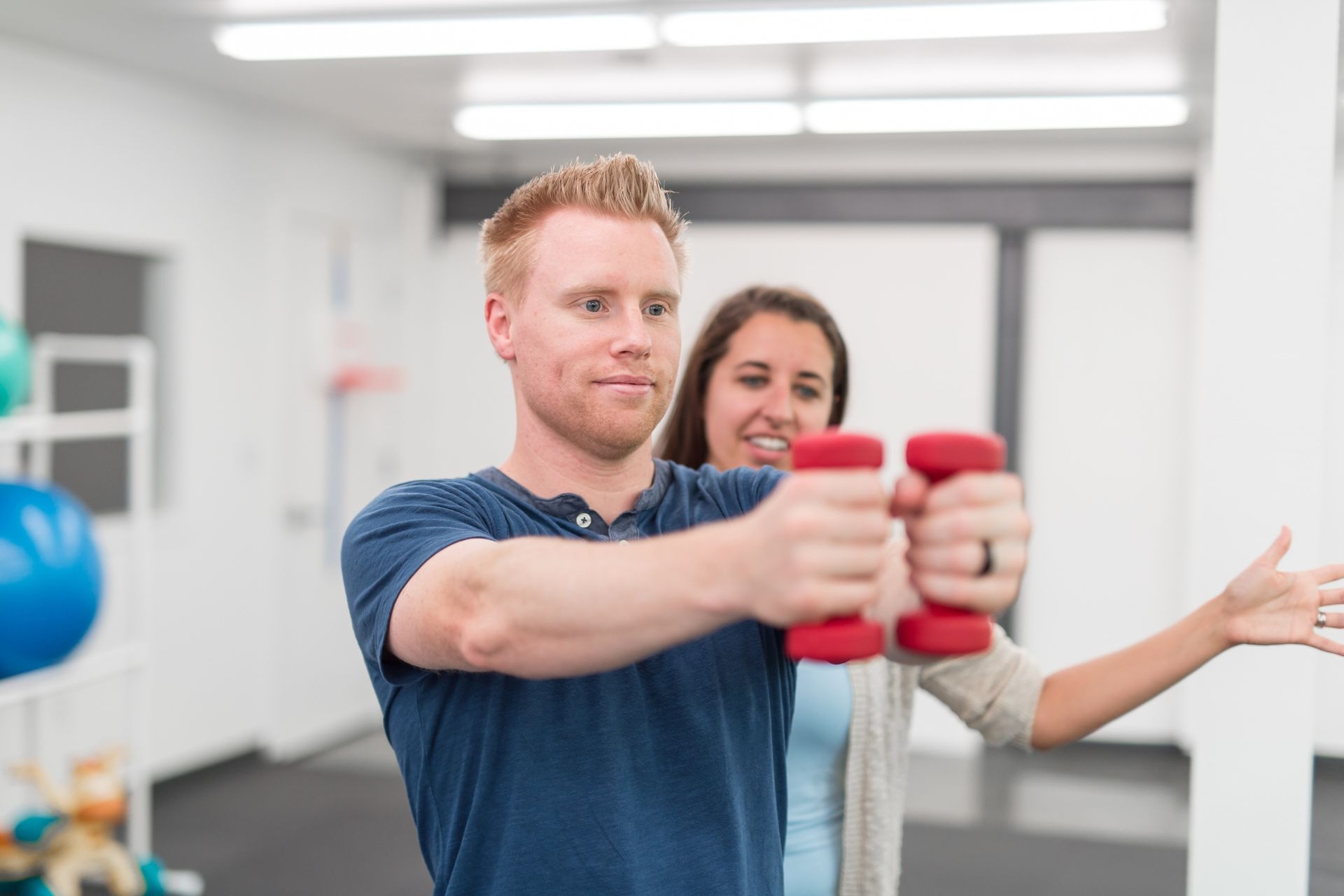


Aquatic physical therapy is highly effective in improving balance and coordination. The buoyancy of water reduces the impact on joints and provides a supportive environment for individuals to practice and refine their balance skills. The resistance of the water also helps to engage and strengthen the muscles responsible for maintaining balance. Additionally, the multidirectional resistance of water forces individuals to use their core muscles to stabilize themselves, further enhancing their coordination. By incorporating various exercises and movements in the water, such as walking, jumping, and reaching, aquatic physical therapy helps individuals improve their balance and coordination skills in a safe and controlled manner.
