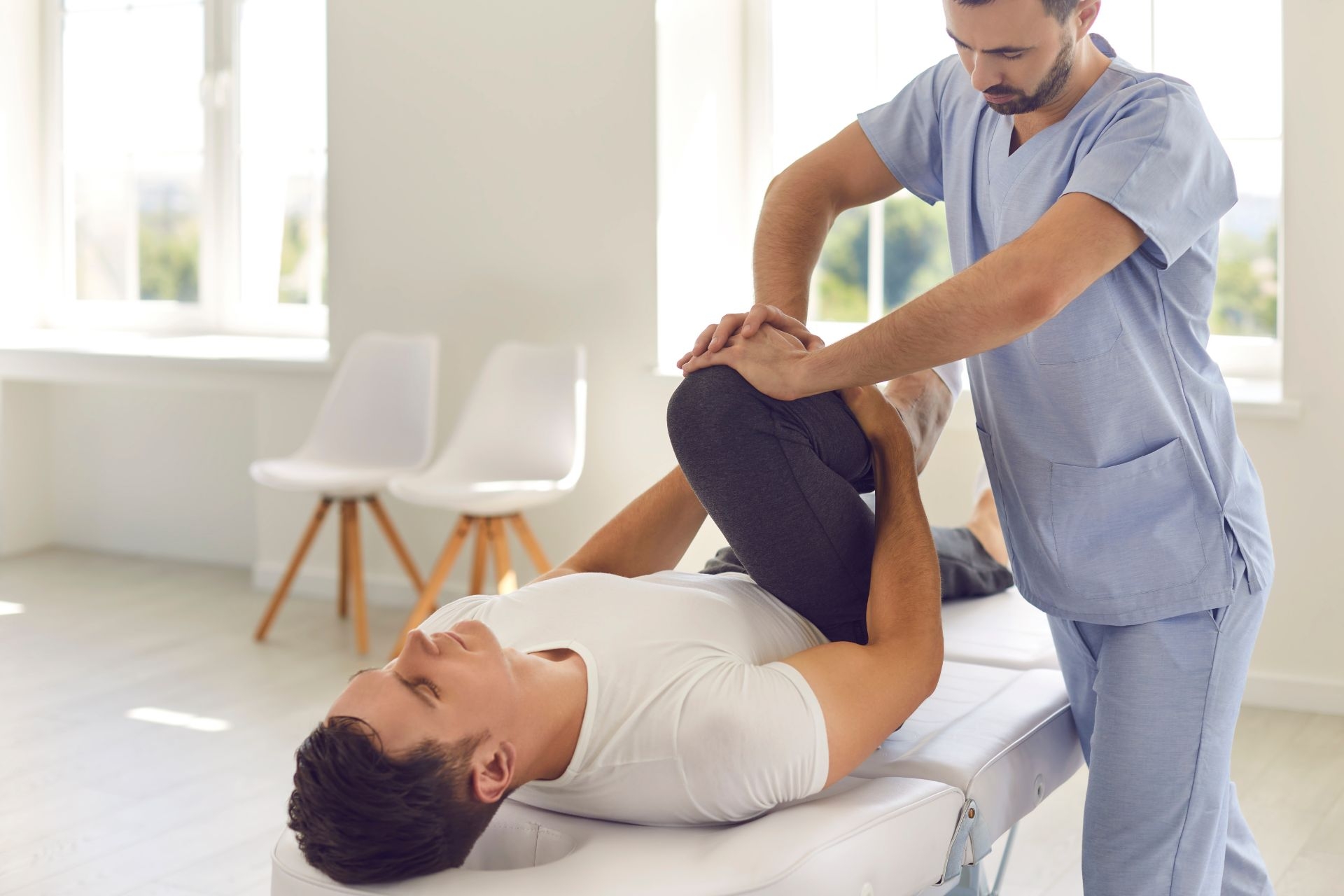

The most common orthopedic conditions that require physical therapy include fractures, sprains, strains, tendonitis, bursitis, and joint replacements. Fractures often require physical therapy to help regain strength and mobility in the affected area. Sprains and strains may require physical therapy to reduce pain and inflammation and improve range of motion. Tendonitis and bursitis can benefit from physical therapy to alleviate pain and improve flexibility. Joint replacements, such as hip or knee replacements, often require physical therapy to help restore function and mobility to the joint.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of orthopedic injuries by promoting healing, reducing pain, and restoring function. Physical therapists use various techniques to achieve these goals, including manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as heat or cold therapy. Manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization and soft tissue mobilization, help improve joint mobility and reduce muscle tension. Therapeutic exercises are designed to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance overall function. Movement Therapist Modalities like heat or cold therapy can help reduce pain and inflammation. By combining these approaches, physical therapy helps patients regain their independence and return to their normal activities.
