
Functional dry needling can be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with other therapies. Functional Movement Specialist It is often integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan that may include exercises, manual therapy, and other modalities. The combination of therapies can help address the underlying causes of pain and promote optimal healing and recovery.
Whether functional dry needling is covered by insurance depends on your specific insurance plan. Some plans may cover it as part of physical therapy or pain management services, while others may not. It is best to check with your insurance provider to determine your coverage and any potential out-of-pocket costs.
While functional dry needling can be beneficial for many individuals, there are certain conditions or contraindications that may make someone ineligible for the treatment. These can include bleeding disorders, pregnancy, certain medications, and certain medical conditions. Neurological Rehabilitation Therapist It is important to discuss your medical history and any concerns with a healthcare professional before undergoing functional dry needling to ensure it is safe and appropriate for you.

Spinal cord injuries can be caused by a variety of factors, including traumatic accidents such as car crashes, falls, or sports injuries. Other common causes include acts of violence, such as gunshot wounds or knife injuries, as well as medical conditions like tumors, infections, or degenerative diseases. These injuries occur when there is damage to the spinal cord, which is a bundle of nerves that carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body. Muscular Strength and Conditioning Coach The severity of the injury can vary, ranging from temporary loss of function to permanent paralysis.
A spinal cord injury can have a significant impact on a person's mobility and sensation. Depending on the location and severity of the injury, individuals may experience partial or complete loss of movement and sensation below the level of the injury. This means that they may have difficulty walking, using their hands, or performing other daily activities. In addition, they may experience changes in their ability to feel touch, temperature, or pain. These changes can have a profound effect on a person's independence and quality of life.
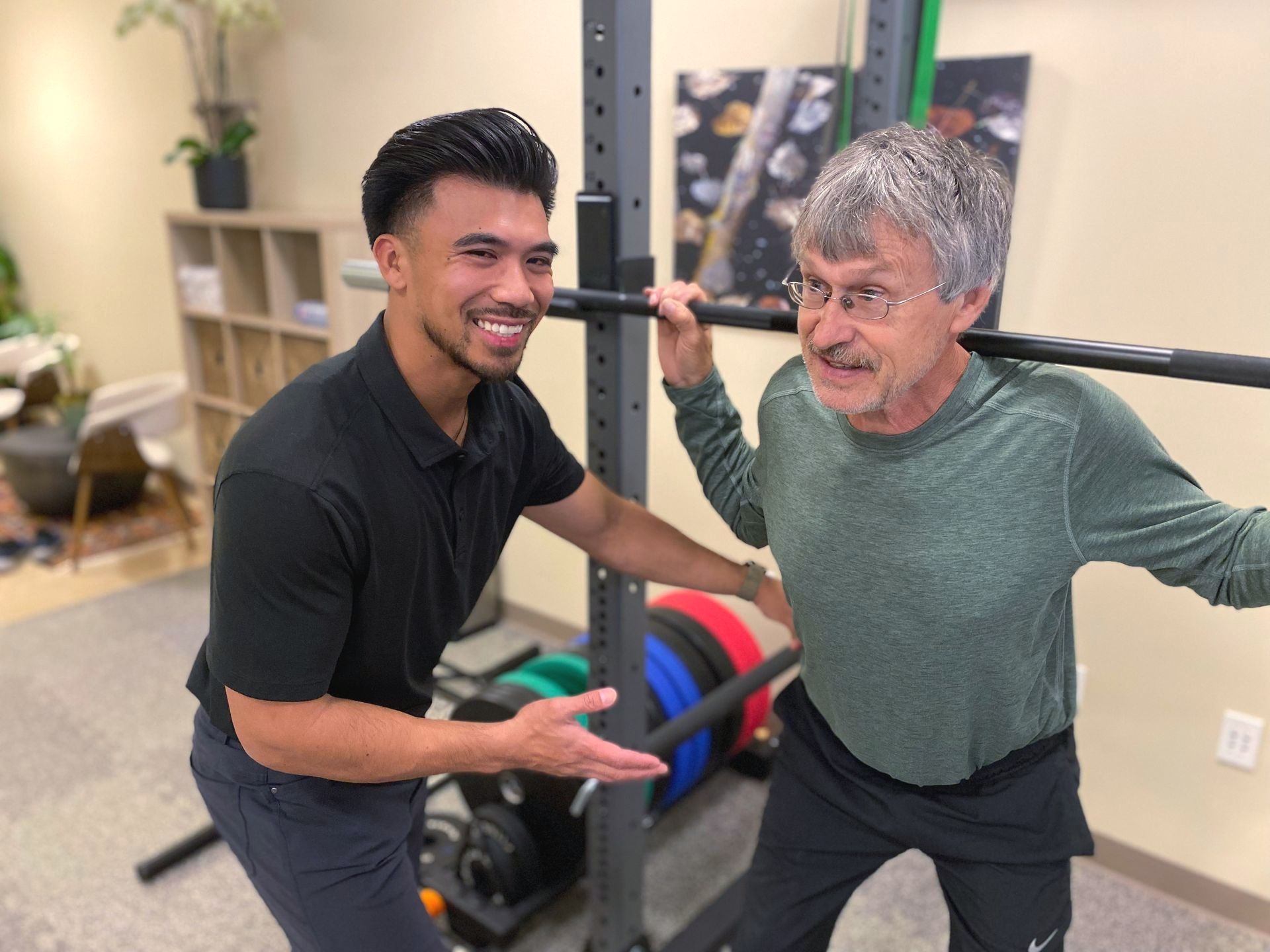

Spinal cord injuries are often classified based on the level of the injury and the resulting loss of function. The spinal cord is divided into different segments, and the level of injury refers to the specific segment that is affected. Mobility and Balance Specialist The higher the level of injury, the more extensive the loss of function. For example, injuries to the cervical (neck) region can result in quadriplegia, which affects both the arms and legs. Injuries to the thoracic (chest) or lumbar (lower back) regions may result in paraplegia, which affects the lower body.