Aquatic physical therapy offers numerous benefits for individuals with arthritis. The warm water in the therapy pool helps to relax muscles and reduce pain, allowing individuals to move more freely. The buoyancy of water also reduces the weight-bearing load on joints, relieving pressure and minimizing discomfort. Aquatic exercises, such as gentle stretching and range of motion movements, help to improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness. The resistance provided by the water helps to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joints, providing better support and stability. Overall, aquatic physical therapy can help individuals with arthritis manage their symptoms, improve their mobility, and enhance their overall quality of life.
Yes, aquatic physical therapy can be highly beneficial for post-surgical rehabilitation. The buoyancy of water reduces the impact on healing tissues and joints, allowing individuals to start their rehabilitation process earlier than they would on land. The water provides a supportive environment that helps to improve range of motion, reduce pain, and promote healing. Aquatic exercises can be tailored to target specific areas of the body, helping individuals regain strength, flexibility, and function. The resistance of the water also allows for progressive resistance training, which is crucial for rebuilding muscle strength after surgery. Aquatic physical therapy can play a vital role in post-surgical rehabilitation by facilitating a faster and more effective recovery.
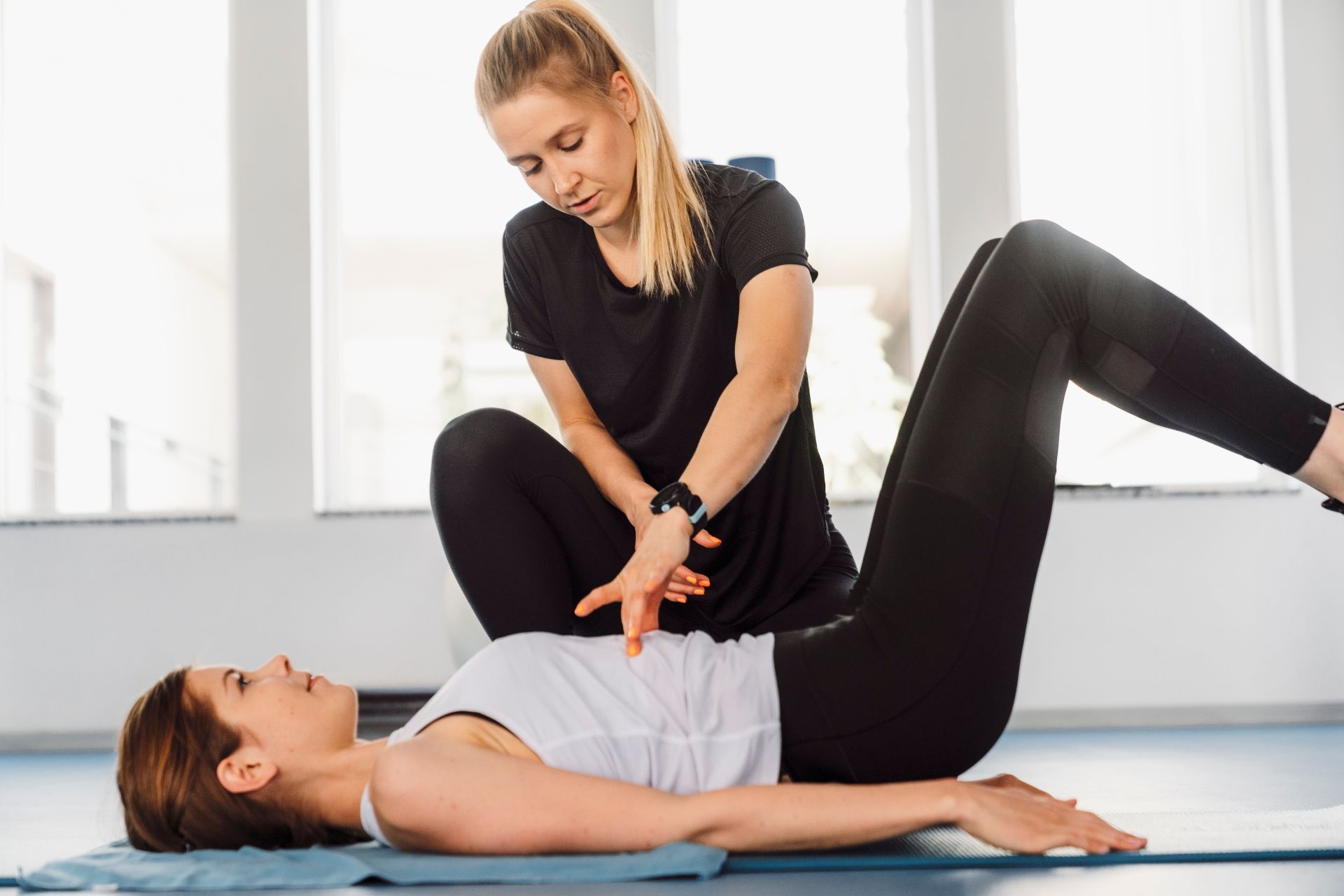

Aquatic physical therapy is an excellent way to improve cardiovascular fitness. The water provides natural resistance, requiring individuals to exert more effort to move through it. This increased resistance helps to strengthen the heart and lungs, improving cardiovascular endurance. Aquatic exercises, such as swimming or water aerobics, elevate the heart rate and provide a low-impact cardiovascular workout. The buoyancy of water also reduces the stress on joints, making it an ideal option for individuals with joint conditions or injuries who may struggle with high-impact land-based exercises. Regular participation in aquatic physical therapy can lead to improved cardiovascular fitness, increased stamina, and enhanced overall cardiovascular health.
