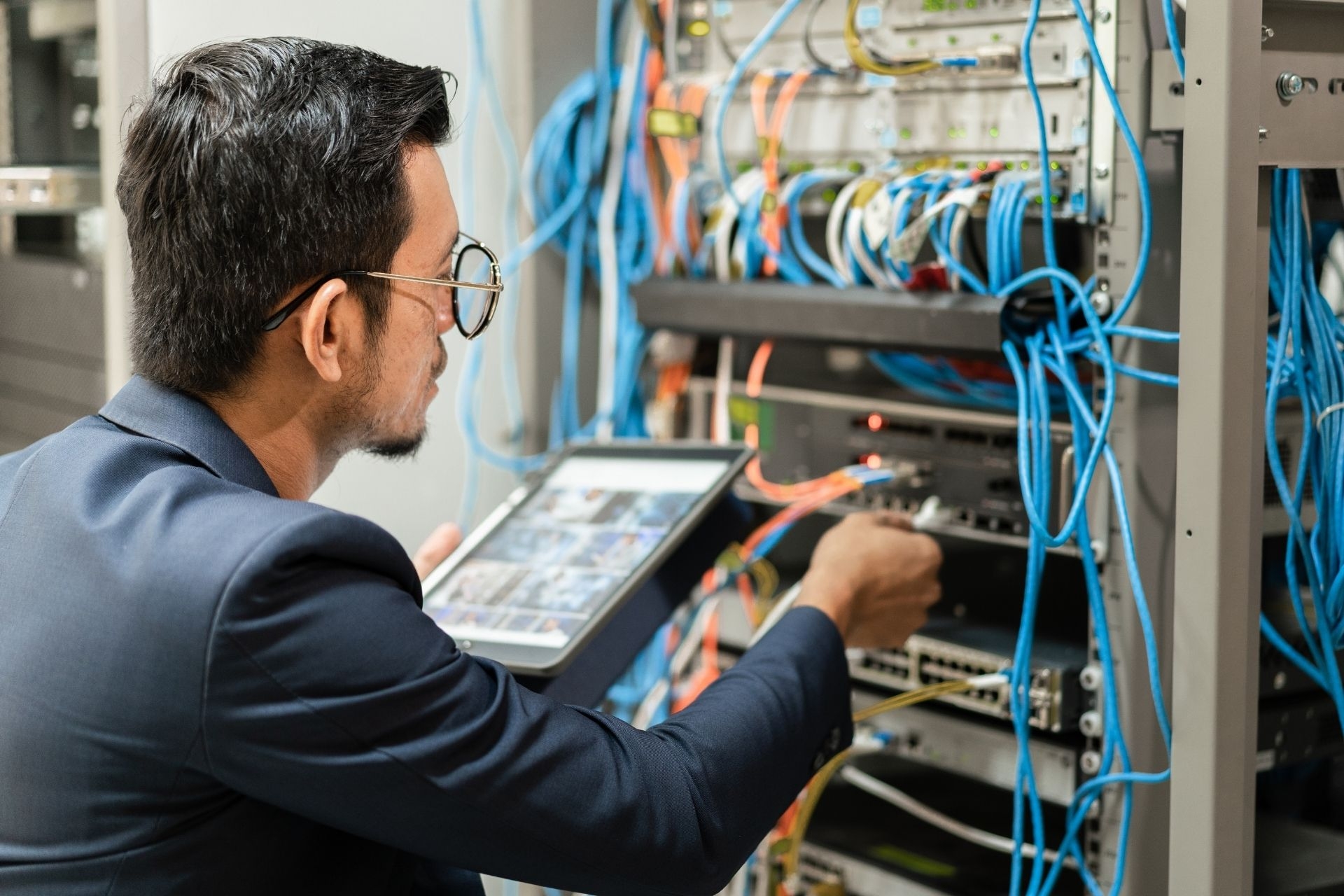


Managed domain name services (DNS) refers to the outsourcing of DNS management to a third-party provider. Internet Performance Testing Services Unlike regular DNS, where the responsibility of managing DNS records lies with the website owner or their hosting provider, managed DNS services offer a more comprehensive and specialized approach. Managed DNS providers typically offer advanced features such as traffic management, load balancing, and DNS-based security solutions. They also have a global network of DNS servers, ensuring faster and more reliable DNS resolution for websites.
There are several benefits of using managed DNS services for a website. Firstly, managed DNS providers offer enhanced reliability and uptime. With their global network of DNS servers, they can distribute DNS queries across multiple locations, reducing the risk of downtime due to server failures or network issues. Secondly, managed DNS services often include advanced traffic management features, such as load balancing and failover, which can help optimize website performance and ensure high availability. Additionally, managed DNS providers typically offer robust security features to protect against DDoS attacks and other threats, providing an added layer of protection for websites.
