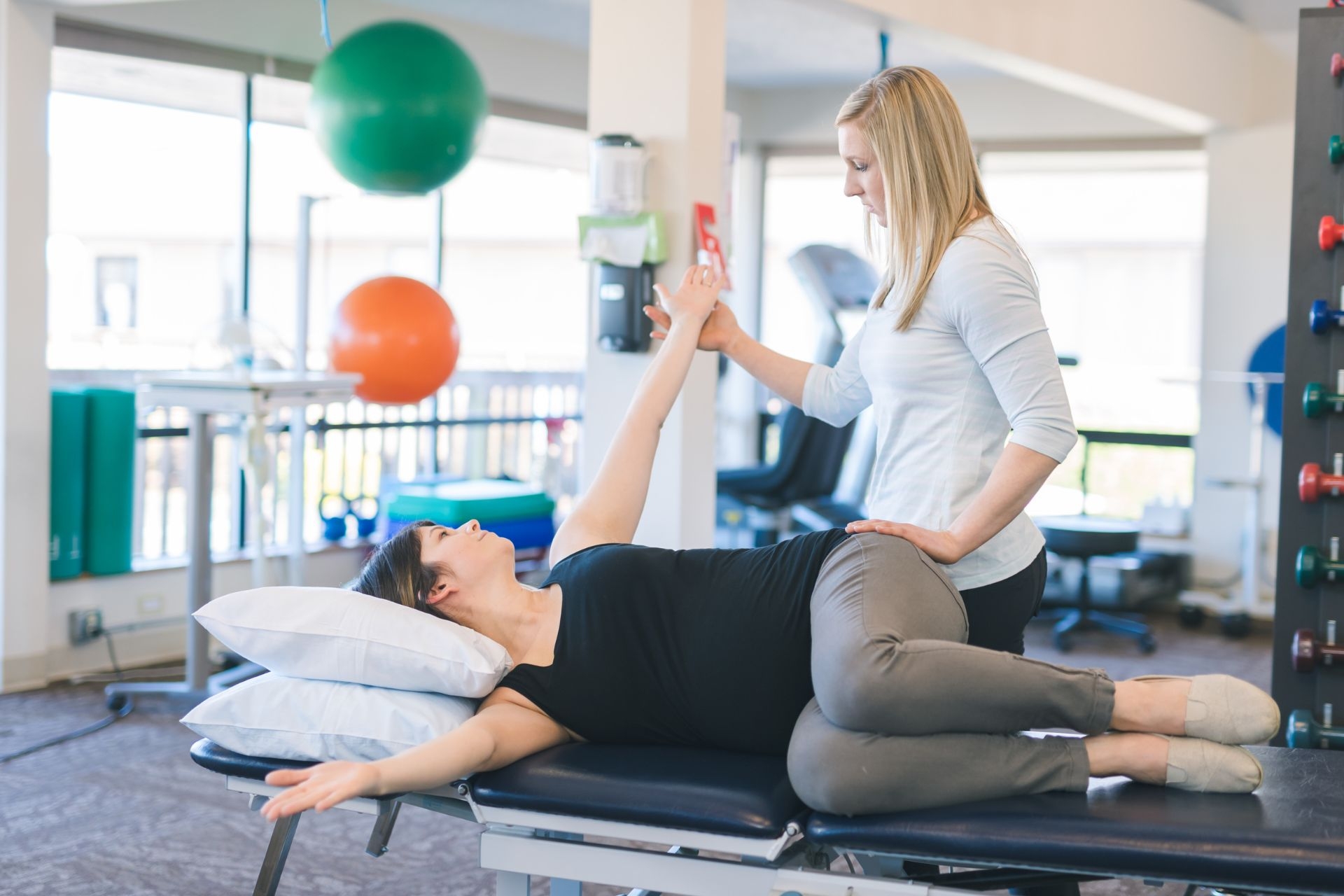


Like any form of physical therapy or exercise, there are potential risks and side effects associated with PNF. These may include muscle soreness, fatigue, or temporary discomfort during or after the session. It is important to work with a qualified healthcare professional or certified PNF therapist to ensure proper technique and progression to minimize the risk of injury. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions or injuries should consult with their healthcare provider before starting PNF to determine if it is appropriate for their specific needs.
Injury Prevention SpecialistThe time it takes to see results from PNF sessions can vary depending on several factors, including the individual's starting level of flexibility and strength, the frequency and intensity of the sessions, and the specific goals of the individual. Some individuals may experience improvements in range of motion and strength after just a few sessions, while others may require more time and consistent practice to see significant changes. Adapted Pilates Instructor It is important to have realistic expectations and to commit to a consistent PNF program to achieve the desired results.
PNF can be used as a standalone treatment or in conjunction with other therapies, depending on the individual's needs and goals. In some cases, PNF may be the primary treatment modality, especially for individuals seeking to improve flexibility, strength, and coordination. In other cases, PNF may be used as a complementary therapy alongside other treatments such as manual therapy, exercise therapy, or functional training. The decision to use PNF as a standalone treatment or in combination with other therapies will depend on the individual's specific condition, goals, and the recommendations of their healthcare provider or therapist.

When it comes to tendinopathy rehabilitation, there are several effective exercises that can help promote healing and strengthen the affected tendons. Eccentric exercises, such as the eccentric heel drop for Achilles tendinopathy, have been shown to be particularly beneficial. These exercises involve lengthening the tendon while under tension, which helps to stimulate collagen production and improve tendon strength. Functional Capacity Evaluator Other exercises that may be effective include isometric exercises, which involve holding a muscle contraction without movement, and isotonic exercises, which involve moving a muscle through a full range of motion. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to determine the most appropriate exercises for your specific condition.
