Manual Muscle Testing Techniques
How is manual muscle testing used to assess muscle strength in physical therapy?
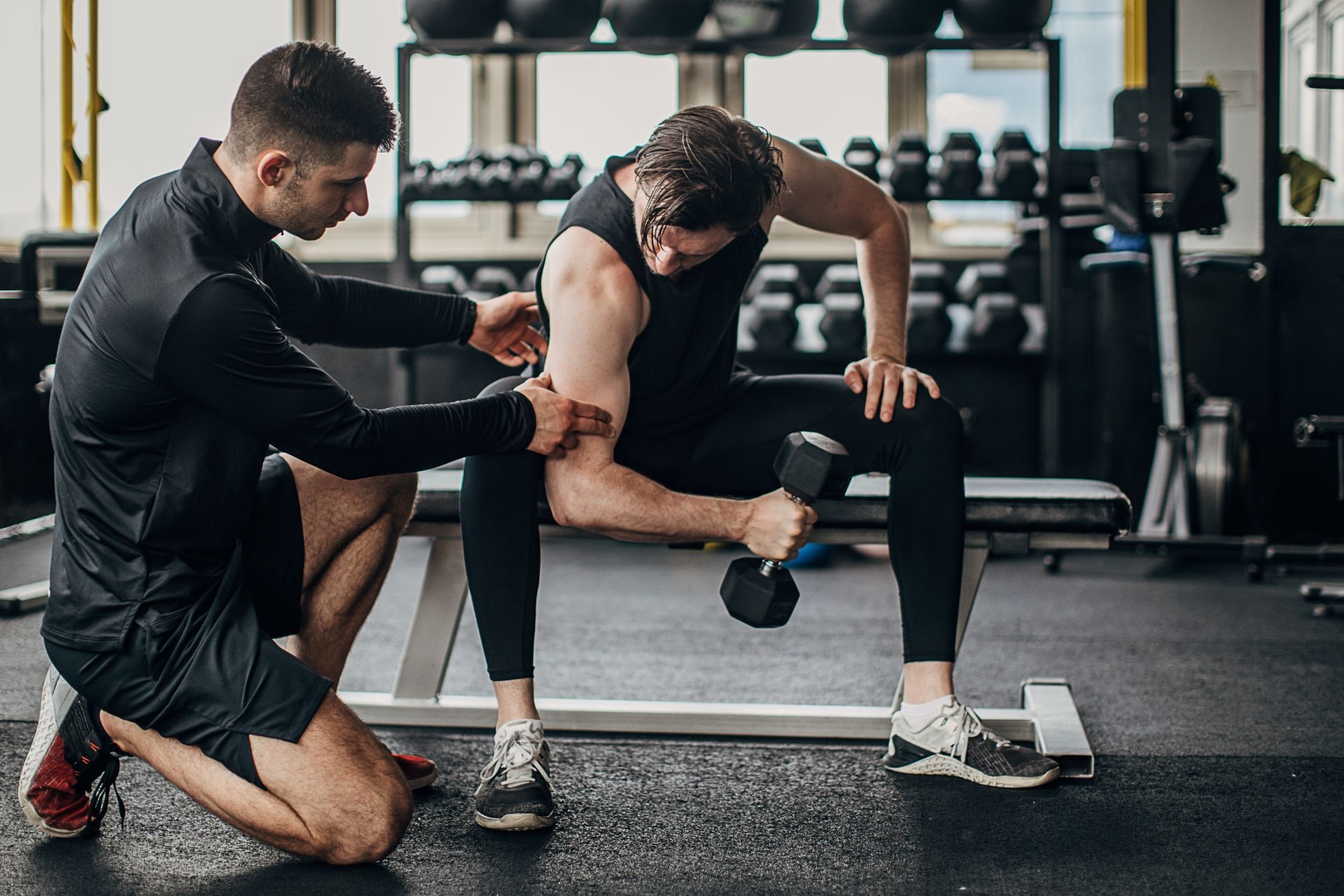
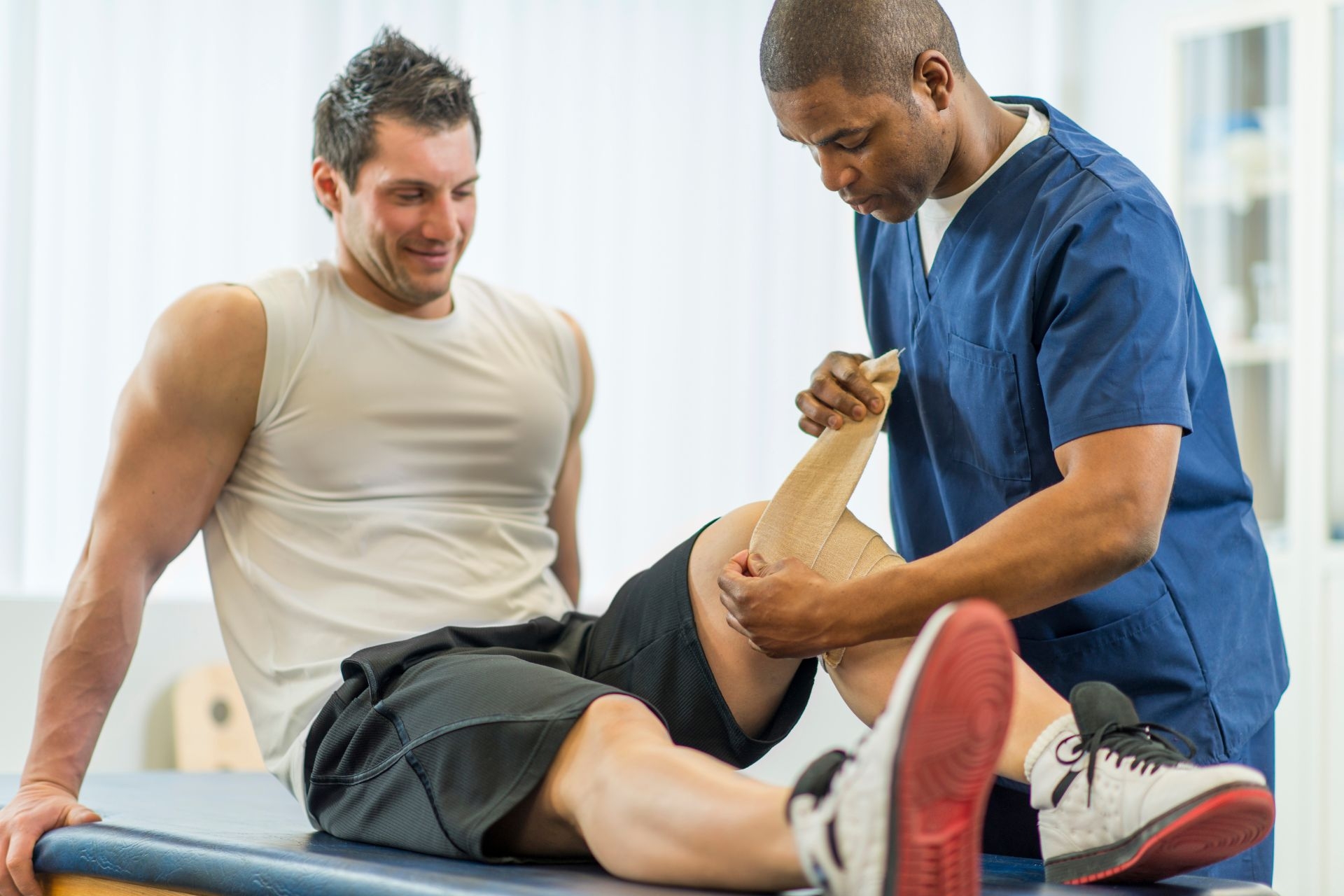
Manual muscle testing is a common method used in physical therapy to assess muscle strength by evaluating the ability of a patient to resist applied force. This technique involves the therapist applying pressure against a specific muscle or muscle group while the patient performs a specific movement or holds a position. By grading the patient's ability to resist the force, the therapist can determine the strength and function of the muscle being tested.