Aquatic physical therapy sessions typically involve a variety of exercises that target different areas of the body. These exercises can include walking or jogging in the water, which helps to improve cardiovascular fitness and lower body strength. Water aerobics exercises, such as jumping jacks or leg kicks, provide a full-body workout and help to improve overall muscle tone and endurance. Range of motion exercises, such as arm circles or leg swings, help to improve flexibility and joint mobility. Resistance exercises, such as using water dumbbells or resistance bands, help to strengthen muscles. The specific exercises performed during aquatic physical therapy sessions are tailored to the individual's needs and goals, ensuring a comprehensive and effective rehabilitation program.
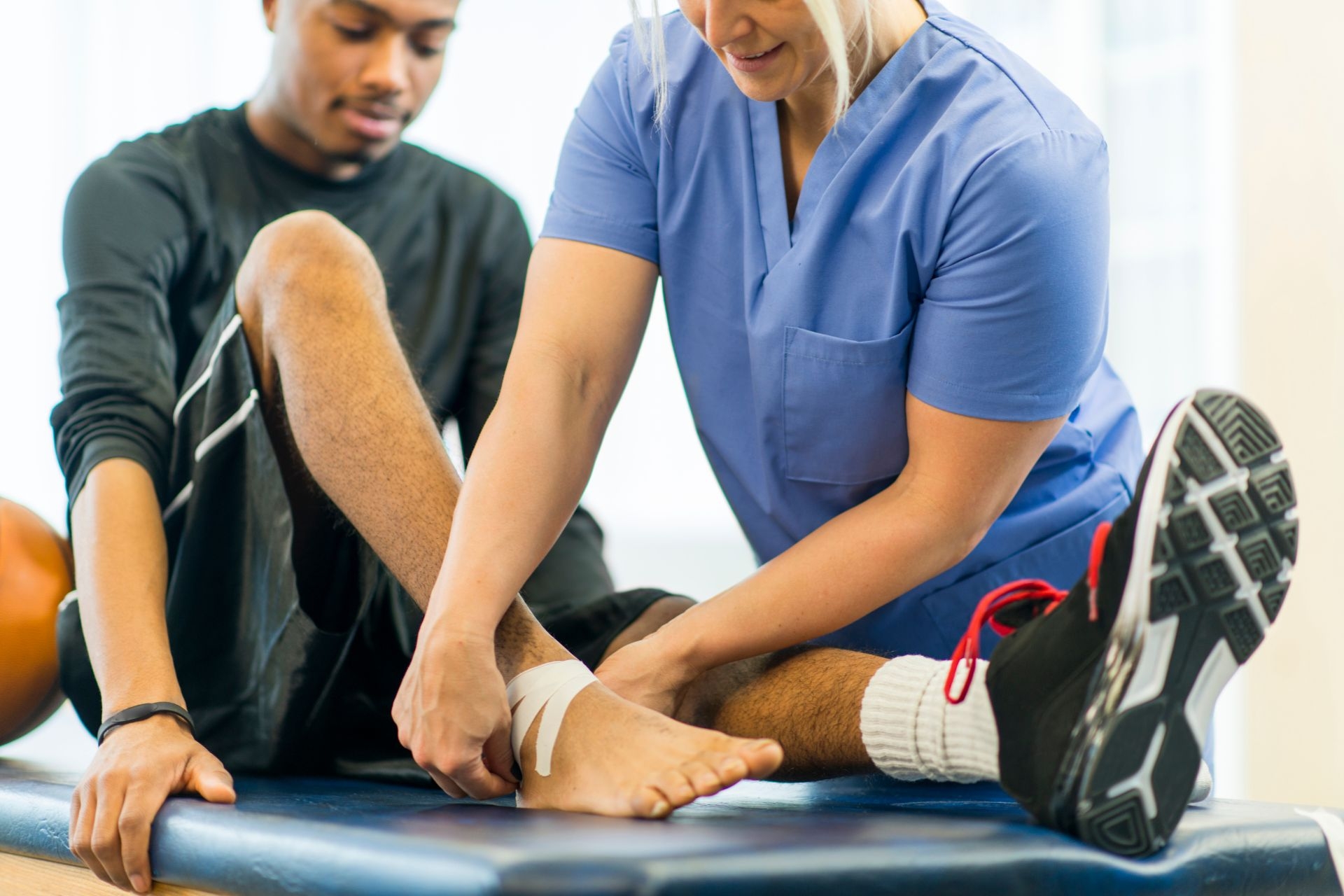
Aquatic physical therapy can be highly beneficial for individuals with chronic pain conditions. The buoyancy of water reduces the impact on joints and provides a supportive environment that helps to alleviate pain. The warm water in the therapy pool also helps to relax muscles and promote relaxation, reducing muscle tension and discomfort. Aquatic exercises, such as gentle stretching and low-impact movements, can help to improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness. The resistance provided by the water helps to strengthen muscles, providing better support and stability for individuals with chronic pain. Additionally, the water's hydrostatic pressure can have a soothing effect on the nervous system, further reducing pain sensations. Aquatic physical therapy can be a valuable tool in managing chronic pain and improving overall well-being.
Aquatic physical therapy is highly effective in improving muscle strengthening and flexibility. The resistance provided by the water helps to engage and challenge muscles, leading to increased strength and endurance. Water exercises, such as walking or jogging, require individuals to work against the resistance of the water, effectively targeting and strengthening the muscles of the lower body. The multidirectional resistance of water also engages the core muscles, helping to improve stability and balance. Additionally, the buoyancy of water reduces the impact on joints, allowing individuals to perform exercises with less strain and discomfort. This enables individuals to achieve a greater range of motion, promoting flexibility and joint mobility. By incorporating a variety of exercises and movements, aquatic physical therapy helps individuals improve muscle strength and flexibility in a safe and supportive environment.

