
Spinal cord injury rehabilitation utilizes a variety of therapies and interventions to address the specific needs of individuals. Physical therapy focuses on improving strength, flexibility, and mobility through exercises and specialized equipment. Occupational therapy helps individuals develop skills for activities of daily living, such as dressing, bathing, and cooking. Assistive devices, such as wheelchairs or braces, may be prescribed to enhance mobility and independence. Additionally, psychological counseling and support groups are often provided to address the emotional and mental health aspects of living with a spinal cord injury.
Myofascial Release TherapistThe duration of spinal cord injury rehabilitation varies depending on the individual and the severity of the injury. Physical Rehabilitation Practitioner Rehabilitation programs can range from a few weeks to several months or even years. The length of time is influenced by factors such as the extent of the injury, the individual's overall health, and their progress in achieving rehabilitation goals. It is important to note that spinal cord injury rehabilitation is an ongoing process, and individuals may continue to benefit from therapy and support throughout their lives.
Spinal cord injuries can lead to various complications and long-term effects. These can include chronic pain, muscle spasms, bladder and bowel dysfunction, sexual dysfunction, respiratory problems, and pressure sores. Joint Mobilization Expert Additionally, individuals with spinal cord injuries may be at a higher risk for secondary health conditions such as urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and osteoporosis. Psychological and emotional challenges, such as depression, anxiety, and adjustment disorders, are also common. It is crucial for individuals with spinal cord injuries to receive comprehensive medical care and ongoing support to manage these potential complications and optimize their overall well-being.

Sensory integration therapy is a type of therapy that aims to help individuals with sensory processing disorders by addressing difficulties in processing and responding to sensory information. It works by providing a controlled and structured environment where individuals can engage in activities that stimulate their senses in a therapeutic way. The therapy focuses on improving the brain's ability to process and integrate sensory information, leading to better overall functioning and behavior.
There are several signs and symptoms that may indicate a need for sensory integration therapy. These can include hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to sensory input, difficulty with coordination and motor skills, poor attention and concentration, frequent meltdowns or emotional outbursts, and difficulty with transitions and changes in routine. Additionally, individuals may exhibit sensory-seeking behaviors, such as constantly seeking out intense sensory experiences or engaging in repetitive movements.
Sensory integration therapy utilizes a variety of techniques and activities to help individuals with sensory processing disorders. Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Rehabilitation Expert These can include swinging, spinning, and other forms of vestibular input, deep pressure and tactile stimulation, balance activities, and proprioceptive input. The therapy may also incorporate activities that target visual and auditory processing, as well as activities that promote motor planning and coordination. The specific techniques and activities used will depend on the individual's needs and goals.
The duration and frequency of sensory integration therapy can vary depending on the individual's needs and progress. Typically, therapy sessions last for about 45 minutes to an hour. The frequency of sessions can range from once a week to multiple times a week, depending on the severity of the individual's sensory processing difficulties and their ability to tolerate therapy. The therapy may be conducted over a period of several months or longer, with regular assessments to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
Neurorehabilitation Specialist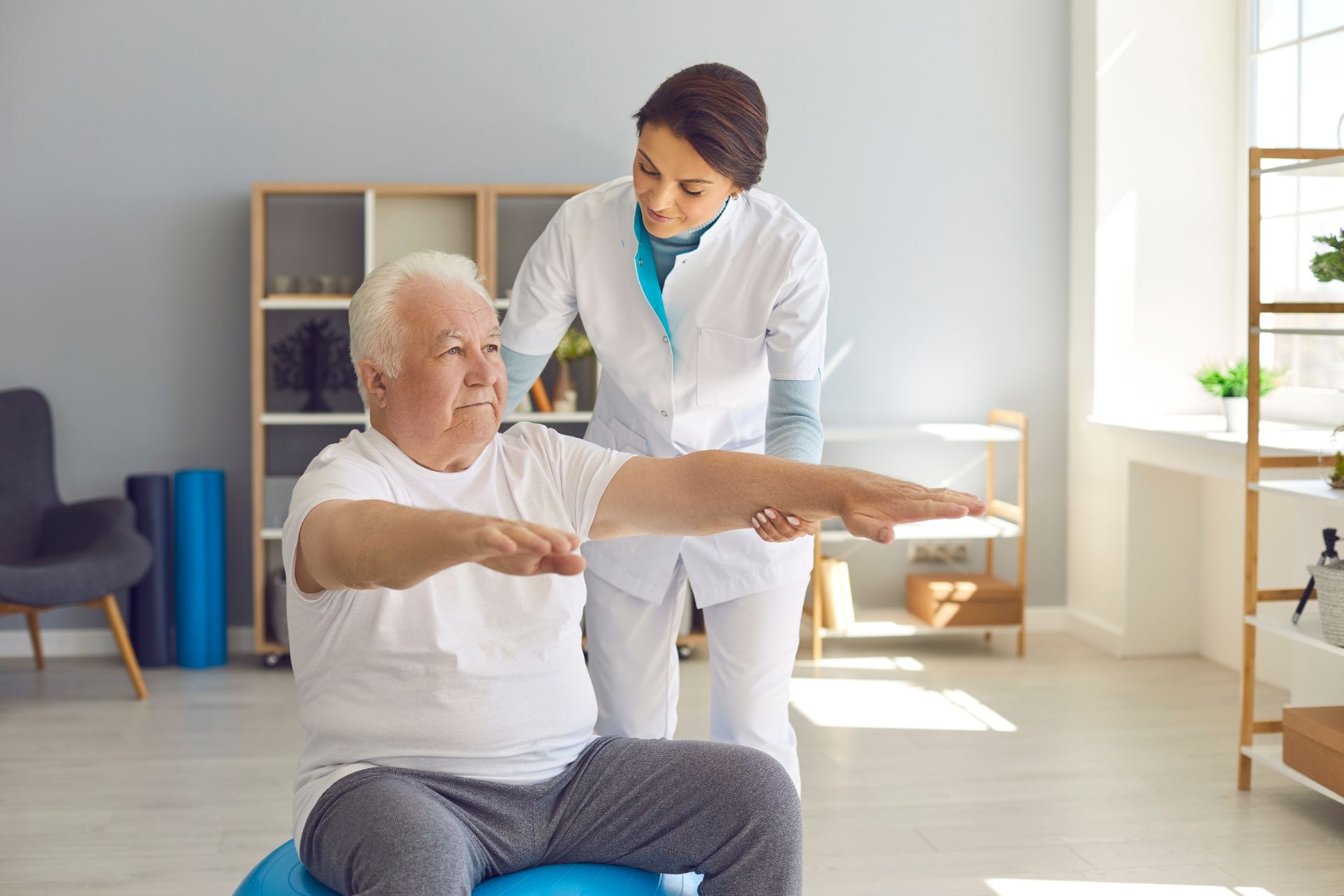
Yes, physical therapists can specialize in treating chronic ankle instability. They have the knowledge and expertise to assess and diagnose the underlying causes of ankle instability, such as ligament laxity, muscle weakness, and proprioceptive deficits. Physical therapists can then develop a comprehensive treatment plan that includes exercises to strengthen the ankle and surrounding muscles, balance and proprioceptive training, manual therapy techniques, and functional training. By addressing these specific issues, physical therapists can help individuals with chronic ankle instability improve their stability, reduce pain, and regain their mobility and function.