Managed DNS plays a crucial role in improving website performance and reducing latency.

Yes, managed DNS services are designed to handle high traffic and ensure website availability during peak times.
Managed DNS providers typically offer a range of security features to protect against DDoS attacks and other threats. These may include traffic filtering and rate limiting capabilities to mitigate the impact of volumetric attacks, as well as DNS-based authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized DNS modifications. Some providers may also offer advanced threat intelligence and real-time monitoring to detect and respond to potential security incidents. Additionally, managed DNS services often have built-in redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous operation even in the face of attacks or disruptions.
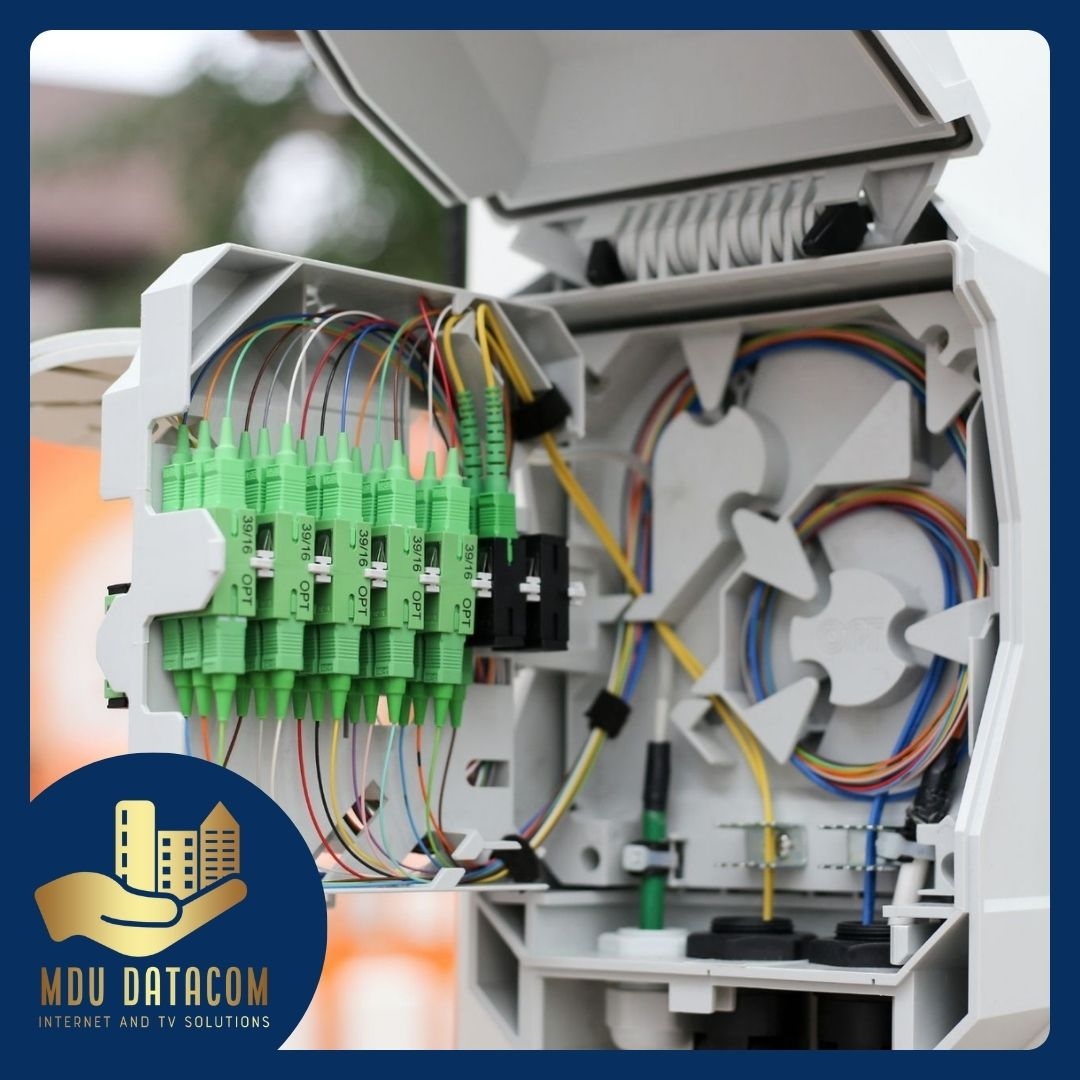
Managed DNS supports domain name redirection and URL forwarding through the use of DNS records such as CNAME and URL forwarding. These records allow website owners to redirect traffic from one domain or URL to another.
