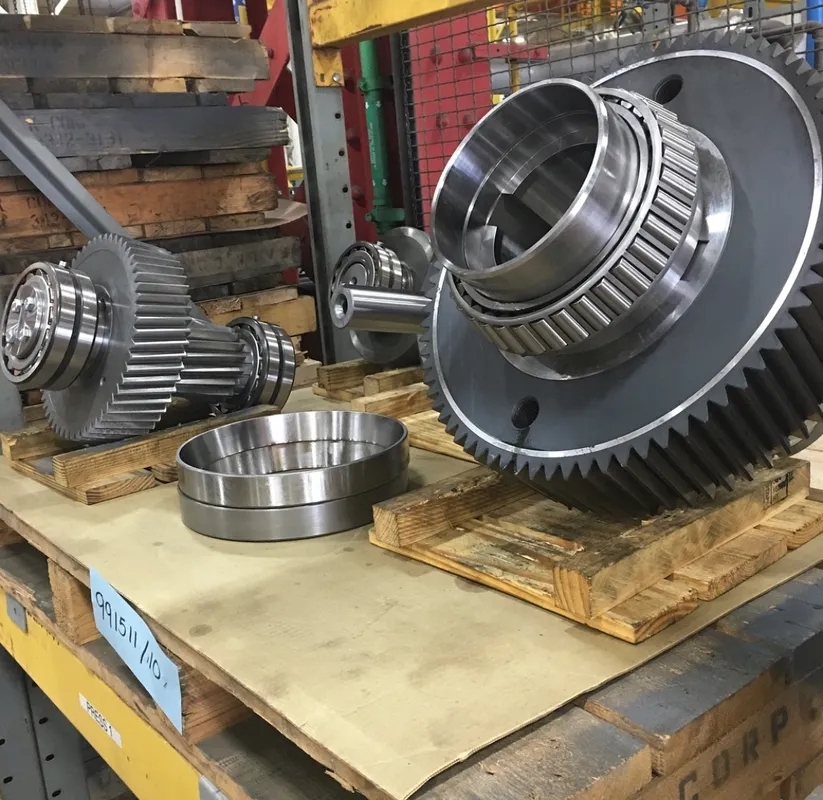


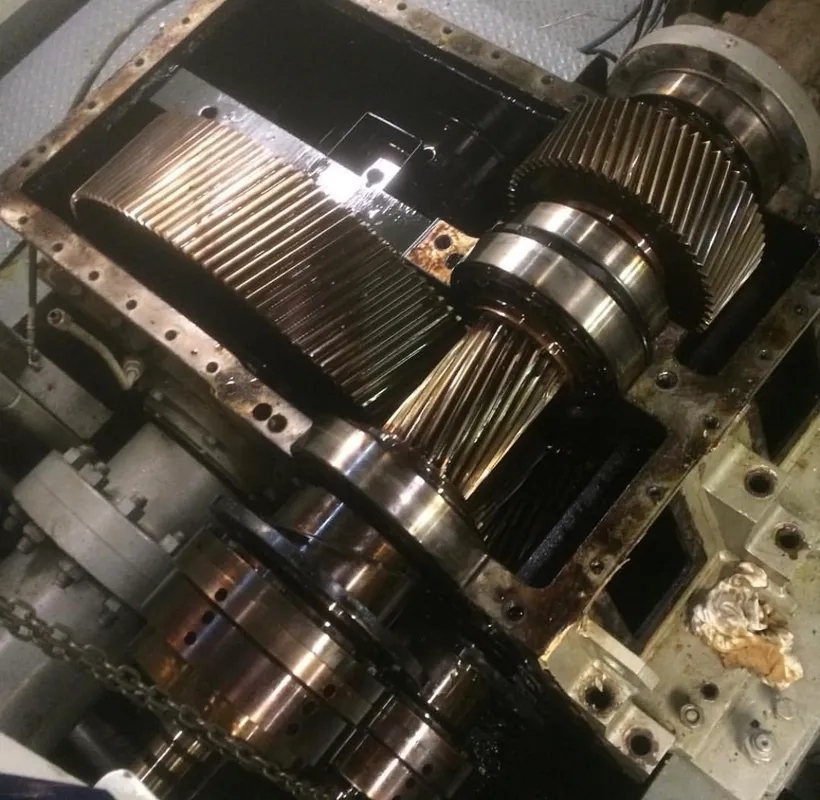
Adjusting the preload in gearbox bearings plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the gearbox. Proper preload adjustment ensures that the bearings are loaded correctly, reducing the risk of excessive vibration, noise, and heat generation. This, in turn, helps to improve the efficiency and longevity of the gearbox by maintaining optimal contact between the bearing elements.
There are several techniques used to adjust the preload in gearbox bearings, including using shims, adjusting the position of the bearing outer ring, or utilizing specialized tools such as a preload wrench. Each technique is designed to achieve the desired amount of preload based on the specific requirements of the gearbox and the manufacturer's recommendations.
Blackstone is a new investor in Dallas-based Aligned Data Centers. The world’s largest alternative asset manager, with $1 trillion in assets, has provided a $600 million senior secured credit facility to support the development of Aligned’s newest and largest data center in Utah, a two-story, 80 MW build-to suit project. “Blackstone’s support contributes to Aligned’s continued growth in … Continued The post Blackstone Provides Aligned Data Centers with $600 Million Credit Facility appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-15
People are coming to North Texas, but they are not moving to Dallas. The regional success story told in this week’s Census data dump—8.1 million people now call the region home for the first time—is not actually a tale about the center of our metro area, Dallas County, which charted a meager growth that was … Continued The post The Depressing Reality About Dallas in the New U.S. Census Numbers appeared first on D Magazine.
