can lead to costly repairs, decreased pump lifespan, and decreased overall system performance. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of wear rings are essential for ensuring the reliable operation of pump systems.

To prevent gearbox bearing overheating, several measures can be taken. One option is to ensure proper lubrication of the bearings with high-quality oil or grease. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the gearbox temperature can also help in detecting any potential issues before they escalate. Installing cooling systems, such as fans or heat exchangers, can help dissipate excess heat generated during operation. Additionally, using bearings with the appropriate load capacity and ensuring proper alignment of the gearbox components can help prevent overheating. Implementing vibration monitoring systems can also help in detecting any abnormalities that could lead to overheating. Overall, a combination of proper lubrication, maintenance, cooling systems, bearing selection, alignment, and monitoring can help prevent gearbox bearing overheating.
Pump cavitation can have significant implications on energy efficiency in various industrial applications. When cavitation occurs, it creates bubbles in the liquid being pumped, leading to the formation of vapor pockets that collapse with high energy, causing damage to the pump components. This can result in increased friction, reduced flow rates, and decreased overall efficiency of the pump system. In order to mitigate the effects of cavitation and improve energy efficiency, proper pump selection, maintenance, and operating conditions are crucial. Utilizing features such as variable speed drives, impeller design optimization, and regular monitoring can help minimize cavitation and ensure optimal energy performance of the pump system. By addressing cavitation issues effectively, industries can enhance energy efficiency, reduce operational costs, and prolong the lifespan of their equipment.
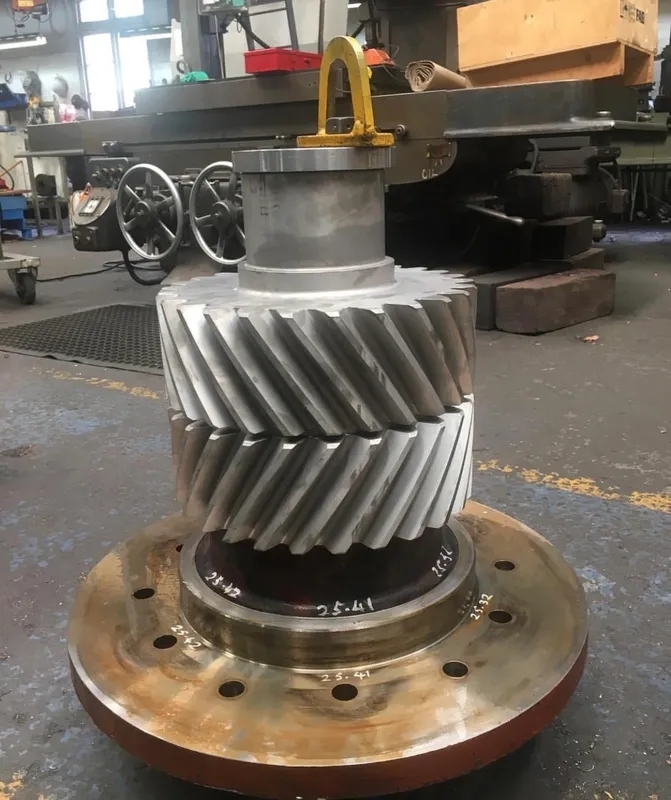
When determining the appropriate gearbox torque for a specific application, it is crucial to consider factors such as the load requirements, operating conditions, gear ratio, efficiency, and power transmission capabilities. Calculating the required torque involves analyzing the maximum load that the gearbox will need to handle, the speed at which the load will be applied, and any additional forces or resistance that may be present during operation. It is also important to take into account the type of gears being used, whether they are spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, as each type has different torque-handling capabilities. Additionally, considering the material and lubrication of the gears, as well as the overall design and construction of the gearbox, can help ensure that the chosen torque rating is suitable for the intended application. Consulting with a mechanical engineer or gearbox specialist can provide valuable insight into selecting the most appropriate torque capacity for a specific application.
The most common causes of pump seal failure include improper installation, lack of proper maintenance, high operating temperatures, abrasive or corrosive fluids, excessive vibration, and inadequate lubrication. Improper installation can lead to misalignment or damage to the seal, while a lack of maintenance can result in wear and tear over time. High operating temperatures can cause the seal material to degrade, reducing its effectiveness. Abrasive or corrosive fluids can also wear down the seal prematurely. Excessive vibration can put stress on the seal, causing it to fail sooner than expected. Inadequate lubrication can lead to increased friction and heat, further contributing to seal failure. Regular inspection and maintenance can help prevent these common causes of pump seal failure.
To prevent pump seal face damage, various measures can be implemented. One effective method is to regularly inspect the pump seal for any signs of wear, corrosion, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of the seal face can also help reduce friction and prevent damage. Additionally, ensuring that the pump is operating within the recommended temperature and pressure limits can help prolong the life of the seal face. Using high-quality materials for the seal face and following manufacturer guidelines for installation and maintenance are also crucial in preventing damage. Implementing a regular maintenance schedule and promptly addressing any issues that arise can help prevent pump seal face damage in the long run.
Diagnosing and repairing pump discharge cavitation involves first identifying the symptoms such as reduced flow rate, increased noise levels, and vibration. The technician should then inspect the pump for any signs of damage or wear, including worn impeller blades, misalignment, or blockages in the discharge line. Utilizing diagnostic tools such as vibration analysis and pressure gauges can help pinpoint the exact location and severity of the cavitation. Once diagnosed, the repair process may involve adjusting the pump speed, replacing damaged components, or redesigning the system to prevent future cavitation. Proper maintenance practices, such as regular inspection and cleaning, can also help prevent pump discharge cavitation in the future.