

The brain processes and interprets pain signals from the body through a complex network of neural pathways. When nociceptors detect a painful stimulus, they send electrical signals to the spinal cord, which then transmit the signals to the brain. Geriatric Rehabilitation Therapist The brain receives these signals and processes them in various regions, including the somatosensory cortex, which is responsible for the perception of physical sensations, and the limbic system, which is involved in emotional and motivational aspects of pain. The brain also integrates information from other sensory modalities, such as touch and temperature, to create a comprehensive perception of pain.
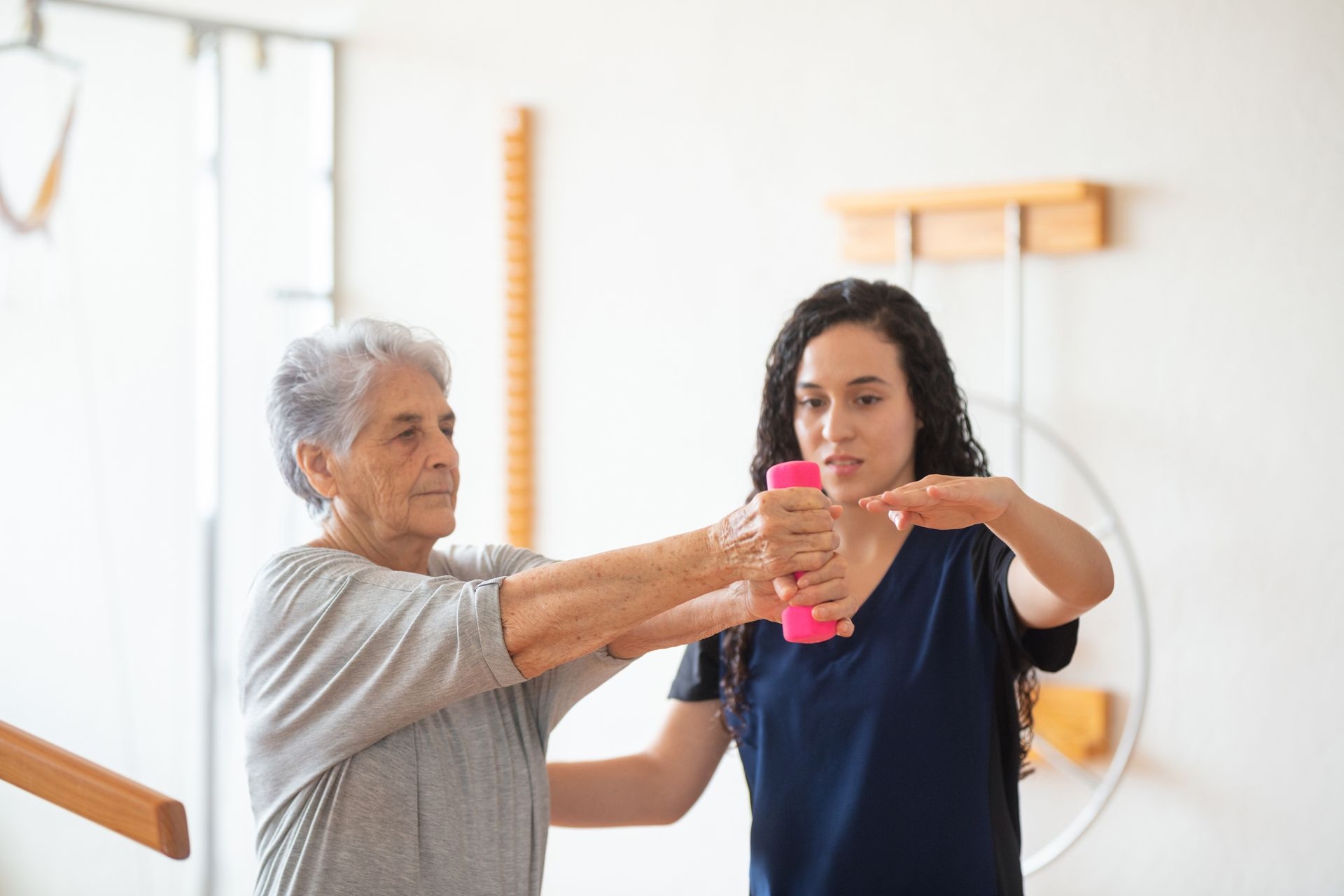
There are several effective strategies for managing chronic pain without relying solely on medication. Physical therapy and exercise can help improve strength, flexibility, and overall function, reducing pain and improving quality of life. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals develop coping skills and change negative thought patterns associated with pain. Techniques such as relaxation exercises, mindfulness, and deep breathing can also help reduce stress and promote relaxation, which can alleviate pain. Neuro-Developmental Therapist Additionally, complementary therapies such as acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic care may provide relief for some individuals.
Understanding the science of pain can help individuals better cope with their pain experiences. By learning about the complex mechanisms involved in pain perception, individuals can gain a sense of control and empowerment over their pain. Understanding that pain is not always an accurate measure of tissue damage can help individuals manage their pain more effectively and avoid unnecessary worry or fear. Additionally, understanding the role of psychological factors in pain can help individuals address and manage stress, anxiety, and other emotional factors that may contribute to their pain. Pain Neuroscience Educator Overall, knowledge about the science of pain can provide individuals with a foundation for developing personalized pain management strategies and improving their overall well-being.

