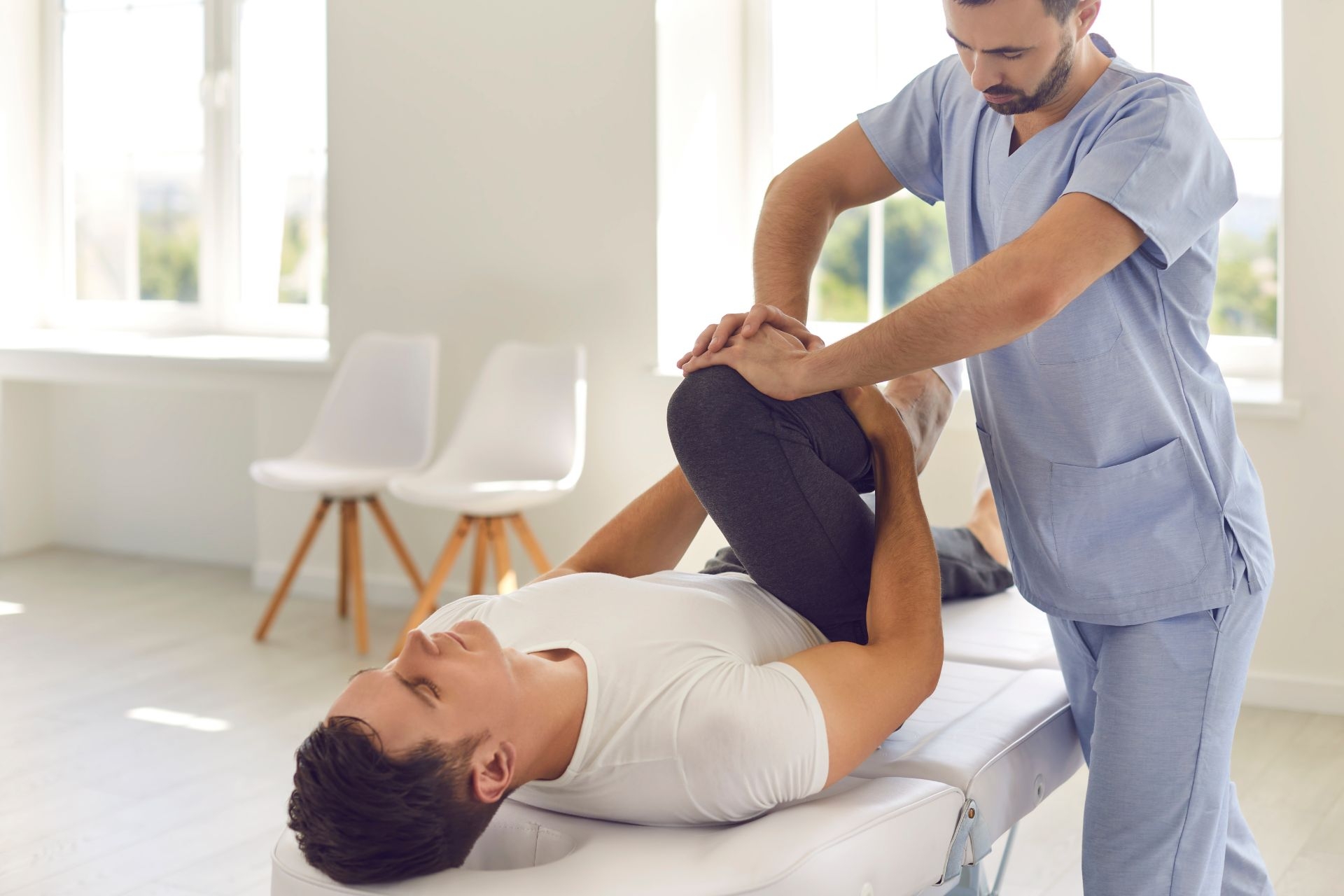

There are several exercises that can improve balance and coordination. One effective exercise is standing on one leg while performing various movements, such as lifting the other leg, reaching for an object, or rotating the torso. This challenges the body's ability to maintain balance and coordinate movements. Another exercise is the heel-to-toe walk, where one foot is placed directly in front of the other with each step. This exercise requires precise coordination and balance. Additionally, exercises that involve unstable surfaces, such as balance boards or stability balls, can help improve balance and coordination by forcing the body to make constant adjustments to maintain stability.
Balance training is highly beneficial for athletes in improving their performance. By enhancing balance and coordination, athletes can improve their agility, reaction time, and overall body control. This can lead to better performance in sports that require quick changes in direction, precise movements, and balance, such as gymnastics, martial arts, and basketball. Balance training also helps athletes prevent injuries by strengthening the muscles that support the joints and improving proprioception, which is the body's awareness of its position in space. This allows athletes to move more efficiently and reduce the risk of falls or missteps.
