

The purpose of electrical equipment grounding is to provide a safe pathway for electrical currents to flow in the event of a fault or malfunction. Grounding helps to prevent electrical shocks by redirecting excess electrical energy into the ground, rather than allowing it to pass through a person or object. This is achieved by connecting the electrical equipment to a grounding system, which consists of a network of conductors that are buried in the earth or connected to a grounding electrode. The grounding system provides a low-resistance path for electrical currents to flow, ensuring that any excess energy is safely dissipated.
Electrical equipment grounding prevents electrical shocks by creating a path of least resistance for electrical currents to follow. When a fault occurs, such as a short circuit or a ground fault, excess electrical energy can flow through the grounding system instead of passing through a person or object. This is because the grounding system is designed to have a lower resistance than the human body or other objects, allowing the electrical energy to be safely redirected into the ground. By providing this low-resistance path, grounding helps to protect individuals from electric shock and reduces the risk of injury or death.
Safety Considerations for Dallas-TX-Based Industrial Equipment Maintenance and Repair Companies
Giving back to the community has been a major staple of HGR’s identity since we first opened for business in 1998. This year was no different as employees from the Euclid facility gathered for their annual holiday celebration. This year HGR managed to collect and donate over 473lbs of non-perishable food items to the Euclid Hunger... Read More... The post HGR Gives Back During The Holidays! appeared first on HGR Inc..

Posted by on 2023-01-06
U.S. Inflation Slowed Sharply to 7.1% Over Past 12 Months Christopher Rugaber | Nov 13, 2022 | IEN Inflation in the United States slowed again last month in the latest sign that price increases are cooling despite the pressures they continue to inflict on American households. Economists expect the Fed to further slow its rate... Read More... The post Weekly Roundup – U.S. Inflation Slowing Down? Predictions for Manufacturing in 2023, Embracing Automation Technologies – Week of 12/12/22 appeared first on HGR Inc..

Posted by on 2022-12-15
Could These Risks Derail Your 2023 Engineering Projects? Design News | Dec 6, 2022 | Design News Design News asked Matthew Bey, senior global analyst for RANE, a risk intelligence company, about the current supply chain risks that could impact engineering projects in 2023. Around this time each year, RANE shares the key global trends and constraints that... Read More... The post Weekly Roundup – Could These Risks Derail Your 2023 Engineering Projects? 3 Critical Factors for Industry’s Future, Can Robotics Solve Labor Shortages – Week of 12/05/22 appeared first on HGR Inc..

Posted by on 2022-12-08
7 Ways Product Roadmap Management Software Helps Manufacturers Scott Dowell | Nov 11, 2022 | IEN Many global companies have learned to embrace technology over the past few years and not just by adapting to video conferencing with remote teams. Managing a product portfolio in one central location makes it easier to make adjustments, spot... Read More... The post Weekly RoundUp – Improving Roadmap Management, Is the Chip Shortage Over? What lies in Automation’s Future – Week of 11/28/22 appeared first on HGR Inc..

Posted by on 2022-12-02
There are several types of grounding systems used in electrical equipment, including the single-point grounding system, the multiple-point grounding system, and the isolated grounding system. The single-point grounding system involves connecting all electrical equipment to a common grounding point, such as a grounding busbar or a grounding electrode. This ensures that all equipment is at the same electrical potential and reduces the risk of electrical shock. The multiple-point grounding system involves connecting different pieces of equipment to separate grounding points, which can help to reduce the risk of electrical noise and interference. The isolated grounding system is used in sensitive electronic equipment and involves isolating the grounding conductor from other electrical conductors to minimize the risk of electrical noise.

The requirements for grounding electrical equipment in residential buildings vary depending on the local electrical codes and regulations. However, some common requirements include grounding the electrical service panel, grounding metal water pipes, and grounding metal electrical enclosures. The grounding system in a residential building typically consists of a grounding electrode, such as a metal rod or plate, that is connected to the electrical service panel. This provides a path for electrical currents to flow into the ground in the event of a fault. Additionally, any metal water pipes or electrical enclosures must be bonded to the grounding system to ensure that they are at the same electrical potential.
Electrical equipment grounding helps to protect against electrical fires by preventing the buildup of excess electrical energy. When electrical equipment is properly grounded, any fault or malfunction that causes an excess of electrical energy will be safely redirected into the ground. This prevents the electrical energy from overheating or igniting nearby combustible materials, reducing the risk of fire. Grounding also helps to ensure that electrical equipment operates within its designed parameters, reducing the risk of overheating or electrical arcing, which can also lead to fires.
Not properly grounding electrical equipment can have serious consequences. One of the main risks is the increased likelihood of electrical shocks. Without a proper grounding system, electrical energy can pass through a person or object, leading to electric shock and potential injury or death. In addition, not grounding electrical equipment can increase the risk of electrical fires. Without a path for excess electrical energy to flow into the ground, the energy can build up and cause overheating or electrical arcing, which can ignite nearby combustible materials. Improper grounding can also lead to electrical noise and interference, which can affect the performance of sensitive electronic equipment.
There are several common methods used to test the effectiveness of electrical equipment grounding. One method is the use of a ground resistance tester, which measures the resistance of the grounding system to ensure that it is within acceptable limits. This test is typically performed by connecting the tester to the grounding electrode and measuring the resistance between the electrode and a remote ground point. Another method is the use of a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI), which is a device that can detect and interrupt electrical faults. GFCIs are commonly used in residential buildings and can help to ensure that electrical equipment is properly grounded and protected against electrical shocks. Additionally, visual inspections of the grounding system can be conducted to check for any signs of damage or corrosion that could affect its effectiveness.