The primary goals of spinal cord injury rehabilitation are to maximize independence, improve quality of life, and promote overall well-being. Rehabilitation programs are designed to help individuals regain as much function as possible and learn new ways to perform daily activities. This may involve physical therapy to improve strength and mobility, occupational therapy to develop skills for daily living, and psychological support to address emotional and mental health challenges. The ultimate aim is to help individuals reintegrate into their communities and achieve a fulfilling and meaningful life.
Cardiac Rehabilitation Therapist
Becoming an expert in tibia/fibula fractures requires a physical therapist to undergo specialized training and gain extensive experience in the field. They typically start by completing a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) program, which provides a comprehensive education in musculoskeletal anatomy, biomechanics, and injury management. After obtaining their DPT degree, they may pursue additional certifications or advanced courses specifically focused on tibia/fibula fractures. These certifications and courses may cover topics such as fracture classification, surgical interventions, rehabilitation protocols, and evidence-based treatment approaches. Additionally, physical therapists can enhance their expertise by actively participating in research, attending conferences, and collaborating with orthopedic surgeons and other healthcare professionals specializing in lower extremity injuries. Through continuous learning and hands-on experience, physical therapists can develop the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively evaluate, diagnose, and treat tibia/fibula fractures, helping patients achieve optimal recovery and functional outcomes.
Physical therapists who specialize in foot osteoarthritis typically have a strong educational background and specific qualifications. They typically hold a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) degree, which requires completion of a rigorous program that includes coursework in anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, and therapeutic interventions. Additionally, they may have completed specialized training or certifications in foot and ankle rehabilitation, orthopedics, or sports medicine. These qualifications enable them to assess and treat foot osteoarthritis using evidence-based techniques such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercise, gait analysis, and the use of assistive devices. They also stay up-to-date with the latest research and advancements in the field to provide the most effective and comprehensive care for individuals with foot osteoarthritis.
To become a specialist in jumper's knee (patellar tendinitis), a physical therapist must first complete a bachelor's degree in physical therapy or a related field. After obtaining their degree, they must then pass the national licensing exam to become a licensed physical therapist. To further specialize in jumper's knee, they can pursue additional certifications or advanced training in sports physical therapy or orthopedic physical therapy. This may involve completing post-graduate courses or participating in specialized workshops and conferences focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of patellar tendinitis. Additionally, they may choose to gain practical experience by working with athletes who are prone to developing jumper's knee or by collaborating with other healthcare professionals who specialize in sports medicine. By staying up-to-date with the latest research and advancements in the field, a physical therapist can develop the expertise needed to effectively treat and manage jumper's knee.
Becoming an expert in pelvic floor dysfunction requires a physical therapist to undergo specialized training and education in this specific area of practice. They may pursue advanced certifications or post-graduate courses that focus on pelvic floor rehabilitation, such as courses on pelvic floor anatomy, assessment techniques, and treatment interventions. Additionally, they may engage in continuing education opportunities, attend conferences, and participate in research related to pelvic floor dysfunction. By staying up-to-date with the latest advancements and evidence-based practices in this field, a physical therapist can develop the expertise necessary to effectively evaluate and treat patients with pelvic floor dysfunction.
Yes, physical therapists can specialize in the management of thoracic outlet syndrome. Thoracic outlet syndrome is a condition that occurs when the nerves and blood vessels in the thoracic outlet, which is the space between the collarbone and the first rib, become compressed. Physical therapists who specialize in this area have extensive knowledge and training in the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of thoracic outlet syndrome. They use a variety of techniques and modalities, such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, postural retraining, and ergonomic education, to help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and restore function in individuals with thoracic outlet syndrome. These specialized physical therapists work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans that address their specific needs and goals, helping them to achieve optimal outcomes and improve their quality of life.