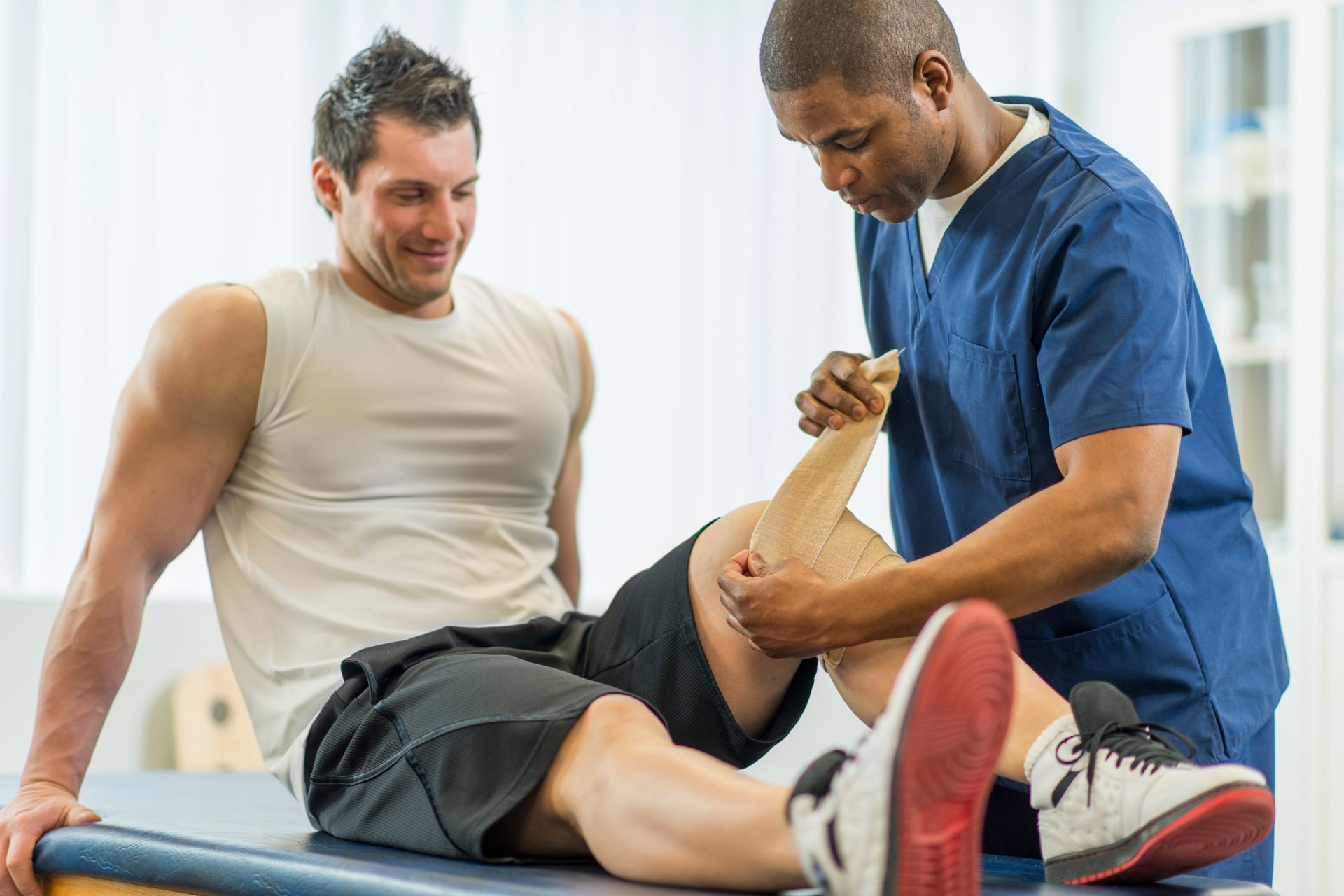

Physical therapy utilizes various types of diagnostic technology to assess and diagnose different conditions. One common type is electromyography (EMG), which measures the electrical activity of muscles. This technology helps in diagnosing muscle disorders by detecting abnormal muscle activity, such as muscle weakness or spasms. EMG can provide valuable information about the functioning of muscles and nerves, helping physical therapists identify the underlying cause of muscle-related issues and develop appropriate treatment plans.
