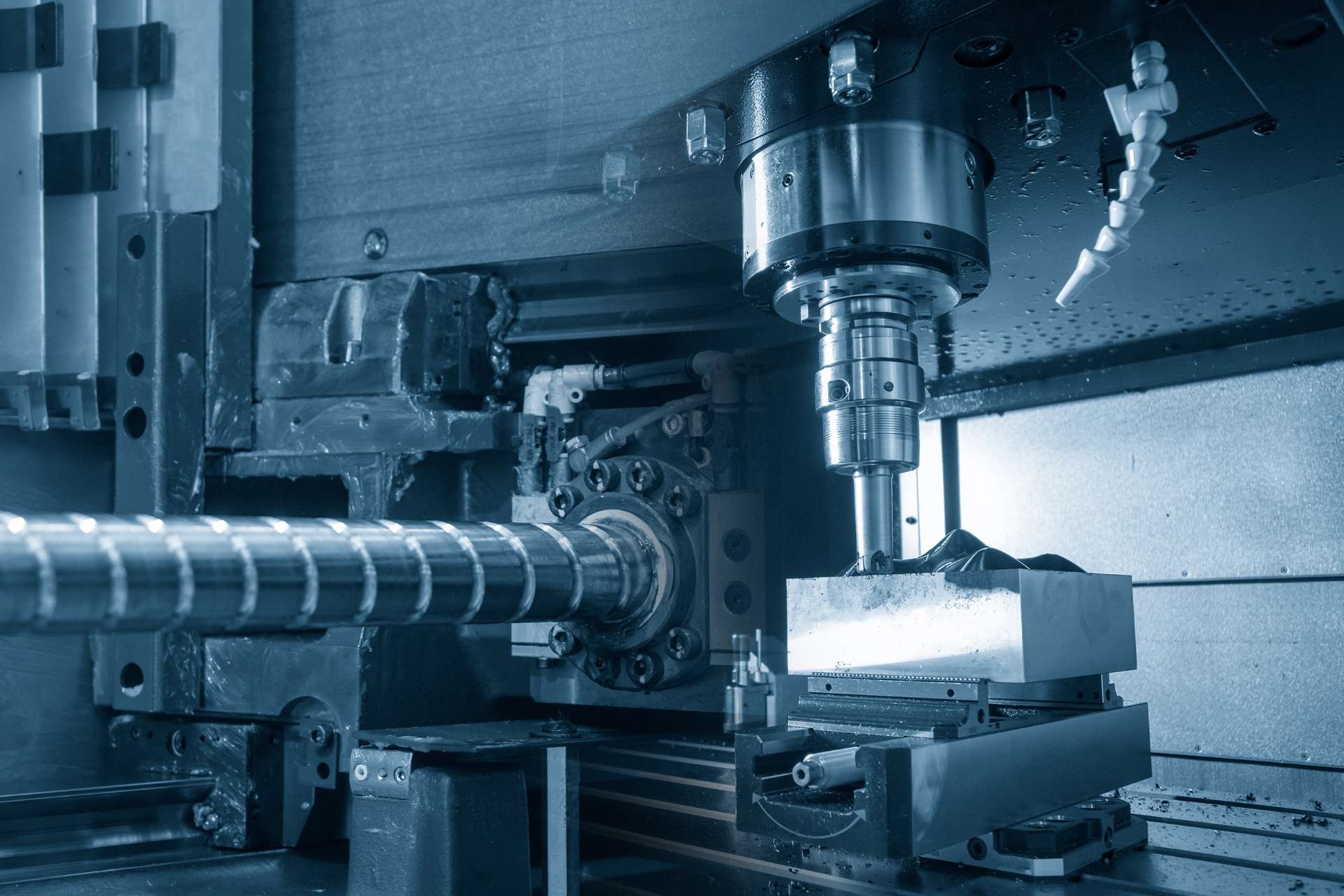

The purpose of Process Safety Management (PSM) is to prevent or minimize the occurrence of catastrophic accidents and incidents in industrial facilities that handle hazardous materials. PSM is a systematic approach that focuses on identifying, evaluating, and controlling the hazards associated with the processes used in these facilities. Its ultimate goal is to protect the safety and health of workers, the public, and the environment.
Process Safety Management helps prevent accidents and incidents in industrial facilities by implementing a comprehensive set of practices and procedures. These include conducting thorough hazard assessments, developing and implementing safe operating procedures, providing adequate training to employees, conducting regular inspections and audits, and maintaining effective communication channels. By following these practices, PSM helps identify potential hazards, assess their risks, and implement appropriate control measures to prevent accidents and incidents from occurring.
Giving back to the community has been a major staple of HGR’s identity since we first opened for business in 1998. This year was no different as employees from the Euclid facility gathered for their annual holiday celebration. This year HGR managed to collect and donate over 473lbs of non-perishable food items to the Euclid Hunger... Read More... The post HGR Gives Back During The Holidays! appeared first on HGR Inc..