While balance and coordination training can be highly beneficial, there are potential risks and injuries associated with it. One common risk is falling, especially when performing exercises on unstable surfaces or challenging movements. It is important to start with exercises that match one's current abilities and gradually progress to more challenging ones to minimize the risk of injury. Additionally, overtraining or pushing beyond one's limits can lead to muscle strains, sprains, or joint injuries. It is crucial to listen to the body and take appropriate rest and recovery periods to avoid overuse injuries.

Yes, balance and coordination training can be beneficial for rehabilitation after an injury. When an injury occurs, the body's balance and coordination may be compromised due to pain, muscle weakness, or altered movement patterns. Balance and coordination exercises can help restore these abilities by targeting specific muscles, improving joint stability, and retraining the body's movement patterns. For example, after an ankle sprain, balance exercises that challenge the ankle's stability can help regain strength and proprioception. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to ensure that the exercises are appropriate for the specific injury and stage of rehabilitation.
Balance and coordination training can benefit individuals of all age groups and populations. However, certain age groups or populations may benefit more due to specific needs or challenges. For example, older adults may experience a decline in balance and coordination due to age-related changes in the sensory systems and muscle strength. Balance and coordination training can help improve their stability and reduce the risk of falls. Similarly, individuals with neurological conditions, such as Parkinson's disease or stroke, may have impaired balance and coordination. Targeted exercises can help improve their motor skills and functional abilities.
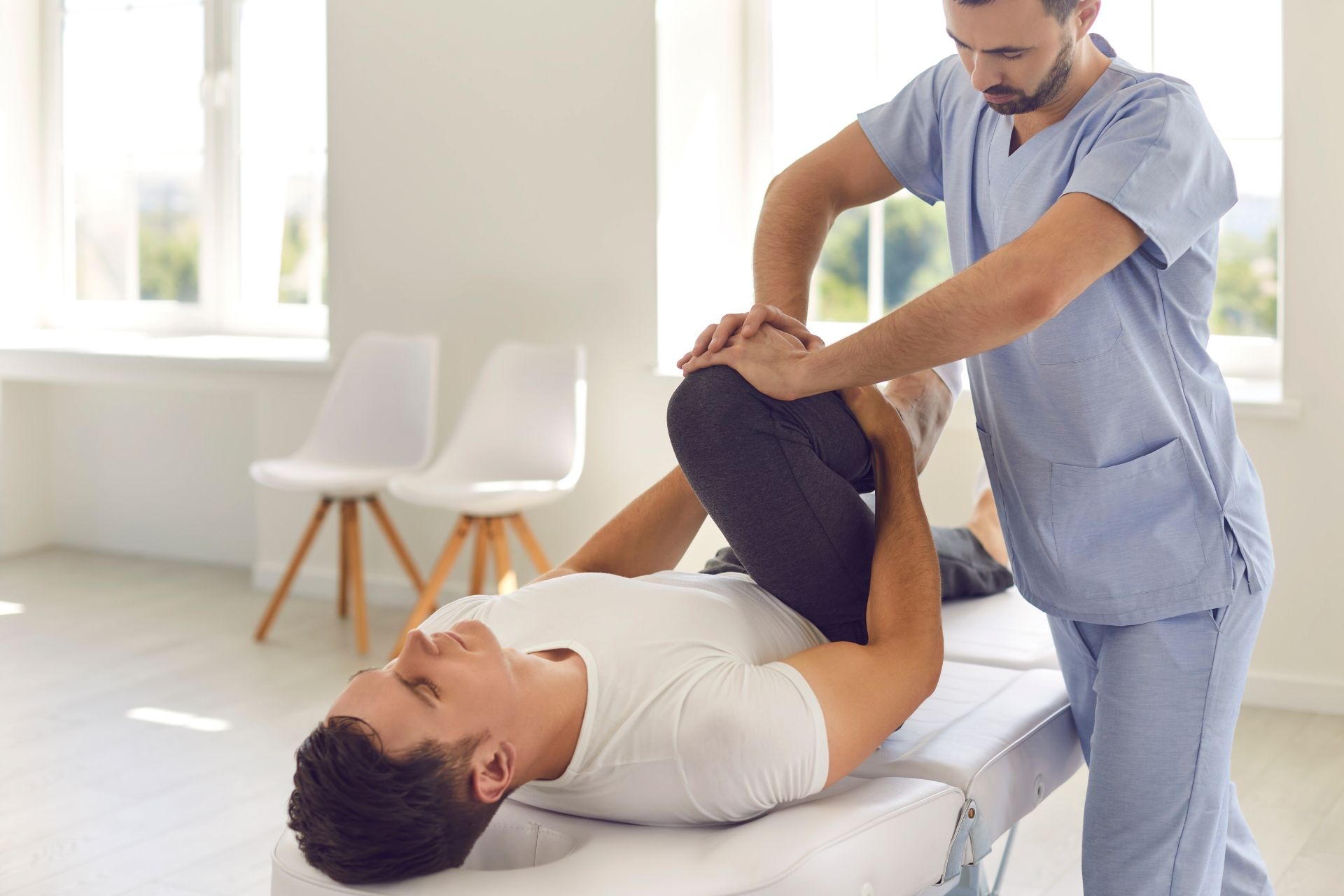
There are several signs or symptoms that indicate a need for balance and coordination training. These include frequent falls or near falls, difficulty maintaining balance during activities, unsteady gait, clumsiness, and poor coordination. Other signs may include difficulty with tasks that require precise movements, such as handwriting or buttoning clothes. Additionally, individuals who participate in sports or activities that require balance and coordination, such as dancing or martial arts, may benefit from training to enhance their performance and reduce the risk of injuries.