Incorporating advanced diagnostic technology like diagnostic musculoskeletal ultrasound for physical therapy significantly enhances the accuracy of diagnoses and the effectiveness of treatment plans. By leveraging these innovative tools, therapists can tailor their approaches to meet the unique needs of each patient, improving recovery times and overall health outcomes.
Electromyography (EMG) plays a crucial role in diagnosing muscle disorders in physical therapy. By measuring the electrical activity of muscles, EMG can identify abnormalities in muscle function, such as muscle weakness, muscle fatigue, or muscle spasms. This diagnostic technology helps physical therapists pinpoint the specific muscles or muscle groups affected by a disorder, allowing for targeted treatment interventions. EMG can also assess the severity of muscle dysfunction and track progress throughout the course of therapy, enabling therapists to adjust treatment plans accordingly.
In the dynamic realm of healthcare, advancements in technology continuously reshape the landscape of physical therapy. From cutting-edge therapeutic technologies to revolutionary tools for physiotherapy, the field is witnessing a rapid evolution. In this blog, we delve into the latest trends and innovations in physical therapy, exploring advanced techniques for rehabilitation and highlighting the [...]
Posted by on 2024-02-10
In the fast-paced world we live in today, maintaining optimal health and well-being has become more critical than ever. As individuals face various challenges that limit their ability to access traditional healthcare settings, the importance of home-based solutions has risen significantly. Home exercise programs and physical therapy at home have emerged as valuable alternatives, [...]
Posted by on 2023-12-26
In the pursuit of effective pain relief and improved mobility, finding innovative treatments is crucial. Town PT in Maywood introduces Shockwave Therapy as a cutting-edge approach to addressing various musculoskeletal conditions. Discover how this revolutionary therapy could transform your journey to recovery and wellness. Understanding Shockwave Therapy Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive treatment that [...]
Posted by on 2023-12-15
Navigating insurance coverage for physical therapy services can often feel like navigating a maze. Understanding the ins and outs of physical therapy insurance coverage, reimbursement policies, and maximizing insurance benefits is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the theme of physical therapy insurance coverage, comparing different [...]
Posted by on 2024-02-25
Ultrasound imaging is a valuable diagnostic tool in physical therapy for diagnosing soft tissue injuries. This technology uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the body's soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints. Ultrasound imaging allows physical therapists to visualize and assess the extent of soft tissue damage, such as tears, strains, or inflammation. It helps in identifying the precise location and nature of the injury, guiding the development of appropriate treatment strategies and monitoring the healing process over time.

Gait analysis using motion capture technology is a valuable tool in diagnosing walking abnormalities in physical therapy. This technology involves the use of specialized cameras and sensors to capture and analyze the movement patterns of an individual while walking. By tracking joint angles, body alignment, and timing of movements, gait analysis provides valuable insights into abnormalities or imbalances in the way a person walks. Physical therapists can use this information to identify the underlying causes of walking abnormalities, such as muscle weakness, joint stiffness, or poor coordination. This allows for targeted interventions to improve gait and overall mobility.
Force plates are essential tools in assessing balance and weight distribution in physical therapy. These plates are equipped with sensors that measure the forces exerted by an individual's feet while standing or walking. By analyzing the distribution of forces, physical therapists can assess balance and identify any asymmetries or abnormalities in weight distribution. Force plates provide objective data that helps in evaluating the effectiveness of balance training interventions and monitoring progress over time. They are particularly useful in rehabilitation programs for individuals with balance disorders, postural instability, or lower limb injuries.
