

Neurofeedback is a non-invasive technique that targets stroke rehabilitation and recovery by training the brain to regulate its own activity. Specifically, neurofeedback helps stroke patients by promoting neuroplasticity, which is the brain's ability to reorganize and form new neural connections. Brainwaves This can aid in restoring motor function, speech, and cognitive abilities that may have been affected by the stroke. By providing real-time feedback on brainwave activity, neurofeedback helps stroke patients learn to self-regulate their brain function, leading to improved rehabilitation outcomes.
In stroke patients, neurofeedback aims to address specific brainwave patterns such as beta and theta waves. Beta waves are associated with focused attention and cognitive function, while theta waves are linked to relaxation and creativity. In stroke rehabilitation, neurofeedback targets these brainwave patterns to help improve attention, memory, and emotional regulation, which are often affected by stroke-related brain damage. By training the brain to modulate these patterns, neurofeedback can support the recovery of cognitive and emotional functions in stroke patients.
MeditationNeurofeedback can indeed be used in conjunction with traditional physical therapy for stroke rehabilitation. While physical therapy focuses on improving motor function and mobility, neurofeedback targets the brain's neural activity, enhancing the overall rehabilitation process. By combining these approaches, stroke patients can benefit from a more comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both physical and neurological aspects of recovery, potentially leading to improved outcomes and a more holistic approach to rehabilitation.
Breath Control
Incorporating neurofeedback into a stroke rehabilitation program can offer potential long-term benefits for patients. By promoting neuroplasticity and improving brain function, neurofeedback may contribute to sustained improvements in motor skills, speech, cognitive abilities, and emotional regulation. This can lead to greater independence and quality of life for stroke survivors, as well as potentially reducing the risk of long-term cognitive and emotional complications associated with stroke.
Neurofeedback can be effective for various types of strokes and severity levels. Thresholds Whether a patient has experienced an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, or has mild to severe impairment, neurofeedback can be tailored to address individual needs. The flexibility of neurofeedback allows for personalized treatment plans that can be adapted to the specific challenges and goals of each stroke patient, making it a versatile and potentially effective approach across different stroke types and severity levels.
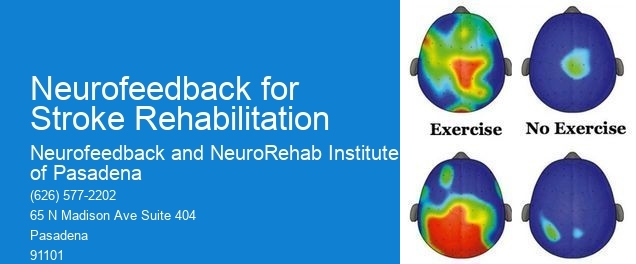
Neurofeedback helps with cognitive and emotional challenges that often accompany stroke recovery by targeting specific brainwave patterns associated with these functions. By training the brain to regulate these patterns, neurofeedback can support improvements in attention, memory, executive function, and emotional regulation. EEG Biofeedback Software This can help stroke patients overcome cognitive deficits, such as difficulties with attention and memory, as well as emotional challenges, such as anxiety and depression, which are common in stroke recovery.
Key considerations for integrating neurofeedback into a comprehensive stroke rehabilitation plan include the need for qualified professionals who are trained in both neurofeedback and stroke rehabilitation. It's important to ensure that the neurofeedback protocol is tailored to the specific needs and abilities of each stroke patient, and that it complements other aspects of the rehabilitation program. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and assessment of the patient's progress and response to neurofeedback are essential for optimizing the effectiveness of the treatment. By carefully integrating neurofeedback into the overall rehabilitation plan, healthcare providers can maximize the potential benefits for stroke patients.

Neurofeedback therapy has been shown to have a positive impact on depressive symptoms in individuals by targeting specific brainwave patterns associated with mood regulation and emotional processing. By utilizing real-time monitoring of brain activity and providing feedback to the individual, neurofeedback therapy aims to train the brain to self-regulate and optimize its functioning. This process can lead to improvements in mood, emotional stability, and overall well-being. Research has indicated that neurofeedback can modulate neural networks related to depression, such as the prefrontal cortex and limbic system, promoting more adaptive patterns of brain activity. Additionally, by addressing underlying neurological dysregulation, neurofeedback therapy may offer a promising approach for individuals with treatment-resistant depression or those seeking non-pharmacological interventions. Overall, the targeted and personalized nature of neurofeedback therapy holds potential for alleviating depressive symptoms and enhancing mental health outcomes.