Orthopedic physical therapists utilize a range of treatment techniques to address the specific needs of their patients. These techniques may include manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, modalities, and functional training. Ergonomics Specialist Manual therapy techniques involve hands-on manipulation of joints and soft tissues to improve mobility and reduce pain. Therapeutic exercises are tailored to the individual's condition and may include strengthening exercises, stretching, and balance training. Modalities such as heat, cold, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation can be used to reduce pain and inflammation. Functional training focuses on improving movement patterns and enhancing overall function to help patients return to their daily activities.

In some cases, physical therapy can help prevent the need for surgery in orthopedic cases. Physical therapists work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans that aim to address the underlying issues causing pain or dysfunction. By strengthening muscles, improving flexibility, and optimizing movement patterns, physical therapy can often alleviate symptoms and improve function without the need for surgical intervention. However, it is important to note that the decision to pursue surgery ultimately depends on the severity and nature of the orthopedic condition, and physical therapy may not be suitable for all cases.
Musculoskeletal Health SpecialistThe recovery time for an orthopedic injury with the help of physical therapy can vary depending on the type and severity of the injury, as well as individual factors such as age and overall health. In general, physical therapy can significantly expedite the recovery process by promoting healing, reducing pain, and restoring function. Adapted Fitness Trainer The duration of physical therapy treatment can range from a few weeks to several months, with regular sessions typically scheduled 1-3 times per week. The therapist will assess the progress and adjust the treatment plan accordingly to ensure optimal recovery.

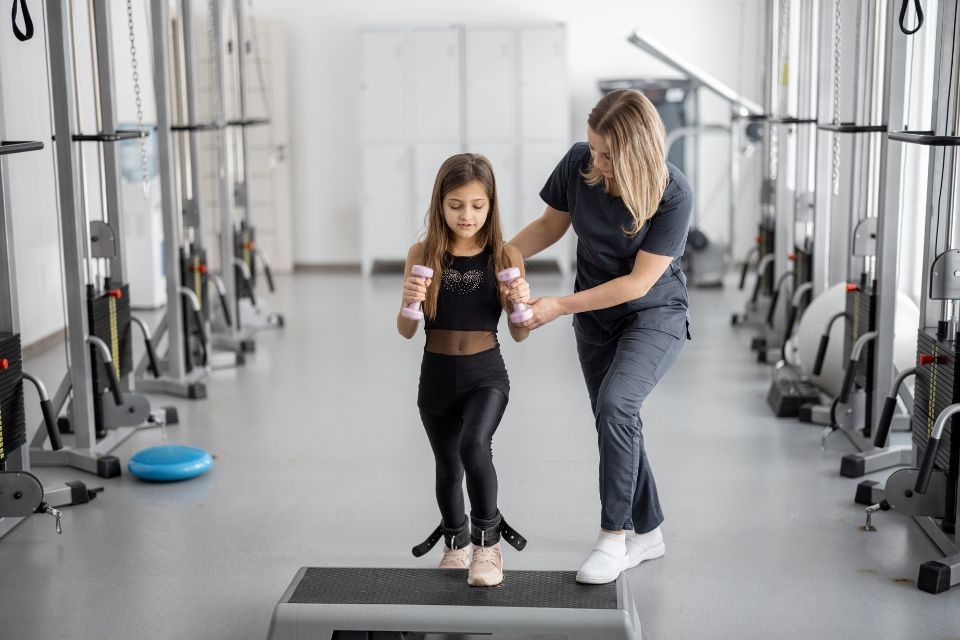
Orthopedic physical therapists prescribe a variety of exercises and stretches to address specific needs and goals of their patients. Sports Rehabilitation Expert These may include strengthening exercises to target specific muscle groups, such as the quadriceps or rotator cuff muscles. Stretching exercises are often prescribed to improve flexibility and range of motion in affected joints or muscles. Balance and coordination exercises may also be incorporated to enhance stability and prevent future injuries. The specific exercises and stretches prescribed will depend on the individual's condition and treatment goals, and the physical therapist will provide guidance and instruction on proper technique and progression.