Yes, there are physical therapists who specialize in postural restoration techniques. These therapists have undergone specialized training and have a deep understanding of the musculoskeletal system and how it relates to posture. They use a variety of techniques and exercises to help patients improve their posture and alleviate any associated pain or discomfort. These therapists may also incorporate other modalities such as manual therapy, stretching, and strengthening exercises to address any underlying issues contributing to poor posture. By focusing on postural restoration, these therapists aim to help patients achieve optimal alignment and function in their daily activities.
Physical therapists who wish to specialize in stress fractures of the foot typically undergo extensive training and education in order to provide the highest level of care to their patients. This specialized training often includes completing a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) program, which typically takes three years to complete. During their DPT program, aspiring physical therapists may take courses in anatomy, biomechanics, kinesiology, and exercise physiology, all of which are essential for understanding the complexities of the foot and its associated structures. Additionally, physical therapists may pursue further education and certifications in areas such as orthopedics or sports physical therapy, which can provide them with a deeper understanding of the specific issues related to stress fractures in the foot. By combining their foundational knowledge with specialized training, physical therapists can effectively diagnose and treat stress fractures, helping their patients recover and regain optimal foot function.
To become a vestibular rehabilitation specialist in physical therapy, individuals must possess a strong educational background and acquire specific qualifications. Typically, this includes completing a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) program from an accredited institution. Additionally, specialized training in vestibular rehabilitation is necessary, which can be obtained through post-graduate courses or certifications. These courses cover topics such as the anatomy and physiology of the vestibular system, assessment and diagnosis of vestibular disorders, and treatment techniques for vestibular rehabilitation. It is also beneficial for individuals to gain clinical experience in working with patients with vestibular disorders under the supervision of experienced vestibular rehabilitation specialists. This combination of education, specialized training, and clinical experience equips individuals with the necessary qualifications to become proficient vestibular rehabilitation specialists in the field of physical therapy.
Yes, physical therapists can specialize in providing services for multiple sclerosis (MS) exclusively. These specialized physical therapists have extensive knowledge and experience in treating the unique needs and challenges of individuals with MS. They are trained in specific techniques and interventions that can help manage symptoms such as muscle weakness, spasticity, balance and coordination issues, and fatigue. Additionally, they can provide education and guidance on energy conservation strategies, adaptive equipment, and exercises to improve mobility and overall quality of life for individuals with MS. By focusing exclusively on MS, these physical therapists can provide targeted and personalized care to help individuals with MS optimize their physical function and independence.
Yes, there are physical therapists who specialize in treating individuals with posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. These therapists have extensive knowledge and experience in diagnosing and treating this specific condition. They are skilled in assessing the biomechanics of the foot and ankle, as well as designing personalized treatment plans that address the underlying causes of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. These therapists may use a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation to help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and restore function. By focusing exclusively on this condition, these specialized physical therapists can provide targeted and effective care for individuals with posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.