Neurofeedback has shown promise in addressing specific phobias such as agoraphobia by targeting the underlying neural mechanisms associated with fear and anxiety. By utilizing real-time monitoring of brain activity and providing feedback to the individual, neurofeedback can help regulate and retrain the brain's response to fear-inducing stimuli. This process involves enhancing self-regulation of neural networks, promoting relaxation, and reducing hyperarousal, which are all crucial in managing agoraphobia symptoms. Through repeated sessions, neurofeedback aims to modify maladaptive neural patterns, leading to improved emotional regulation and reduced phobic responses. Additionally, neurofeedback may also enhance cognitive flexibility and resilience, contributing to a more comprehensive approach in addressing agoraphobia.
Neurofeedback therapy has shown promise in addressing the specific needs of individuals with complex trauma histories by targeting the dysregulated neural networks associated with trauma-related symptoms. By utilizing real-time monitoring of brain activity and providing feedback to the individual, neurofeedback therapy aims to modulate neural oscillations, enhance connectivity within the brain's networks, and promote self-regulation. This approach can potentially help individuals with complex trauma histories in managing symptoms such as hypervigilance, emotional dysregulation, and intrusive memories. Additionally, neurofeedback therapy may contribute to improving cognitive functioning, emotional resilience, and overall well-being in this population. The personalized nature of neurofeedback training allows for tailoring the intervention to the unique needs and experiences of individuals with complex trauma histories, offering a potentially valuable adjunct to traditional trauma-focused therapies.
Neurofeedback, also known as EEG biofeedback, has shown promise in alleviating symptoms of generalized anxiety in teenagers. By providing real-time feedback on brainwave activity, neurofeedback aims to train the brain to regulate its own functioning, potentially reducing anxiety symptoms. Studies have indicated that neurofeedback may help improve emotional regulation, attention, and cognitive flexibility, all of which are relevant to managing anxiety. Additionally, neurofeedback sessions often involve relaxation techniques and mindfulness practices, which can further contribute to reducing anxiety symptoms. While individual responses to neurofeedback may vary, it is worth considering as a non-invasive and drug-free option for addressing generalized anxiety in teenagers.
Neurofeedback therapy for children with ADHD has been found to have minimal side effects, with most studies reporting no adverse effects. The treatment is generally well-tolerated, with children experiencing improvements in attention, impulse control, and hyperactivity. Some potential side effects that have been reported include mild headaches, fatigue, or dizziness, but these are typically temporary and resolve quickly. Additionally, neurofeedback therapy is non-invasive and does not involve the use of medication, making it a safe and appealing option for parents seeking alternative treatments for their children with ADHD. It is important for parents to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine if neurofeedback therapy is a suitable option for their child.
Neurofeedback therapy has been shown to positively impact cognitive function in individuals with depression by targeting specific brainwave patterns associated with mood regulation, attention, and emotional processing. By utilizing real-time monitoring of brain activity and providing feedback to the individual, neurofeedback aims to train the brain to self-regulate and optimize its functioning. This can lead to improvements in executive function, working memory, and overall cognitive flexibility, which are often impaired in individuals with depression. Additionally, neurofeedback therapy may help modulate neural networks involved in emotional regulation, leading to reduced symptoms of depression and improved overall cognitive performance. Studies have indicated that neurofeedback can lead to significant improvements in cognitive function, providing promising results for individuals struggling with depression.
Yes, neurofeedback therapy can be customized to address specific anxiety disorders such as phobias. By utilizing neurofeedback techniques, therapists can target the specific neural pathways and brainwave patterns associated with the individual's phobia, allowing for a personalized and targeted approach to treatment. This tailored approach can help individuals retrain their brain's responses to the specific triggers of their phobia, leading to reduced anxiety and improved overall well-being. Additionally, neurofeedback therapy can be adapted to address the unique cognitive and emotional aspects of different phobias, providing a comprehensive and individualized treatment plan.
The typical duration of neurofeedback treatment for panic disorder can vary depending on the individual's response to the therapy, the severity of the symptoms, and the specific protocol used by the healthcare provider. Generally, neurofeedback treatment for panic disorder may involve regular sessions over a period of several months, with some individuals requiring ongoing maintenance sessions to sustain the benefits. The treatment plan may be tailored to address the unique neurophysiological patterns associated with panic disorder, aiming to regulate brainwave activity and promote self-regulation of emotional responses. Additionally, adjunctive therapies and lifestyle modifications may complement the neurofeedback treatment to optimize outcomes and long-term management of panic disorder symptoms. It's important for individuals considering neurofeedback treatment to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate and personalized treatment plan for their specific needs.