Posted by on 2024-03-15
Improper preload adjustment can indeed lead to premature wear and failure of gearbox bearings. If the preload is too low, the bearings may experience excessive internal clearance, leading to increased friction and potential misalignment. On the other hand, if the preload is too high, it can cause the bearings to overheat and wear out quickly. Regular maintenance and proper adjustment of preload are essential to prevent such issues.
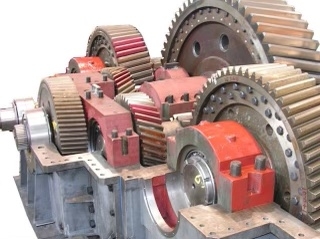
To adjust the preload in gearbox bearings, various tools may be required depending on the specific method chosen. Common tools include torque wrenches, dial indicators, bearing pullers, and specialized preload adjustment tools. These tools help to accurately measure and set the preload to the recommended values for optimal gearbox performance.
There are specific guidelines and recommended values for setting the preload in gearbox bearings, typically provided by the gearbox manufacturer. These values are based on factors such as the type of bearings used, the operating conditions of the gearbox, and the desired level of performance. Following these guidelines ensures that the bearings are properly loaded and aligned to prevent premature wear and failure.

The preload in gearbox bearings should be checked and adjusted regularly as part of routine maintenance procedures. The frequency of checks may vary depending on the operating conditions of the gearbox, but it is generally recommended to inspect and adjust the preload during scheduled maintenance intervals or whenever unusual noise or vibration is detected.
Signs that indicate the preload in gearbox bearings may need to be readjusted include increased noise levels, excessive vibration, elevated operating temperatures, or irregular wear patterns on the bearings. If any of these symptoms are observed, it is important to inspect the preload and make necessary adjustments to prevent further damage to the gearbox and bearings. Regular monitoring and maintenance can help to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the gearbox.
Pump impeller imbalance can have several implications on the overall performance and efficiency of a pumping system. When the impeller is not properly balanced, it can lead to increased vibration, noise, and wear on the pump components. This imbalance can also result in reduced flow rates, decreased energy efficiency, and potential damage to the pump shaft and bearings. Additionally, an imbalanced impeller can cause cavitation, which can further deteriorate the pump performance and lead to costly repairs. It is crucial to address pump impeller imbalance promptly to prevent these negative consequences and ensure the smooth operation of the pumping system. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the impeller balance are essential to avoid any potential issues.
Helical gears and spur gears are two common types of gears used in gearboxes, each with its own unique characteristics. Helical gears have teeth that are cut at an angle to the gear axis, resulting in a smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears, which have straight teeth that are parallel to the gear axis. The helical gears also have a larger contact area, which allows for higher torque transmission and better load distribution. However, helical gears tend to produce axial thrust, requiring additional bearings to support the shaft. On the other hand, spur gears are simpler in design and easier to manufacture, making them more cost-effective. They are also more efficient in terms of power transmission due to less sliding friction. Overall, the choice between helical and spur gears in gearboxes depends on factors such as noise level, load capacity, efficiency, and cost.
When deciding between repairing or replacing gearbox components, it is important to consider factors such as the extent of damage, cost of repairs, availability of replacement parts, and overall performance of the gearbox. If the damage is minor and can be easily fixed with a simple repair, it may be more cost-effective to opt for repairing the components. However, if the damage is extensive and the cost of repairs is close to or exceeds the cost of replacement parts, it may be more practical to replace the components altogether. Additionally, if the gearbox is older and showing signs of wear and tear, replacing the components may improve overall performance and longevity. Ultimately, the decision should be based on a thorough assessment of the situation and weighing the pros and cons of each option.
During gear repair, it is possible to reprofile gear teeth instead of replacing them entirely. This process involves reshaping the teeth to restore their proper form and function. By using specialized tools and equipment, technicians can adjust the profile of the teeth to ensure proper meshing and alignment within the gear system. Reprofiling gear teeth can help extend the lifespan of the gear and prevent the need for costly replacements. However, it is important to consult with a professional to determine the best course of action for repairing damaged gear teeth.
To address overheating issues in a pump motor, it is important to first check the cooling system, such as the fan, cooling fins, and coolant levels. Ensure that the motor is properly ventilated and that there are no obstructions blocking airflow. Inspect the motor for any signs of wear or damage that may be causing excessive heat generation. Consider installing a thermal overload protection device to prevent overheating. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and lubricating moving parts, can also help prevent overheating issues in the pump motor. If the problem persists, it may be necessary to consult a professional technician for further diagnosis and repair.
When it comes to storing spare gearbox parts, it is important to follow best practices to ensure their longevity and functionality. One key practice is to store the parts in a clean, dry environment to prevent corrosion and damage. It is also recommended to organize the parts in a systematic manner, labeling each part clearly for easy identification. Additionally, using proper packaging materials such as plastic bins or containers can help protect the parts from dust and debris. Regularly inspecting the stored parts for any signs of wear or damage is also crucial in maintaining their quality. By following these best practices, individuals can ensure that their spare gearbox parts remain in optimal condition for future use.