The recovery time for tendinopathy can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's response to treatment. With proper rehabilitation, it is possible to see improvements within a few weeks to a few months. However, it is important to note that tendinopathy can be a chronic condition, and complete recovery may take longer. Consistency with rehabilitation exercises, following a proper treatment plan, and allowing for adequate rest and recovery are key factors in promoting healing and reducing recovery time.
Physical Rehabilitation Practitioner
Stretching can be a beneficial component of tendinopathy rehabilitation, but it is important to approach it with caution. While stretching can help improve flexibility and range of motion, certain stretches may aggravate the condition and should be avoided. It is generally recommended to focus on gentle, controlled stretches that do not cause pain or discomfort. Sensory Integration Therapy Practitioner Stretching exercises that target the muscles and tendons surrounding the affected area can help improve flexibility and reduce tension. Again, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to determine the most appropriate stretches for your specific condition.
There are several common mistakes that individuals should avoid during tendinopathy rehabilitation. One common mistake is pushing through pain or overexerting the affected area. It is important to listen to your body and avoid activities or exercises that cause pain or discomfort. Another mistake is neglecting rest and recovery. Tendons need time to heal, and overtraining or not allowing for adequate rest can hinder the healing process. It is also important to follow a proper treatment plan and not rely solely on exercises or therapies that may not be effective for your specific condition. Consulting with a healthcare professional or physical therapist can help ensure that you are avoiding these common mistakes and following an appropriate rehabilitation plan.
Becoming a specialist in paraneoplastic pemphigus rehabilitation as a physical therapist requires a combination of specialized education, clinical experience, and ongoing professional development. Physical therapists interested in this area of expertise typically pursue advanced training and certification in dermatology and autoimmune disorders. They may also seek out opportunities to work in specialized clinics or research settings that focus on paraneoplastic pemphigus rehabilitation. Additionally, staying up-to-date with the latest research and treatment approaches through attending conferences, participating in continuing education courses, and collaborating with other healthcare professionals in the field is crucial for providing the highest level of care to patients with paraneoplastic pemphigus. By acquiring the necessary knowledge and experience, physical therapists can effectively contribute to the rehabilitation and management of individuals with paraneoplastic pemphigus, helping them regain function and improve their quality of life.
Yes, there are physical therapists who specialize in treating individuals with tibial stress fractures. These specialized physical therapists have extensive knowledge and experience in managing and rehabilitating this specific type of injury. They are trained to assess the severity of the fracture, develop personalized treatment plans, and guide patients through a comprehensive rehabilitation program. Their expertise includes techniques such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, gait analysis, and modalities like ultrasound and electrical stimulation. By focusing exclusively on tibial stress fractures, these physical therapists can provide targeted and effective care to help individuals recover and regain their mobility and strength.
Yes, there are physical therapists who specialize in treating individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). These therapists have extensive knowledge and experience in managing the unique challenges and symptoms associated with ALS. They are trained to provide a comprehensive approach to care, focusing on maintaining mobility, improving strength and flexibility, managing pain and discomfort, and enhancing overall quality of life for individuals with ALS. These specialized physical therapists work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as neurologists and occupational therapists, to develop personalized treatment plans that address the specific needs and goals of each individual with ALS.
Becoming an expert in aquatic physical therapy requires a physical therapist to undergo specialized training and gain extensive experience in this specific field. They may pursue additional certifications or advanced degrees in aquatic therapy, which provide them with in-depth knowledge of the principles, techniques, and applications of aquatic therapy. These programs typically cover topics such as hydrodynamics, aquatic exercise physiology, aquatic manual therapy, and aquatic rehabilitation for various conditions. Additionally, a physical therapist can enhance their expertise by attending workshops, conferences, and seminars focused on aquatic therapy, where they can learn from leading experts in the field and stay updated on the latest advancements. By actively engaging in research and staying abreast of current literature, a physical therapist can further refine their skills and knowledge in aquatic physical therapy, ultimately becoming an expert in this specialized area of practice.
Becoming an expert in treating tibial stress fractures requires a physical therapist to undergo specialized training and gain extensive experience in this specific area of orthopedic rehabilitation. They may pursue advanced certifications or post-graduate courses that focus on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of tibial stress fractures. These courses may cover topics such as biomechanics, gait analysis, exercise prescription, manual therapy techniques, and the use of therapeutic modalities. Additionally, a physical therapist may actively seek out opportunities to work with athletes or individuals who are prone to tibial stress fractures, allowing them to gain hands-on experience and refine their skills in this particular area. By staying up-to-date with the latest research and advancements in the field, a physical therapist can continuously enhance their expertise in treating tibial stress fractures and provide the most effective and evidence-based care to their patients.
Physical therapists can specialize in working with individuals with cerebral palsy, as they possess the knowledge and expertise to address the unique needs and challenges associated with this condition. These therapists are trained in various therapeutic techniques and interventions that can help improve mobility, coordination, and overall physical function in individuals with cerebral palsy. They may utilize techniques such as neurodevelopmental treatment, constraint-induced movement therapy, and assistive technology to enhance motor skills and promote independence. Additionally, physical therapists may collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as occupational therapists and speech-language pathologists, to provide comprehensive care and support for individuals with cerebral palsy.