Instrument-assisted joint mobilization is a technique used by healthcare professionals, such as physical therapists and chiropractors, to improve joint mobility and reduce pain in patients with musculoskeletal conditions. Neuro-IFRAH Approach Practitioner Unlike other forms of joint mobilization, which typically involve manual manipulation of the joint, instrument-assisted joint mobilization utilizes specialized tools or instruments to apply controlled force to the joint. These instruments can vary in shape and size, but they are designed to target specific areas of the joint and provide a more precise and targeted treatment approach.
There are several benefits of instrument-assisted joint mobilization for patients with musculoskeletal conditions. Firstly, it can help improve joint range of motion by breaking up scar tissue or adhesions that may have formed within the joint. This can lead to increased flexibility and improved functional movement. Additionally, instrument-assisted joint mobilization can help reduce pain by stimulating the nervous system and promoting the release of endorphins, which are natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body. Post-Surgery Scar Management Practitioner It can also help improve blood circulation to the joint, which can aid in the healing process and reduce inflammation.

While instrument-assisted joint mobilization can be a beneficial treatment option, there are some contraindications and precautions to consider. It is not recommended for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as fractures, infections, or tumors in the joint area. Additionally, caution should be exercised when using instrument-assisted joint mobilization on individuals with osteoporosis or other conditions that may weaken the bones. It is important for healthcare professionals to thoroughly assess each patient's medical history and condition before determining if instrument-assisted joint mobilization is appropriate for them.
Instrument-assisted joint mobilization helps improve joint range of motion and reduce pain through several mechanisms. Firstly, the controlled force applied to the joint helps break up scar tissue or adhesions that may have formed, allowing for smoother movement of the joint. This can lead to increased flexibility and improved range of motion. Additionally, the stimulation of the nervous system during instrument-assisted joint mobilization can help reduce pain by promoting the release of endorphins, which are natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body. The improved blood circulation to the joint can also aid in reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
Yes, there are physical therapists who specialize in treating individuals with Lisfranc fractures. These therapists have extensive knowledge and experience in managing the specific rehabilitation needs of patients with this type of foot injury. They are skilled in providing targeted interventions to promote healing, reduce pain, restore range of motion, and improve strength and function in the affected foot and ankle. Additionally, they may employ various modalities such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, gait training, and functional activities to optimize the recovery process. By working closely with patients and their healthcare team, these specialized physical therapists play a crucial role in helping individuals with Lisfranc fractures regain their mobility and return to their normal activities.
Physical therapists who wish to specialize in peroneal tendonitis typically need to complete additional training and education beyond their basic physical therapy degree. This may include attending specialized courses or workshops that focus specifically on the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of peroneal tendonitis. These courses may cover topics such as anatomy and biomechanics of the peroneal tendons, assessment and evaluation techniques, manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and modalities for pain management and inflammation reduction. Additionally, physical therapists may also benefit from gaining practical experience through clinical rotations or internships in settings that specialize in treating foot and ankle conditions. By obtaining this specialized training, physical therapists can develop the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively assess, treat, and manage peroneal tendonitis in their patients.
Yes, there are physical therapists who specialize in treating individuals with Friedreich's ataxia. These therapists have extensive knowledge and experience in working with patients who have this specific condition. They are trained to address the unique challenges and symptoms associated with Friedreich's ataxia, such as balance and coordination issues, muscle weakness, and difficulties with walking and mobility. These specialized physical therapists use a variety of techniques and interventions, including exercises, stretches, and assistive devices, to help improve functional abilities and enhance quality of life for individuals with Friedreich's ataxia. They work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans that target their specific needs and goals. By focusing exclusively on Friedreich's ataxia, these physical therapists are able to provide specialized care and support to individuals with this condition.
Becoming an expert in rehabilitation after metatarsal stress fractures requires a physical therapist to undergo specialized training and gain extensive experience in this specific area of treatment. They may pursue advanced certifications or attend specialized courses that focus on the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of metatarsal stress fractures. Additionally, they may engage in ongoing professional development activities, such as attending conferences or workshops, to stay up-to-date with the latest research and techniques in this field. By actively seeking out opportunities to expand their knowledge and skills, a physical therapist can become a trusted expert in rehabilitating patients with metatarsal stress fractures.
Yes, physical therapists can specialize in providing services for post-concussion syndrome exclusively. Post-concussion syndrome is a complex condition that can result from a traumatic brain injury. Physical therapists who focus on this area of expertise have a deep understanding of the specific symptoms and challenges associated with post-concussion syndrome. They are trained to develop individualized treatment plans that address the physical, cognitive, and emotional aspects of the condition. These therapists may use a variety of techniques such as vestibular rehabilitation, balance training, vision therapy, and manual therapy to help patients manage their symptoms and improve their overall function and quality of life. By staying up-to-date with the latest research and advancements in the field, these specialized physical therapists can provide the most effective and evidence-based care for individuals with post-concussion syndrome.
Yes, there are physical therapists who specialize in treating individuals with fibrous dysplasia. These therapists have extensive knowledge and experience in working with patients who have this condition. They are trained to develop personalized treatment plans that address the specific needs and challenges associated with fibrous dysplasia. These plans may include exercises to improve strength and flexibility, manual therapy techniques to reduce pain and improve mobility, and education on proper body mechanics and posture. By working closely with these specialized physical therapists, individuals with fibrous dysplasia can receive the targeted care they need to manage their condition and improve their quality of life.