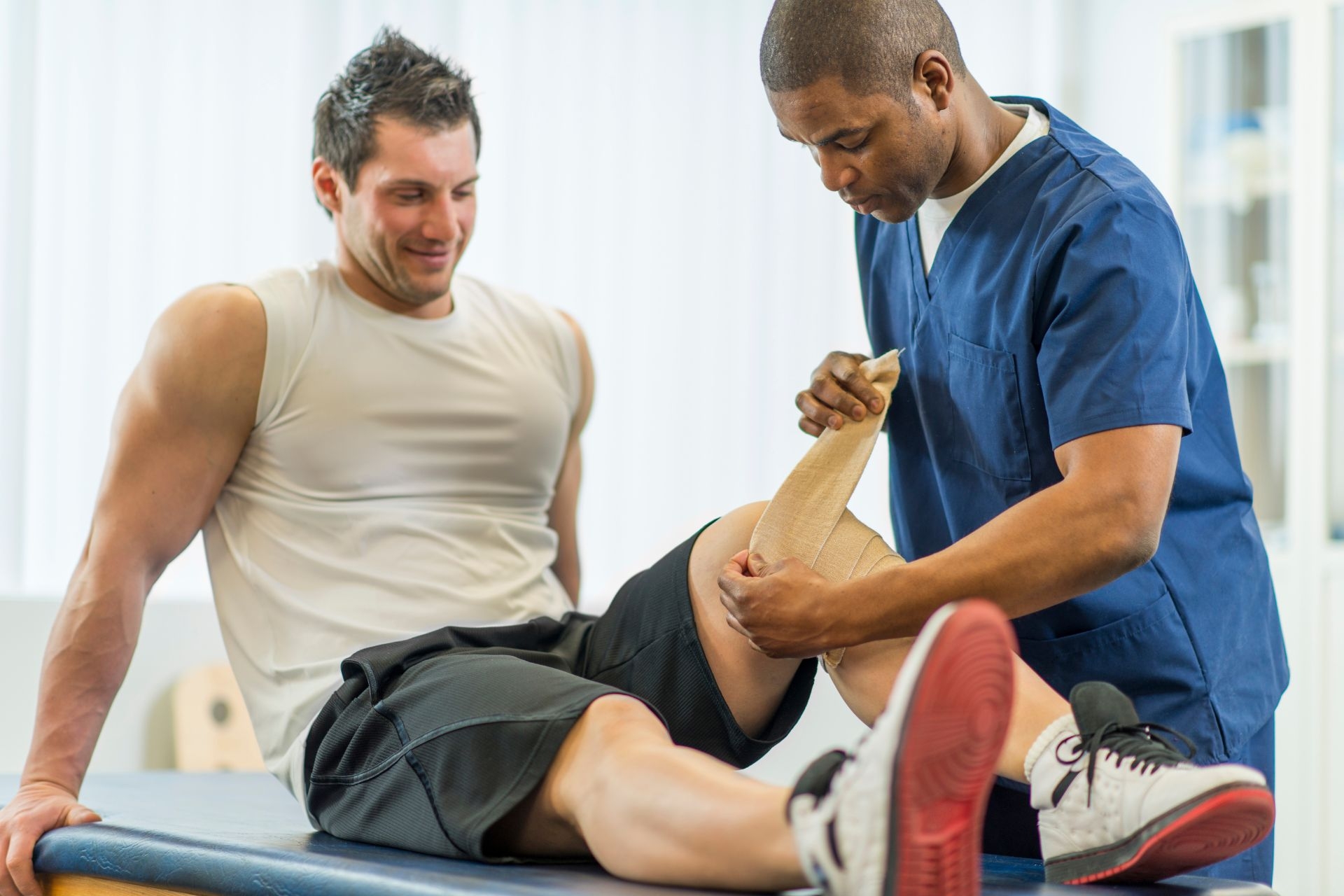
Thermography is a diagnostic technology that aids in diagnosing inflammation and circulation issues in physical therapy. It involves the use of infrared cameras to detect and measure the heat emitted by the body's tissues. By capturing thermal images, thermography can identify areas of increased or decreased temperature, indicating inflammation, poor circulation, or nerve dysfunction. This information helps physical therapists assess the extent and location of tissue damage, guide treatment interventions, and monitor the effectiveness of therapies aimed at reducing inflammation and improving circulation.
Diagnostic imaging techniques such as X-rays and MRI scans play a significant role in physical therapy. X-rays provide detailed images of bones and can help in diagnosing fractures, dislocations, or degenerative changes in joints. MRI scans, on the other hand, provide more detailed images of soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, and discs. These imaging techniques help physical therapists identify the specific structures involved in an injury or condition, allowing for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. They provide valuable information about the extent of damage, the presence of any underlying abnormalities, and help in monitoring the progress of healing or the effectiveness of interventions.