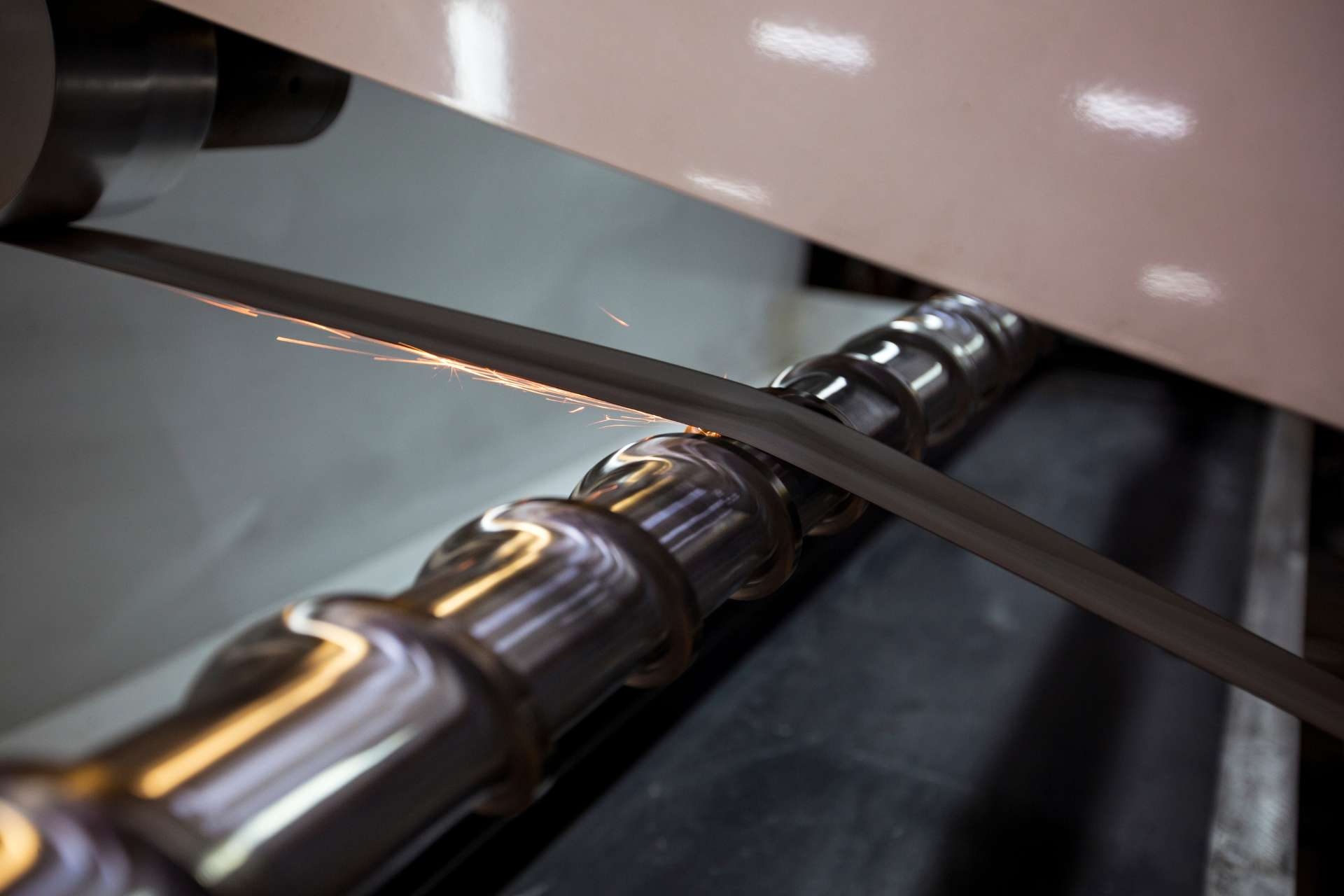
When arc welding, several safety measures are necessary to ensure the well-being of the welder and those in the surrounding area. Firstly, it is crucial to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as a welding helmet with a proper shade lens to protect the eyes from the intense light and harmful ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation emitted during the welding process. Additionally, welders should wear flame-resistant clothing, including a welding jacket, gloves, and boots, to safeguard against potential burns and sparks. Adequate ventilation is also essential to prevent the inhalation of hazardous fumes and gases produced during welding. Therefore, working in a well-ventilated area or using local exhaust ventilation systems is highly recommended. Furthermore, it is crucial to inspect and maintain welding equipment regularly to ensure its proper functioning and prevent any potential accidents. Lastly, welders should be trained in safe welding practices and be aware of emergency procedures, such as how to extinguish fires or respond to electrical shocks, to minimize the risks associated with arc welding.
Fall arrest anchor points should be installed in strategic locations throughout a facility to ensure the safety of workers who may be at risk of falling. These anchor points should be placed in areas where workers frequently access elevated surfaces or work at heights, such as rooftops, scaffolding, or elevated platforms. It is important to consider the specific needs of the facility and the tasks being performed when determining the placement of anchor points. Additionally, anchor points should be installed in accordance with relevant safety regulations and standards to ensure their effectiveness in preventing falls. By installing fall arrest anchor points in the appropriate locations, facilities can provide a safe working environment for their employees and minimize the risk of accidents and injuries.