Posted by on 2023-01-06
U.S. Inflation Slowed Sharply to 7.1% Over Past 12 Months Christopher Rugaber | Nov 13, 2022 | IEN Inflation in the United States slowed again last month in the latest sign that price increases are cooling despite the pressures they continue to inflict on American households. Economists expect the Fed to further slow its rate... Read More... The post Weekly Roundup – U.S. Inflation Slowing Down? Predictions for Manufacturing in 2023, Embracing Automation Technologies – Week of 12/12/22 appeared first on HGR Inc..

Posted by on 2022-12-15
Could These Risks Derail Your 2023 Engineering Projects? Design News | Dec 6, 2022 | Design News Design News asked Matthew Bey, senior global analyst for RANE, a risk intelligence company, about the current supply chain risks that could impact engineering projects in 2023. Around this time each year, RANE shares the key global trends and constraints that... Read More... The post Weekly Roundup – Could These Risks Derail Your 2023 Engineering Projects? 3 Critical Factors for Industry’s Future, Can Robotics Solve Labor Shortages – Week of 12/05/22 appeared first on HGR Inc..

Posted by on 2022-12-08
7 Ways Product Roadmap Management Software Helps Manufacturers Scott Dowell | Nov 11, 2022 | IEN Many global companies have learned to embrace technology over the past few years and not just by adapting to video conferencing with remote teams. Managing a product portfolio in one central location makes it easier to make adjustments, spot... Read More... The post Weekly RoundUp – Improving Roadmap Management, Is the Chip Shortage Over? What lies in Automation’s Future – Week of 11/28/22 appeared first on HGR Inc..

Posted by on 2022-12-02
Gear Up for the Grand Unveiling! Subscribe Now and Get the Inside Scoop! The clock is ticking! Are you on our email and SMS notification list yet? Brace yourself for some thrilling announcement that is coming your way soon! To get ahead of the pack, sign up for both email and SMS updates at... Read More... The post A Thrilling Surprise is on Its Way… Are You Onboard? appeared first on HGR Inc..

Posted by on 2022-12-02
The key elements of a Process Safety Management program include process safety information, process hazard analysis, operating procedures, training, contractor management, pre-startup safety reviews, mechanical integrity, hot work permits, management of change, incident investigation, emergency planning and response, and compliance audits. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe operation of industrial facilities and preventing accidents and incidents.

Process Safety Management addresses the identification and evaluation of hazards through a process hazard analysis (PHA). A PHA is a systematic and structured approach to identify and evaluate potential hazards associated with a process. It involves reviewing process information, conducting interviews with knowledgeable personnel, and using various analysis techniques to identify potential hazards. By conducting a PHA, organizations can identify and evaluate hazards, prioritize them based on their risks, and implement appropriate control measures to mitigate those risks.
Employee participation is a crucial requirement in Process Safety Management. It ensures that employees are actively involved in the identification, evaluation, and control of hazards in the workplace. The requirements for employee participation include providing employees with access to process safety information, involving them in the development and implementation of safe operating procedures, conducting training programs to enhance their understanding of process hazards, and establishing effective communication channels to encourage their input and feedback.
Safety Considerations for Dallas-TX-Based Industrial Equipment Maintenance and Repair Companies

Process Safety Management ensures that operating procedures are followed through various means. These include developing clear and concise operating procedures that are readily accessible to employees, providing adequate training to ensure employees understand and follow the procedures, conducting regular audits and inspections to verify compliance, and implementing a system for reporting and addressing deviations from the procedures. By implementing these measures, organizations can ensure that operating procedures are consistently followed, reducing the risk of accidents and incidents.
Management of change is a critical aspect of Process Safety Management. It involves a systematic approach to assess and manage changes to processes, equipment, personnel, or procedures that may impact the safety and health of workers or the surrounding environment. The management of change process includes identifying and evaluating potential hazards associated with the proposed changes, implementing appropriate control measures to mitigate those hazards, and communicating the changes to all affected personnel. By effectively managing changes, organizations can prevent unintended consequences and maintain the integrity of their process safety management systems.