The time it takes to see improvements in balance and coordination with regular training can vary depending on various factors, such as the individual's starting level of ability, consistency of training, and the specific exercises performed. Generally, with regular training, individuals can start to notice improvements in balance and coordination within a few weeks to a few months. However, it is important to note that progress may be gradual and individualized. Consistency and progressive overload, gradually increasing the difficulty of exercises, are key factors in achieving noticeable improvements. It is also important to continue practicing and maintaining balance and coordination exercises to sustain the benefits over time.
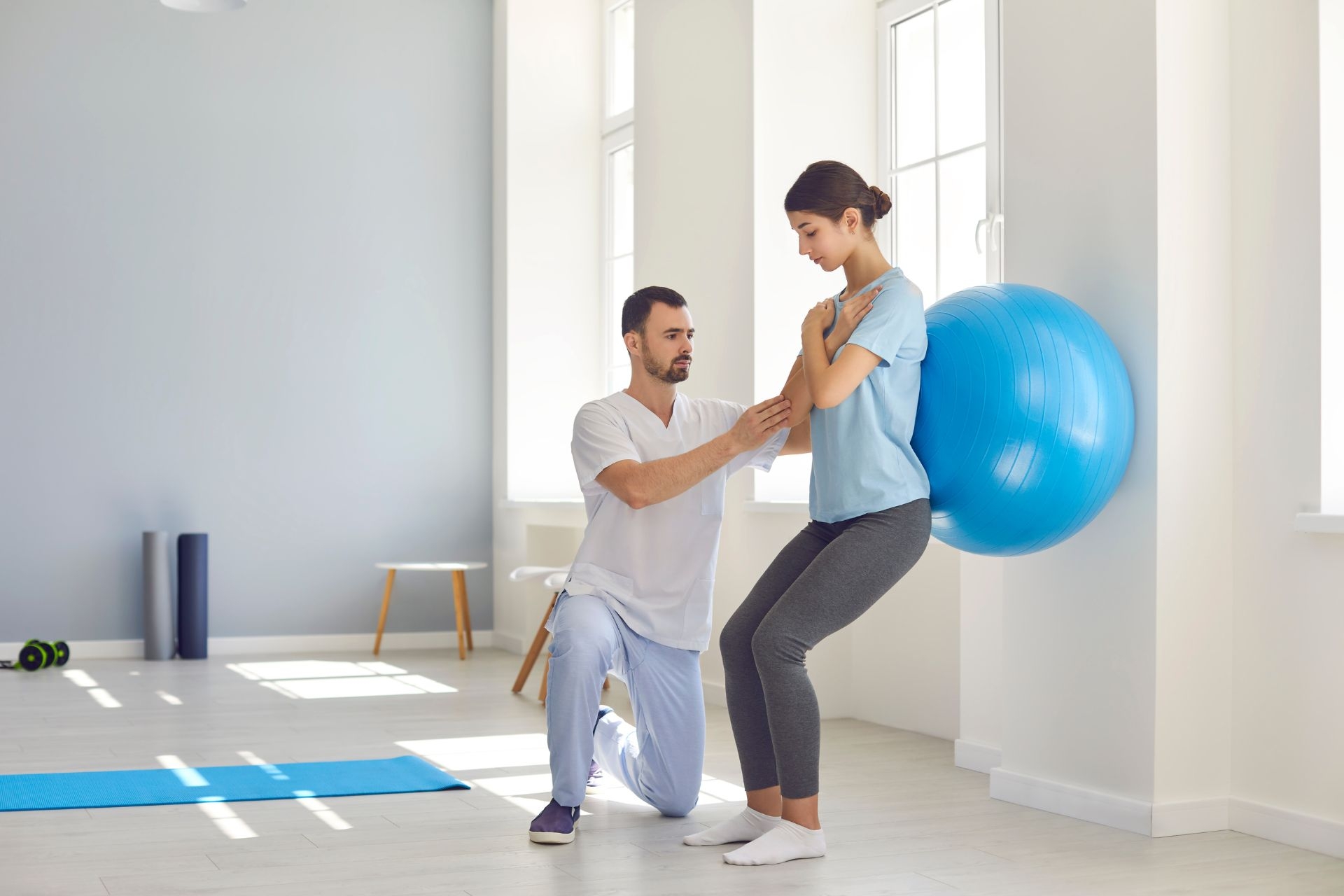

Yes, virtual reality technology can indeed be integrated into physical therapy sessions to enhance the overall outcomes. By incorporating virtual reality into physical therapy, patients can engage in immersive and interactive experiences that simulate real-life scenarios, allowing them to practice and improve their motor skills in a controlled and safe environment. This technology can provide a wide range of therapeutic exercises and activities, such as balance training, gait rehabilitation, and hand-eye coordination exercises. Additionally, virtual reality can offer personalized and adaptive interventions, tracking the patient's progress and adjusting the difficulty level accordingly. This integration of virtual reality technology in physical therapy sessions has shown promising results in improving patient motivation, engagement, and overall rehabilitation outcomes.
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) plays a crucial role in muscle re-education and functional recovery post-injury. NMES involves the application of electrical currents to stimulate the nerves and muscles, promoting muscle contraction and enhancing neuromuscular control. By targeting specific muscle groups, NMES helps to restore muscle strength, improve muscle coordination, and increase range of motion. This technique also aids in preventing muscle atrophy and reducing muscle spasms, facilitating the recovery process. Additionally, NMES can enhance proprioception, balance, and overall functional performance, allowing individuals to regain their pre-injury level of function more efficiently. Overall, NMES serves as an effective adjunct therapy in the rehabilitation process, promoting muscle re-education and facilitating functional recovery post-injury.