During orthopedic physical therapy sessions, patients should be aware of certain precautions and limitations to ensure their safety and maximize the effectiveness of the treatment. It is important to follow the therapist's instructions and guidelines regarding proper body mechanics and technique during exercises to avoid further injury. Patients should communicate any pain or discomfort experienced during the session to the therapist, as this can help guide adjustments to the treatment plan. It is also important to adhere to any activity restrictions or modifications recommended by the therapist to prevent exacerbation of the injury. Overall, open communication with the therapist and adherence to their guidance will help ensure a safe and successful orthopedic physical therapy experience.

Physical therapists who work with individuals with cervical dystonia must meet certain requirements to provide effective treatment. Firstly, they should have a strong educational background in physical therapy, with a focus on neurology and movement disorders. Additionally, they should possess specialized knowledge and training in the assessment and treatment of cervical dystonia. This includes understanding the underlying causes and mechanisms of the condition, as well as the latest evidence-based interventions. Furthermore, physical therapists working with individuals with cervical dystonia should have excellent communication and interpersonal skills, as they will need to collaborate with other healthcare professionals and educate patients on self-management strategies. They should also stay updated on advancements in the field and participate in continuing education to ensure they are providing the best possible care. Overall, physical therapists working with individuals with cervical dystonia should have a comprehensive skill set and a deep understanding of the condition to effectively address the unique needs of their patients.
Physical therapists are highly skilled healthcare professionals who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of various musculoskeletal conditions. While they have a broad range of expertise, they can certainly focus on treating IT band syndrome exclusively. IT band syndrome, also known as iliotibial band syndrome, is a common overuse injury that affects the outer side of the knee. Physical therapists can employ a variety of techniques and modalities to address this condition, including manual therapy, stretching exercises, strengthening exercises, and biomechanical analysis. By utilizing their knowledge and experience in treating IT band syndrome, physical therapists can help patients alleviate pain, improve mobility, and restore function.
To become a proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) practitioner as a physical therapist, individuals must complete the necessary training and education. This typically involves obtaining a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) degree from an accredited program. During their education, aspiring PNF practitioners will learn about the principles and techniques of PNF, as well as other related topics such as anatomy, physiology, and biomechanics. Additionally, they may choose to pursue specialized courses or certifications in PNF to further enhance their skills and knowledge in this area. Continuous professional development and staying up-to-date with the latest research and advancements in PNF are also important for PNF practitioners to provide the best possible care to their patients.
Becoming a specialist in Lisfranc injuries as a physical therapist typically involves a combination of advanced education, specialized training, and clinical experience. Physical therapists interested in this area of expertise may pursue post-graduate certifications or advanced degrees in orthopedic physical therapy or sports physical therapy, which often include coursework and clinical rotations focused on foot and ankle injuries. Additionally, they may seek out opportunities to work with experienced physical therapists who specialize in treating Lisfranc injuries, allowing them to gain hands-on experience and mentorship in this specific area. By staying up-to-date with the latest research and treatment techniques, attending relevant conferences and workshops, and actively participating in professional organizations related to foot and ankle rehabilitation, physical therapists can further enhance their knowledge and skills in managing Lisfranc injuries.
Yes, there are physical therapists who specialize in treating individuals with arthrogryposis. These therapists have extensive knowledge and experience in working with the unique challenges and limitations that individuals with arthrogryposis face. They are trained in specific techniques and interventions that can help improve mobility, strength, and function in individuals with this condition. These therapists may also collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as orthopedic surgeons and occupational therapists, to provide comprehensive care for individuals with arthrogryposis.