Spill response teams require specialized training to effectively handle and mitigate hazardous spills. This training typically includes comprehensive instruction on spill prevention, containment, and cleanup techniques. Team members are educated on the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and are trained in the identification and handling of hazardous materials. They also receive instruction on the various types of spills they may encounter, such as oil spills, chemical spills, or biological spills, and the specific protocols for each. Additionally, spill response teams often undergo training in emergency response procedures, communication protocols, and coordination with other emergency personnel. Regular drills and exercises are conducted to ensure that team members are well-prepared to respond quickly and efficiently to any spill incident.
When handling machine lubricants, it is crucial to follow certain precautions to ensure safety and optimal performance. Firstly, individuals should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and protective clothing to protect themselves from potential skin contact or splashes. It is also important to handle lubricants in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling any fumes or vapors. Additionally, one should carefully read and follow the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for proper storage, handling, and disposal of lubricants. This includes keeping lubricants away from heat sources, open flames, and incompatible materials. Regularly inspecting containers for leaks or damage is essential to prevent spills or accidents. Lastly, individuals should be aware of any specific hazards associated with the type of lubricant being used and take necessary precautions accordingly. By adhering to these precautions, one can ensure safe and effective handling of machine lubricants.
Heat stress in workers is monitored through various methods to ensure their safety and well-being. One common approach is the use of wearable devices that measure physiological parameters such as body temperature, heart rate, and sweat rate. These devices, equipped with sensors, provide real-time data that can be analyzed to determine if a worker is experiencing heat stress. Additionally, environmental monitoring is conducted to measure factors such as air temperature, humidity, and radiant heat. This information is combined with the physiological data to assess the risk of heat stress and make informed decisions regarding work schedules, breaks, and the provision of adequate hydration and cooling measures. Regular training and education on recognizing the signs and symptoms of heat stress also play a crucial role in monitoring and preventing its occurrence in workers.
The specific lockout/tagout procedures for pneumatic equipment involve first identifying the energy sources, such as compressed air lines, and isolating them using lockout devices. This may include shutting off the main air supply, releasing any trapped air, and ensuring that all pressure is relieved from the system. Once the energy sources are isolated, a lockout/tagout device is applied to the equipment to prevent it from being energized. This device is then labeled with a tag indicating the reason for the lockout and the name of the authorized personnel performing the procedure. Before any maintenance or servicing is performed on the pneumatic equipment, it is essential to verify that all energy sources have been effectively isolated and that the equipment is safe to work on. Additionally, proper training and communication among the maintenance team are crucial to ensure that the lockout/tagout procedures are followed accurately and consistently.
Machine-specific safety procedures require specialized training to ensure the safe operation and maintenance of specific machines. This training typically includes comprehensive instruction on the machine's specific features, functions, and potential hazards. It may cover topics such as proper machine setup, operation techniques, emergency shutdown procedures, and maintenance protocols. Additionally, training may include information on personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, hazard identification, and risk assessment. By providing machine-specific safety training, individuals can develop the necessary knowledge and skills to operate and maintain machines safely, minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Emergency lighting systems in industrial settings are required to meet certain standards and regulations to ensure the safety of workers and visitors in the event of a power outage or emergency situation. These systems must provide adequate illumination to allow for safe evacuation and must be designed to withstand harsh industrial environments. The lighting must be strategically placed to ensure that all areas of the facility are covered, including stairwells, exits, and other critical areas. Additionally, emergency lighting systems must be regularly tested and maintained to ensure that they are functioning properly and are ready to be used in the event of an emergency. Other requirements may include the use of backup power sources, such as generators or batteries, to ensure that the emergency lighting system remains operational even during a power outage. Overall, emergency lighting systems in industrial settings must be designed and installed with safety as the top priority, and must meet all relevant regulations and standards to ensure that they are effective in the event of an emergency.
In industrial settings, electrical faults are protected against through the implementation of various safety measures and equipment. These measures include the use of circuit breakers, fuses, and surge protectors, which are designed to detect and interrupt abnormal electrical currents. Additionally, ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are commonly installed to prevent electric shock by quickly shutting off power in the event of a ground fault. Furthermore, industrial settings often employ the use of protective relays, which monitor electrical systems and can automatically isolate faulty sections to prevent further damage. Regular inspections and maintenance of electrical equipment are also crucial in identifying and addressing potential faults before they escalate into more serious issues. Overall, a comprehensive approach that combines preventive measures, advanced monitoring systems, and prompt response protocols is essential in safeguarding industrial settings against electrical faults.