Aquatic therapy plays a crucial role in addressing balance deficits in individuals with vestibular disorders. The buoyancy provided by the water allows for a reduced weight-bearing environment, which can help individuals with balance deficits to safely practice and improve their balance skills. The hydrostatic pressure of the water also provides sensory input to the body, which can help individuals with vestibular disorders to better perceive their body position and movement in space. Additionally, the resistance of the water can be used to challenge and strengthen the muscles involved in balance control. Aquatic therapy may also incorporate specific exercises and activities that target the vestibular system, such as head movements and gaze stabilization exercises, to further improve balance and reduce symptoms associated with vestibular disorders. Overall, aquatic therapy offers a unique and effective approach to address balance deficits in individuals with vestibular disorders, providing a safe and supportive environment for rehabilitation and improvement of balance function.
Electrotherapy modalities have been shown to be effective in reducing pain in patients with chronic low back pain. These modalities, such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and electrical muscle stimulation (EMS), work by delivering electrical currents to the affected area, which can help to block pain signals and promote the release of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers. Studies have demonstrated that TENS and EMS can provide significant pain relief in chronic low back pain patients, with improvements in pain intensity, functional ability, and quality of life. Additionally, these modalities have been found to be safe and well-tolerated, making them a viable option for pain management in this patient population.
Incorporating eccentric training into rehabilitation programs for tendinopathies can offer several potential benefits. Tendinopathies, which refer to the degeneration or inflammation of tendons, often require targeted interventions to promote healing and restore function. Eccentric training, which involves lengthening contractions of muscles, has been shown to be particularly effective in addressing tendinopathies. This type of training can help improve tendon strength, increase collagen synthesis, and enhance the overall mechanical properties of the tendon. Additionally, eccentric training can stimulate the production of growth factors and promote angiogenesis, which can facilitate tissue repair and regeneration. By incorporating eccentric training into rehabilitation programs, individuals with tendinopathies may experience reduced pain, improved function, and a faster return to their pre-injury level of activity.
