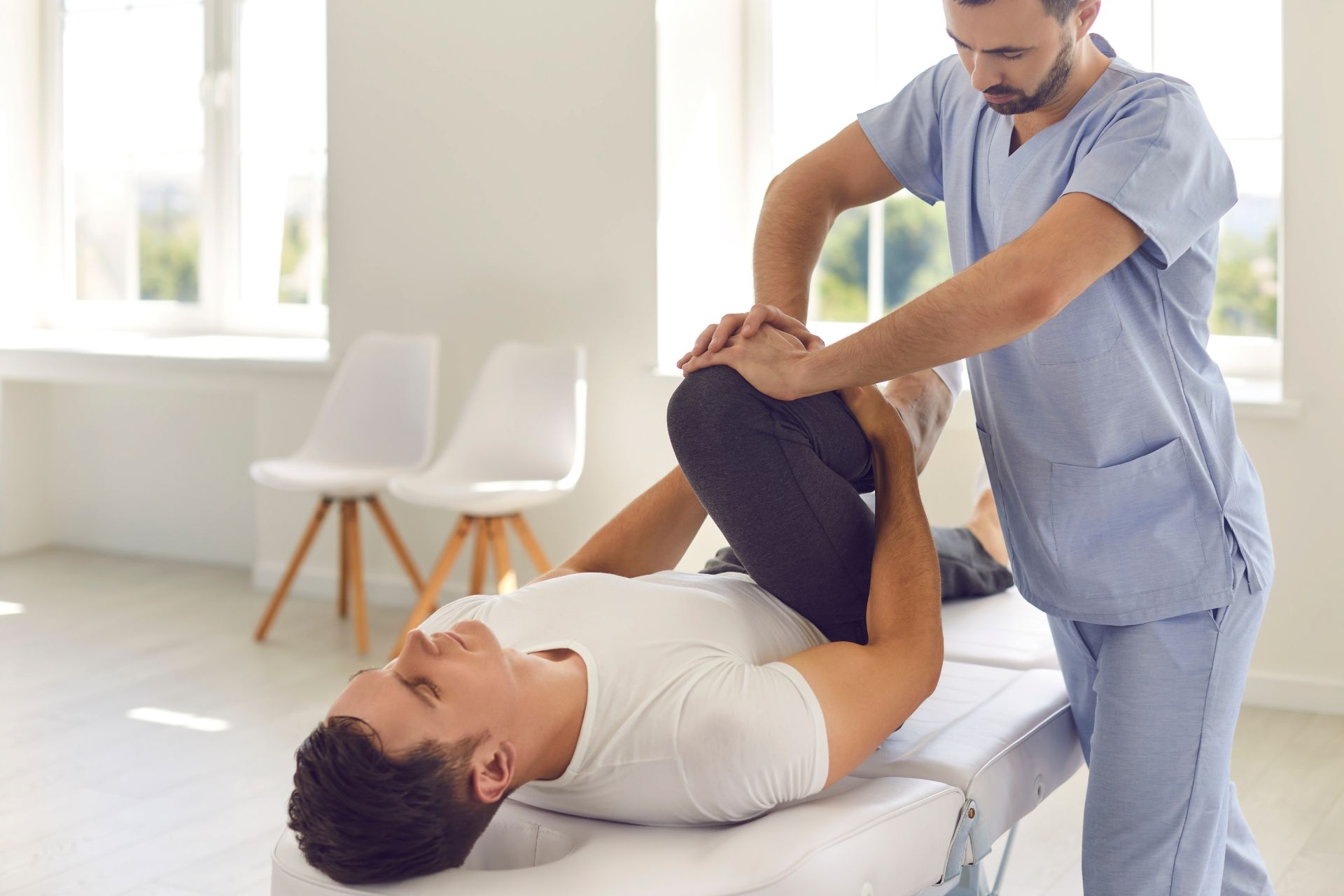
External Rotations
What are the benefits of incorporating external rotations into a workout routine?
Incorporating external rotations into a workout routine offers numerous benefits, including improving shoulder stability, strengthening the rotator cuff muscles, enhancing overall shoulder mobility, and reducing the risk of injuries. By targeting the external rotators of the shoulder, such as the infraspinatus and teres minor, external rotations help to balance out the strength and stability of the shoulder joint, which is crucial for proper function during various movements.