Mirror therapy is a highly effective rehabilitation technique that plays a crucial role in the restoration of upper limb function following a stroke. By utilizing a mirror to create an illusion of movement in the affected limb, mirror therapy stimulates the brain's neural pathways and promotes neuroplasticity. This therapy involves the patient placing their unaffected limb in front of a mirror while performing various exercises, which creates the illusion that the affected limb is also moving. This visual feedback tricks the brain into perceiving movement in the affected limb, leading to the activation of motor neurons and the reestablishment of neural connections. Additionally, mirror therapy enhances proprioception, motor control, and coordination, as it allows the patient to observe and compare the movements of both limbs simultaneously. This technique also aids in reducing pain and swelling, improving range of motion, and increasing muscle strength. Overall, mirror therapy is a valuable tool in the rehabilitation of upper limb function post-stroke, as it facilitates the rewiring of the brain and promotes functional recovery.
Instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization (IASTM) techniques have shown promise in alleviating symptoms of plantar fasciitis. These techniques involve the use of specialized tools to apply controlled pressure and friction to the affected soft tissues, such as the plantar fascia. By targeting the specific areas of inflammation and adhesions, IASTM can help break up scar tissue, improve blood flow, and promote tissue healing. Additionally, IASTM can help improve range of motion and flexibility in the foot and ankle, which can further reduce pain and discomfort associated with plantar fasciitis. Some common IASTM techniques used for plantar fasciitis include scraping, cupping, and vibration therapy. Overall, incorporating IASTM into a comprehensive treatment plan for plantar fasciitis can provide significant relief and improve functional outcomes for individuals suffering from this condition.