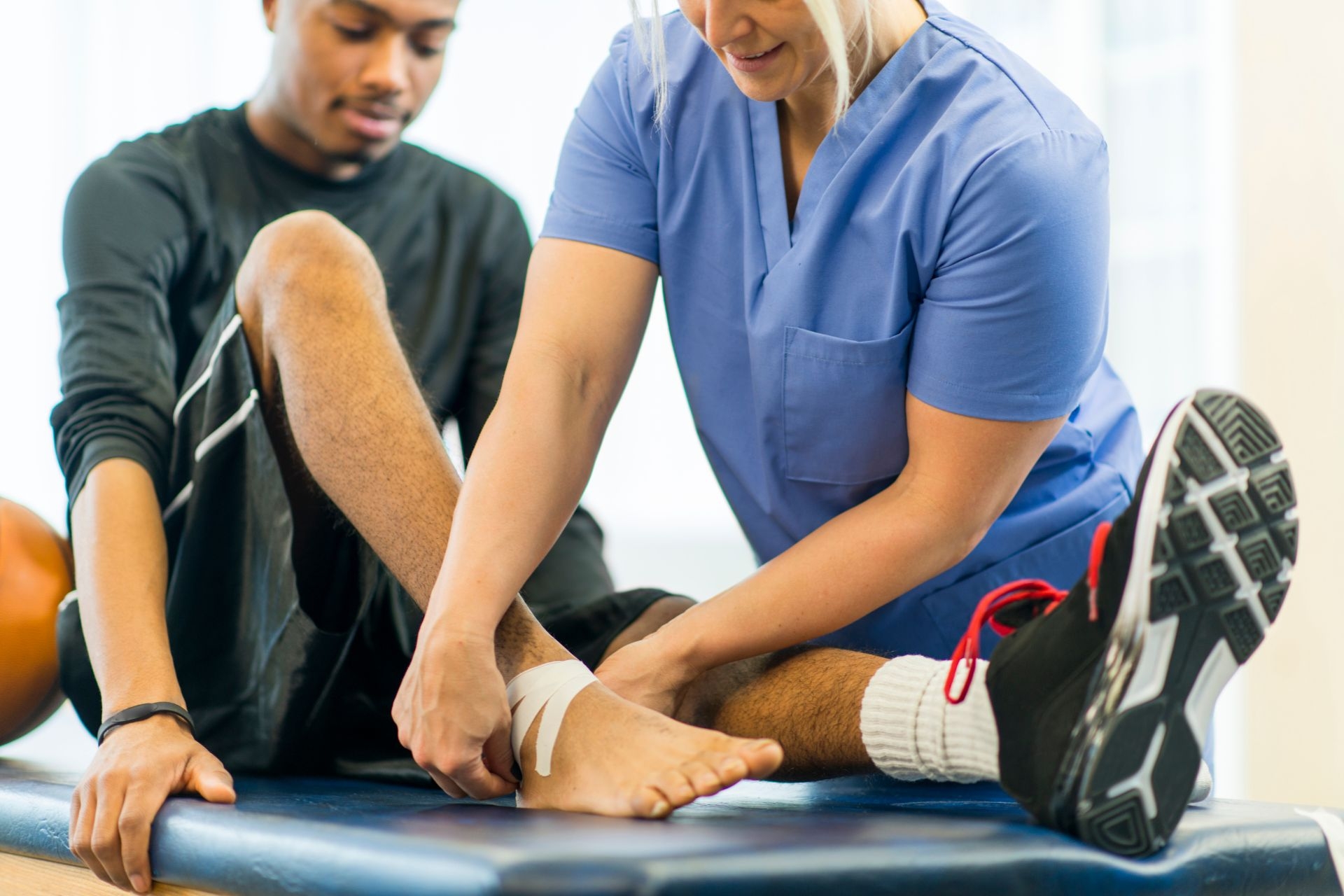
The primary diagnostic technologies used specifically for assessing muscle strength in physical therapy include electromyography (EMG), dynamometry, and isokinetic testing. Electromyography measures the electrical activity of muscles and can provide valuable information about muscle function and recruitment patterns. Dynamometry involves the use of a device called a dynamometer to measure the force exerted by a muscle or group of muscles. Isokinetic testing assesses muscle strength and function by measuring the force produced during a specific movement at a constant speed. These diagnostic technologies allow physical therapists to accurately evaluate muscle strength and design appropriate treatment plans for their patients.