When choosing a managed DNS provider for a business website, there are several key considerations to keep in mind. Fiber Optic Cable Providers Firstly, reliability and uptime are crucial factors. It is important to choose a provider with a robust and redundant infrastructure to ensure high availability and minimize the risk of downtime. Secondly, security features should be carefully evaluated. Look for providers that offer comprehensive DDoS protection, traffic filtering, and other security measures to safeguard your website. Additionally, consider the scalability and performance capabilities of the provider, as well as their ability to handle high traffic and optimize DNS resolution. Finally, consider the level of customer support and technical expertise offered by the provider, as prompt and knowledgeable support can be invaluable in resolving any issues or concerns that may arise.
Bulk internet providers typically offer a range of service level agreements (SLAs) to meet the diverse needs of their customers. These SLAs may include guarantees for uptime, bandwidth availability, and response times for technical support. For example, a bulk internet provider may offer an SLA that guarantees 99.9% uptime, ensuring that their service is available to customers for the majority of the time. They may also offer SLAs that guarantee a certain level of bandwidth availability, ensuring that customers have sufficient internet speeds to meet their business requirements. Additionally, bulk internet providers may include SLAs that outline response times for technical support, ensuring that any issues or outages are addressed promptly. These SLAs are designed to provide customers with peace of mind and assurance that their internet service will meet their specific needs and requirements.
Peering and transit agreements play a crucial role in determining the performance of bulk internet services. Peering refers to the direct interconnection between two networks, allowing them to exchange traffic without the need for a third-party network. This arrangement enables faster and more efficient data transfer between the networks involved, resulting in improved performance for bulk internet services. Transit agreements, on the other hand, involve the use of a third-party network to facilitate the exchange of traffic between networks. While transit agreements may introduce an additional layer of complexity and potential latency, they also provide access to a wider network reach. The performance of bulk internet services can be impacted by the quality and capacity of the peering and transit connections, as well as the geographical proximity of the networks involved. Therefore, establishing robust peering relationships and selecting reliable transit providers are essential for ensuring optimal performance and seamless delivery of bulk internet services.
Bulk internet services can indeed support low-latency applications such as online gaming. These services, which cater to a large number of users simultaneously, are designed to handle high volumes of data traffic efficiently. With their robust infrastructure and advanced network management techniques, bulk internet services can ensure that the latency experienced by online gamers is minimized. They employ technologies like Quality of Service (QoS) and traffic shaping to prioritize gaming traffic and reduce delays. Additionally, these services often have low contention ratios, meaning that the available bandwidth is shared among fewer users, further reducing latency. Overall, bulk internet services are well-equipped to meet the demands of low-latency applications like online gaming, providing gamers with a smooth and responsive gaming experience.
Yes, bulk internet services can support data replication for disaster recovery purposes. Data replication is the process of creating and maintaining copies of data in multiple locations to ensure its availability in the event of a disaster. Bulk internet services, which provide high-speed and large-capacity internet connections, are well-suited for data replication as they can efficiently transfer large amounts of data between different locations. These services utilize advanced networking technologies and protocols to ensure the secure and reliable transmission of data. Additionally, they often offer features such as bandwidth prioritization and traffic management, which can further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of data replication for disaster recovery purposes.
Bulk internet services have the capability to support network virtualization for resource optimization. Network virtualization is a technique that allows for the creation of multiple virtual networks on a single physical network infrastructure. This enables the efficient utilization of resources by dividing them into smaller, isolated virtual networks. By implementing network virtualization, bulk internet services can optimize their resource allocation, leading to improved performance and cost savings. This technology enables the creation of virtual machines, virtual switches, and virtual routers, which can be dynamically allocated and managed based on the specific needs of different applications or users. Additionally, network virtualization allows for the implementation of advanced network services such as load balancing, firewalling, and quality of service (QoS) management, further enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of bulk internet services.
Traffic prioritization in bulk internet networks can have a significant impact on latency. By assigning different levels of priority to various types of traffic, such as video streaming, online gaming, or file downloads, network administrators can ensure that critical or time-sensitive data is given higher priority and therefore experiences lower latency. This can be achieved through techniques like Quality of Service (QoS) or traffic shaping, which allocate bandwidth and resources based on predefined rules. By effectively managing network traffic and prioritizing certain types of data, latency can be reduced, resulting in improved overall network performance and user experience.
Colocation facilities hosting bulk internet infrastructure have specific requirements to ensure optimal performance and reliability. These requirements include high-speed and redundant internet connectivity, with multiple Tier 1 network providers and diverse fiber paths to minimize the risk of downtime. The facilities should have robust power infrastructure, including uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, backup generators, and redundant power feeds to ensure continuous operation. Additionally, they should have advanced cooling systems to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels for the equipment. Security measures such as 24/7 monitoring, video surveillance, biometric access controls, and fire suppression systems are also essential to protect the infrastructure. Furthermore, colocation facilities should offer scalable space options, flexible power configurations, and remote hands services to accommodate the growing needs of internet infrastructure.