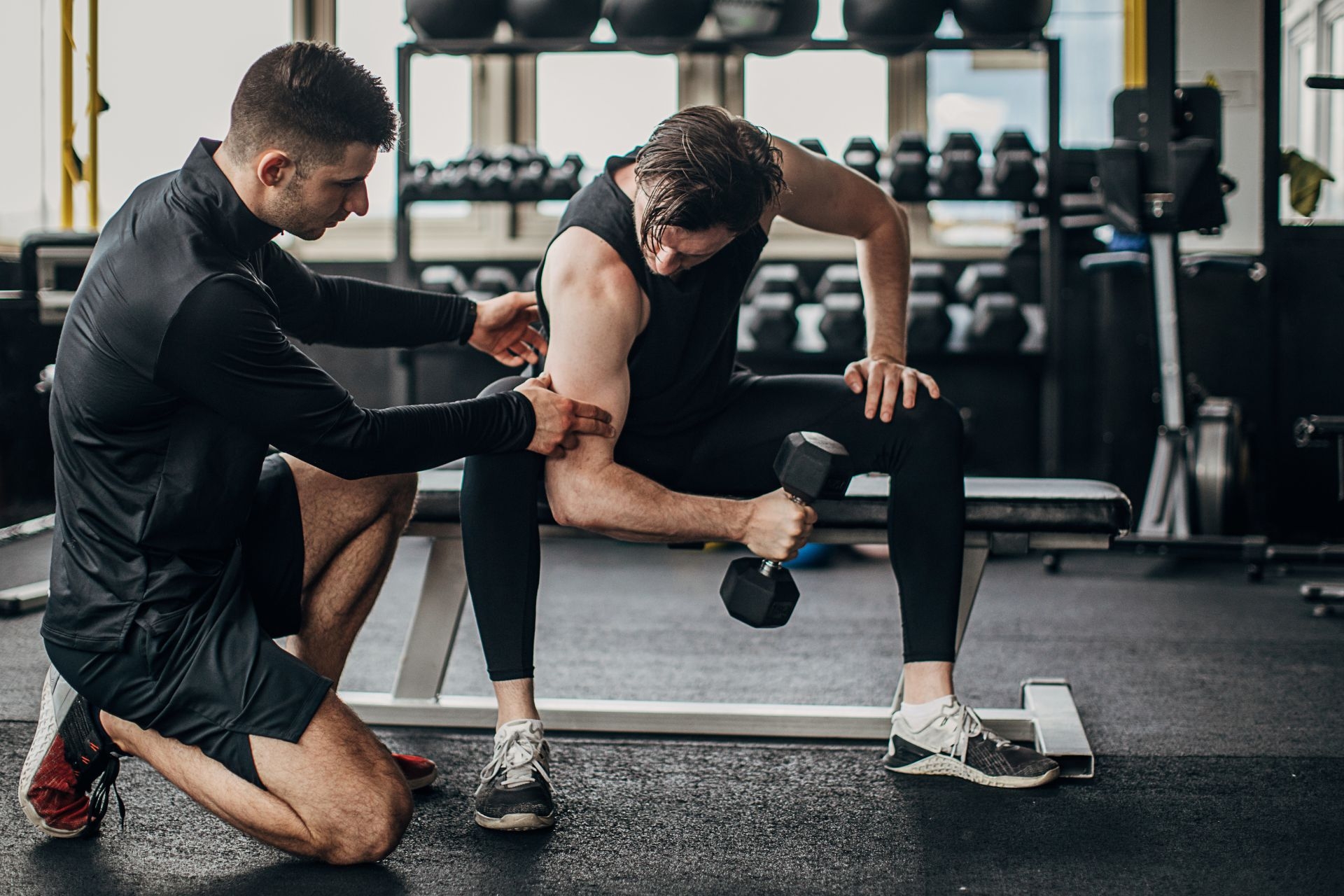
The most effective exercises for improving shoulder stability in rotator cuff rehabilitation include external rotation exercises, internal rotation exercises, scapular stabilization exercises, and shoulder abduction exercises. External rotation exercises, such as the standing external rotation and the side-lying external rotation, target the infraspinatus and teres minor muscles, which are important for stabilizing the shoulder joint. Internal rotation exercises, such as the standing internal rotation and the side-lying internal rotation, target the subscapularis muscle, another key stabilizer of the shoulder. Scapular stabilization exercises, such as scapular retractions and scapular push-ups, help improve the stability of the shoulder blade, which in turn enhances overall shoulder stability. Lastly, shoulder abduction exercises, such as the standing shoulder abduction and the prone shoulder abduction, target the deltoid muscle, which plays a crucial role in shoulder stability. By incorporating these exercises into a comprehensive rotator cuff rehabilitation program, individuals can effectively improve shoulder stability and reduce the risk of future injuries.