Pelvic floor dysfunction is diagnosed in physical therapy patients based on specific diagnostic criteria. These criteria include the presence of symptoms such as urinary or fecal incontinence, pelvic pain, or pelvic organ prolapse. Physical therapists also assess the strength, tone, and coordination of the pelvic floor muscles through manual muscle testing and biofeedback techniques. Additionally, they may use imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI to evaluate the pelvic floor structures and identify any abnormalities. Other diagnostic tools used by physical therapists may include pelvic floor muscle electromyography (EMG) and urodynamic testing to assess bladder function. By considering these specific diagnostic criteria and utilizing various assessment techniques, physical therapists can accurately identify pelvic floor dysfunction in their patients.
3D motion capture systems offer several advantages for diagnostic assessments in physical therapy. Firstly, these systems provide a highly accurate and detailed analysis of a patient's movement patterns, allowing therapists to identify even subtle abnormalities or asymmetries. This level of precision enables more targeted and effective treatment plans. Additionally, the real-time feedback provided by 3D motion capture systems allows therapists to make immediate adjustments to exercises or interventions, optimizing the therapeutic process. Furthermore, these systems can track progress over time, providing objective data to measure improvements and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Overall, the use of 3D motion capture systems in diagnostic assessments enhances the accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness of physical therapy interventions.
The specific diagnostic protocols for assessing sacroiliac joint dysfunction in physical therapy patients involve a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests. The physical therapist will begin by gathering information about the patient's symptoms, such as pain in the lower back or buttocks, difficulty standing or walking, and limited range of motion. They will also inquire about any previous injuries or conditions that may contribute to the dysfunction. During the physical examination, the therapist will assess the patient's posture, gait, and alignment of the pelvis. They will perform various tests to determine the stability and mobility of the sacroiliac joint, including palpation, provocation tests, and functional movements. Additionally, specialized tests such as imaging studies (X-rays, MRI) or diagnostic injections may be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other possible causes of the symptoms. By utilizing these specific diagnostic protocols, physical therapists can accurately assess sacroiliac joint dysfunction and develop an appropriate treatment plan for their patients.
Clinicians in pediatric physical therapy utilize accelerometers as a diagnostic tool to assess and analyze movement patterns in children. These small, wearable devices measure acceleration and provide objective data on various aspects of movement, such as speed, intensity, and duration. By attaching accelerometers to different body parts, clinicians can gather information on specific movements and identify any abnormalities or deviations from typical patterns. This data can then be analyzed to determine the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions, track progress over time, and make informed decisions regarding treatment plans. Additionally, accelerometers can help clinicians monitor compliance with prescribed exercises and provide feedback to both the child and their caregivers, enhancing engagement and motivation in the therapy process. Overall, accelerometers serve as valuable instruments in pediatric physical therapy, enabling clinicians to accurately diagnose movement patterns and tailor interventions to meet the unique needs of each child.
Specialized tools commonly used for diagnosing balance impairments in vestibular physical therapy include videonystagmography (VNG), rotary chair testing, computerized dynamic posturography (CDP), and the head impulse test (HIT). VNG is a non-invasive test that measures eye movements to assess the function of the vestibular system. Rotary chair testing involves placing the patient in a rotating chair and measuring eye movements in response to different stimuli, providing valuable information about the vestibular system's function. CDP utilizes force plates and visual feedback to assess a patient's postural control and balance. The head impulse test is a quick assessment of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, where the therapist rapidly moves the patient's head to evaluate their ability to maintain visual fixation. These specialized tools help vestibular physical therapists accurately diagnose balance impairments and develop targeted treatment plans to improve patients' balance and overall quality of life.
Quantitative sensory testing (QST) is a valuable tool utilized by physical therapists to diagnose sensory abnormalities in patients suffering from neuropathic pain. QST involves the assessment of various sensory modalities, such as thermal, mechanical, and vibration sensations, to evaluate the functioning of the peripheral and central nervous systems. By employing specialized equipment and techniques, physical therapists can measure and quantify sensory thresholds, pain thresholds, and pain tolerance levels in individuals with neuropathic pain. This comprehensive evaluation allows for the identification of specific sensory deficits and abnormalities, aiding in the accurate diagnosis and subsequent treatment planning for patients. Additionally, QST provides objective data that can be used to monitor the progress of therapy interventions and adjust treatment strategies accordingly. Overall, the incorporation of QST within physical therapy practice enhances the precision and effectiveness of sensory assessment in individuals with neuropathic pain.