Dry needling and acupuncture are both techniques used in physical therapy practice, but they have some key differences. Dry needling involves the insertion of thin needles into trigger points or tight muscles to relieve pain and improve muscle function. It focuses on releasing tension and promoting healing in specific areas of the body. On the other hand, acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine practice that involves the insertion of needles into specific points along the body's meridians to restore the flow of energy and promote overall well-being. It is based on the concept of balancing the body's energy, or qi. While both techniques use needles, dry needling is more focused on musculoskeletal issues, while acupuncture takes a holistic approach to address a wide range of conditions. Additionally, dry needling is typically performed by physical therapists, while acupuncture is usually done by licensed acupuncturists.
Blood flow restriction training (BFRT) plays a significant role in both rehabilitation and performance enhancement. In rehabilitation, BFRT involves the use of a specialized cuff or band to partially restrict blood flow to the working muscles during exercise. This technique has been shown to stimulate muscle growth and strength gains, even at lower intensities, which is particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from injuries or surgeries. Additionally, BFRT can improve cardiovascular function and increase the production of growth factors, promoting tissue healing and reducing recovery time. In terms of performance enhancement, BFRT allows athletes to achieve similar physiological adaptations to high-intensity training while using lower loads, reducing the risk of injury and overtraining. It can also enhance muscle hypertrophy, improve muscular endurance, and increase anaerobic capacity. Overall, BFRT is a valuable tool in both rehabilitation and performance enhancement, offering a safe and effective alternative to traditional training methods.
Physical therapists take a comprehensive and individualized approach to rehabilitation for individuals with chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). They understand the unique challenges faced by these individuals and tailor their treatment plans accordingly. The rehabilitation process typically involves a combination of exercise therapy, energy conservation techniques, and education on managing symptoms. Physical therapists may use graded exercise therapy, which involves gradually increasing physical activity levels to improve stamina and reduce fatigue. They may also incorporate relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and mindfulness, to help manage stress and improve overall well-being. Additionally, physical therapists may provide guidance on sleep hygiene, nutrition, and pacing strategies to help individuals with CFS better manage their energy levels and optimize their daily activities. By addressing the specific needs of individuals with CFS, physical therapists play a crucial role in promoting functional improvement and enhancing quality of life.
Incorporating mindfulness-based practices into chronic pain management programs can offer several benefits. Firstly, mindfulness techniques such as meditation and deep breathing can help individuals with chronic pain develop a greater sense of self-awareness and acceptance of their pain, reducing the emotional distress often associated with it. Additionally, mindfulness practices can enhance individuals' ability to focus their attention on the present moment, allowing them to better cope with pain sensations and prevent them from becoming overwhelming. Moreover, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques have been shown to reduce the release of stress hormones, which can contribute to the experience of pain. By incorporating mindfulness into chronic pain management programs, individuals may also experience improved sleep quality, reduced anxiety and depression, and an overall improvement in their quality of life.
Taping techniques have been found to be beneficial in the management of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Patellofemoral pain syndrome, also known as runner's knee, is a common condition characterized by pain around the kneecap. Taping techniques, such as McConnell taping and kinesiology taping, can help alleviate pain and improve patellar alignment. These techniques involve applying adhesive tape to the affected area in a specific pattern to provide support and stability to the patella. The tape acts as a proprioceptive cue, enhancing neuromuscular control and reducing excessive lateral patellar movement. Additionally, taping can help offload the patellofemoral joint, reducing stress on the knee during activities. Overall, taping techniques can be a valuable adjunct to the management of patellofemoral pain syndrome, providing symptomatic relief and promoting optimal knee function.
Virtual coaching platforms have the potential to significantly enhance adherence to home exercise programs prescribed by physical therapists. These platforms utilize advanced technology and interactive features to provide personalized guidance and support to individuals performing their exercises at home. By incorporating features such as real-time feedback, video demonstrations, and progress tracking, virtual coaching platforms can effectively address common barriers to adherence, such as lack of motivation, uncertainty about proper technique, and difficulty in tracking progress. Additionally, these platforms can offer reminders and notifications to ensure individuals stay on track with their prescribed exercise regimen. The use of virtual coaching platforms can also foster a sense of accountability and engagement, as individuals can receive ongoing support and guidance from their physical therapists remotely. Overall, the integration of virtual coaching platforms into home exercise programs has the potential to greatly improve adherence rates and ultimately enhance the effectiveness of physical therapy interventions.