
If left untreated, pediatric torticollis can lead to a range of potential complications. These may include persistent muscle tightness, limited range of motion in the neck, and asymmetrical development of the head and face. Neurorehabilitation Specialist In some cases, untreated torticollis can also result in the development of plagiocephaly, a condition characterized by an abnormal head shape. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can help minimize these complications and promote optimal development.
The recovery time for a child with pediatric torticollis can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. In mild cases, improvement may be seen within a few weeks or months with conservative measures such as stretching exercises and physical therapy. However, more severe cases or those requiring surgical intervention may require a longer recovery period. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan and monitor progress.
Feldenkrais Method PractitionerThere are several exercises and stretches that can help improve the symptoms of pediatric torticollis. These may include gentle stretching of the neck muscles, range of motion exercises, and strengthening exercises for the affected muscles. Functional Movement Specialist Physical therapists can provide guidance on specific exercises and techniques that are appropriate for each individual child. It is important to perform these exercises under the supervision of a healthcare professional to ensure they are done correctly and safely. Consistency and regular practice of these exercises can help promote improved neck mobility and overall function.

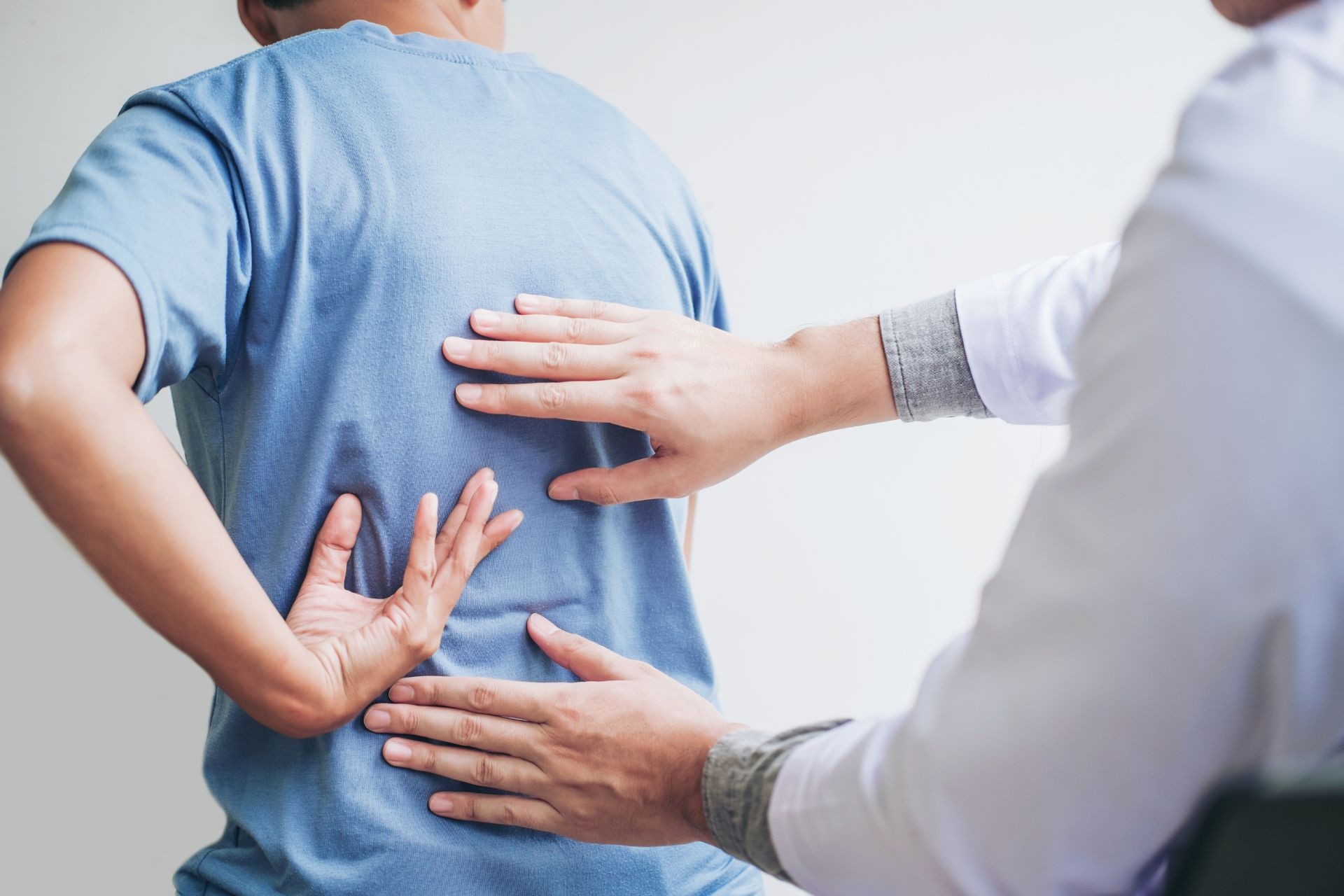
Scar tissue mobilization is a therapeutic technique used to break down and remodel scar tissue that forms as a result of injury or surgery. It involves applying manual pressure and stretching to the affected area to improve the flexibility and function of the scar tissue. The goal of scar tissue mobilization is to reduce pain, improve range of motion, and restore normal tissue texture and movement. This technique works by breaking down the adhesions and restrictions within the scar tissue, promoting collagen remodeling, and stimulating blood flow to the area.
Yes, scar tissue mobilization can help improve range of motion in joints affected by scar tissue. Scar tissue can cause stiffness and limited mobility in the surrounding tissues, leading to decreased range of motion. By applying specific techniques to the scar tissue, such as deep tissue massage, myofascial release, and stretching, scar tissue mobilization can help break down adhesions and increase the flexibility of the tissues. This can result in improved joint mobility and range of motion.

While scar tissue mobilization is generally safe, there are some risks and side effects associated with the technique. These may include temporary discomfort or pain during the treatment, bruising, swelling, and skin irritation. Women's Health Physiotherapist In rare cases, scar tissue mobilization may cause tissue damage or exacerbate existing conditions. It is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or physical therapist before undergoing scar tissue mobilization to ensure it is appropriate for your specific situation and to minimize the risk of complications.
The time it takes to see results from scar tissue mobilization can vary depending on the severity and extent of the scar tissue, as well as individual factors such as healing ability and adherence to treatment. Some individuals may experience improvements in range of motion, pain, and scar appearance after just a few sessions, while others may require several weeks or months of consistent treatment to see significant changes. Muscular Strength and Conditioning Coach It is important to have realistic expectations and to follow the recommended treatment plan to achieve the best results.

Becoming a specialist in hip bursitis management as a physical therapist requires a combination of education, experience, and ongoing professional development. Firstly, a physical therapist must complete a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) program, which provides a comprehensive understanding of musculoskeletal anatomy, biomechanics, and therapeutic techniques. Additionally, they may pursue specialized coursework or certifications in orthopedic physical therapy, sports rehabilitation, or manual therapy, which can further enhance their knowledge and skills in managing hip bursitis. To gain practical experience, physical therapists may seek opportunities to work in orthopedic clinics or sports medicine settings, where they can treat a variety of hip conditions, including bursitis. Continuing education is crucial for staying up-to-date with the latest research and treatment approaches. Attending conferences, workshops, and seminars focused on hip bursitis management can help physical therapists refine their expertise and provide the best possible care for their patients. By combining their education, experience, and ongoing professional development, physical therapists can become specialists in effectively managing hip bursitis.
Physical therapists play a crucial role in the management of Parkinson's disease. They are skilled healthcare professionals who specialize in evaluating and treating movement disorders. In the context of Parkinson's disease, physical therapists work closely with patients to address the motor symptoms associated with the condition, such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. They develop personalized exercise programs that focus on improving strength, flexibility, balance, and coordination. Additionally, physical therapists educate patients on proper body mechanics and posture to minimize the risk of falls and injuries. They also provide guidance on assistive devices and adaptive equipment that can enhance mobility and independence. By working collaboratively with other healthcare professionals, physical therapists contribute to the overall management and improvement of quality of life for individuals with Parkinson's disease.
Becoming proficient in the treatment of patellar dislocation and instability requires a physical therapist to undergo specialized training and education. They must first complete a bachelor's degree in physical therapy and then pursue a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) degree. During their education, they will study courses that focus on musculoskeletal anatomy, biomechanics, and the assessment and treatment of orthopedic conditions. Additionally, they may choose to pursue advanced certifications or specialized training in sports physical therapy or orthopedics. This additional training allows them to develop a deep understanding of the complex mechanisms involved in patellar dislocation and instability, as well as the most effective treatment approaches. They will learn techniques such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercise, and neuromuscular re-education to address the underlying causes of patellar instability and help patients regain strength, stability, and function in the knee joint. Through ongoing professional development and clinical experience, a physical therapist can continue to refine their skills and stay up-to-date with the latest research and treatment techniques in this specialized area.
Physical therapists who wish to specialize in lymphedema management must possess certain qualifications. Firstly, they must have a strong foundation in physical therapy, with a bachelor's or master's degree in the field. Additionally, they should have completed specialized coursework or training in lymphedema management, which may include topics such as anatomy and physiology of the lymphatic system, manual lymphatic drainage techniques, compression therapy, and exercise prescription for lymphedema. It is also beneficial for these therapists to have practical experience working with patients who have lymphedema, as this allows them to develop the necessary skills and expertise in managing this condition. Furthermore, obtaining certification from organizations such as the Lymphology Association of North America (LANA) or the National Lymphedema Network (NLN) can further demonstrate their commitment to excellence in lymphedema management. Overall, a combination of education, training, experience, and certification is essential for physical therapists to specialize in lymphedema management.
Physical therapists who specialize in tibia/fibula fractures typically possess a combination of educational qualifications and clinical experience. They typically hold a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) degree, which requires completion of a rigorous program that includes coursework in anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, and therapeutic interventions. Additionally, they may have completed specialized training or certifications in orthopedic physical therapy or sports rehabilitation. These qualifications provide them with the knowledge and skills necessary to assess and treat tibia/fibula fractures, including the ability to develop individualized treatment plans, perform manual therapy techniques, prescribe therapeutic exercises, and utilize modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation. Furthermore, they may have gained practical experience through internships or clinical rotations in orthopedic or sports medicine settings, allowing them to apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios and refine their clinical skills. Overall, physical therapists specializing in tibia/fibula fractures have the necessary qualifications to provide effective and comprehensive rehabilitation for patients with these specific injuries.
Yes, physical therapists can specialize in providing services for foot fractures exclusively. These specialized physical therapists, known as orthopedic physical therapists, have extensive knowledge and expertise in treating foot fractures. They are trained to assess and diagnose the specific type and severity of the fracture, develop personalized treatment plans, and provide a range of therapeutic interventions to promote healing and restore function. These interventions may include manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, gait training, and the use of assistive devices such as orthotics or braces. By focusing exclusively on foot fractures, these physical therapists can provide targeted and effective care to help patients recover and regain their mobility and independence.